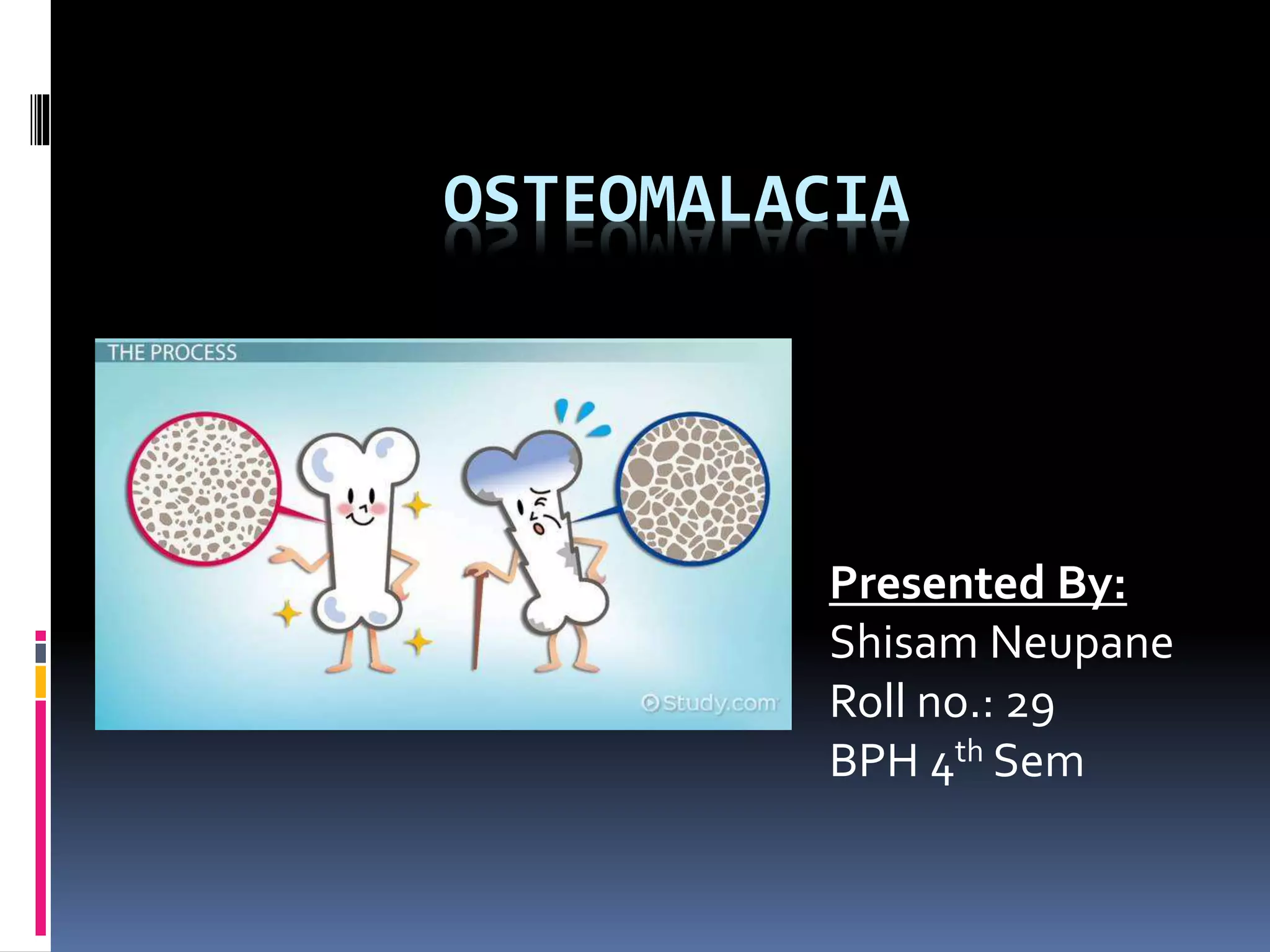
Osteomalacia is the softening of bones caused by defective bone mineralization due to inadequate levels of phosphate and calcium, often caused by vitamin D deficiency. Some key risk groups include homebound adults, vegetarians, and those with limited sun exposure or gastrointestinal disorders that impact absorption. Symptoms include muscle weakness, bone pain, and increased fracture risk. Treatment involves high dose oral vitamin D, calcium, and phosphate supplements, while prevention focuses on diet, sun exposure, and treating underlying conditions.