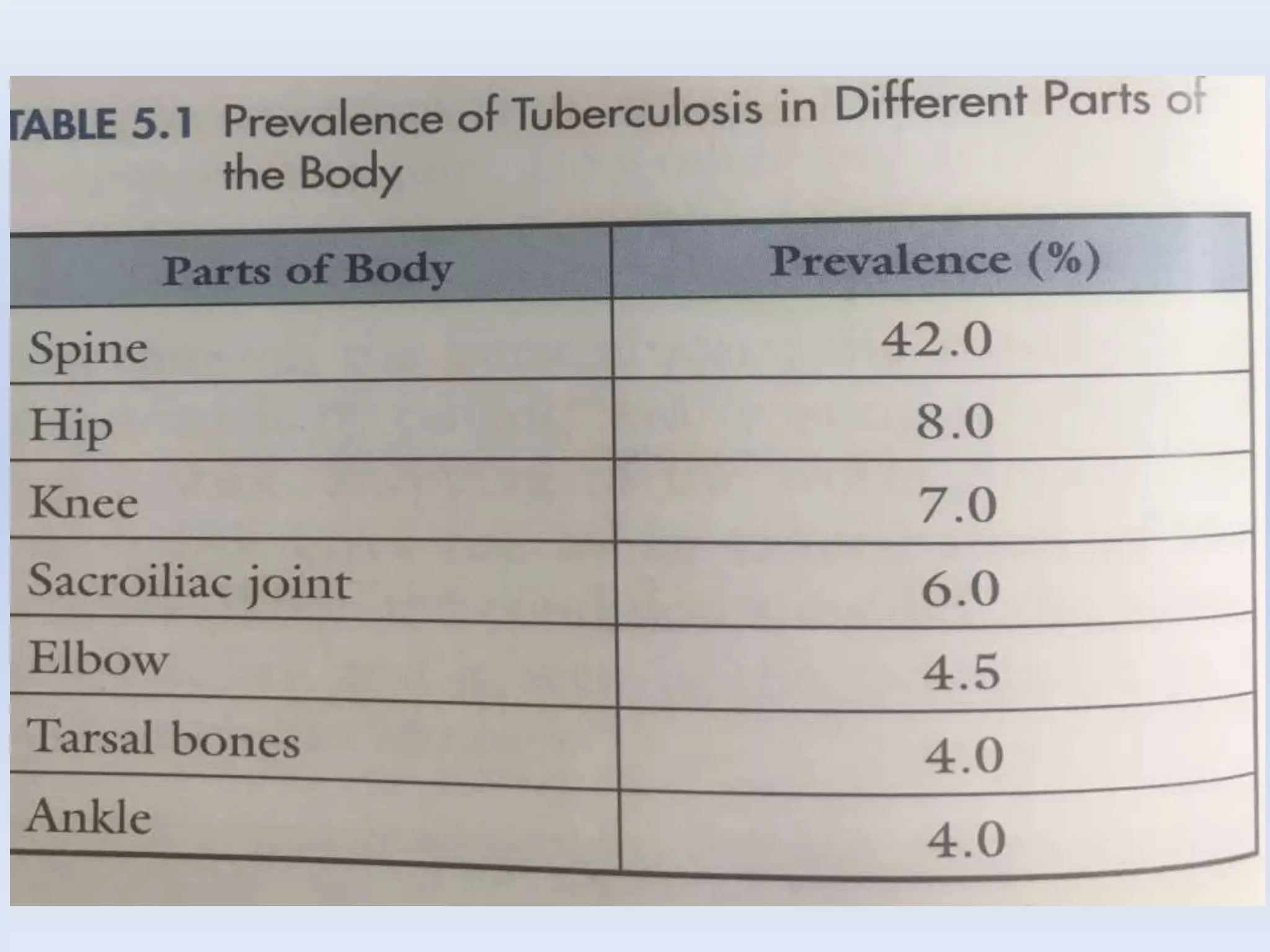
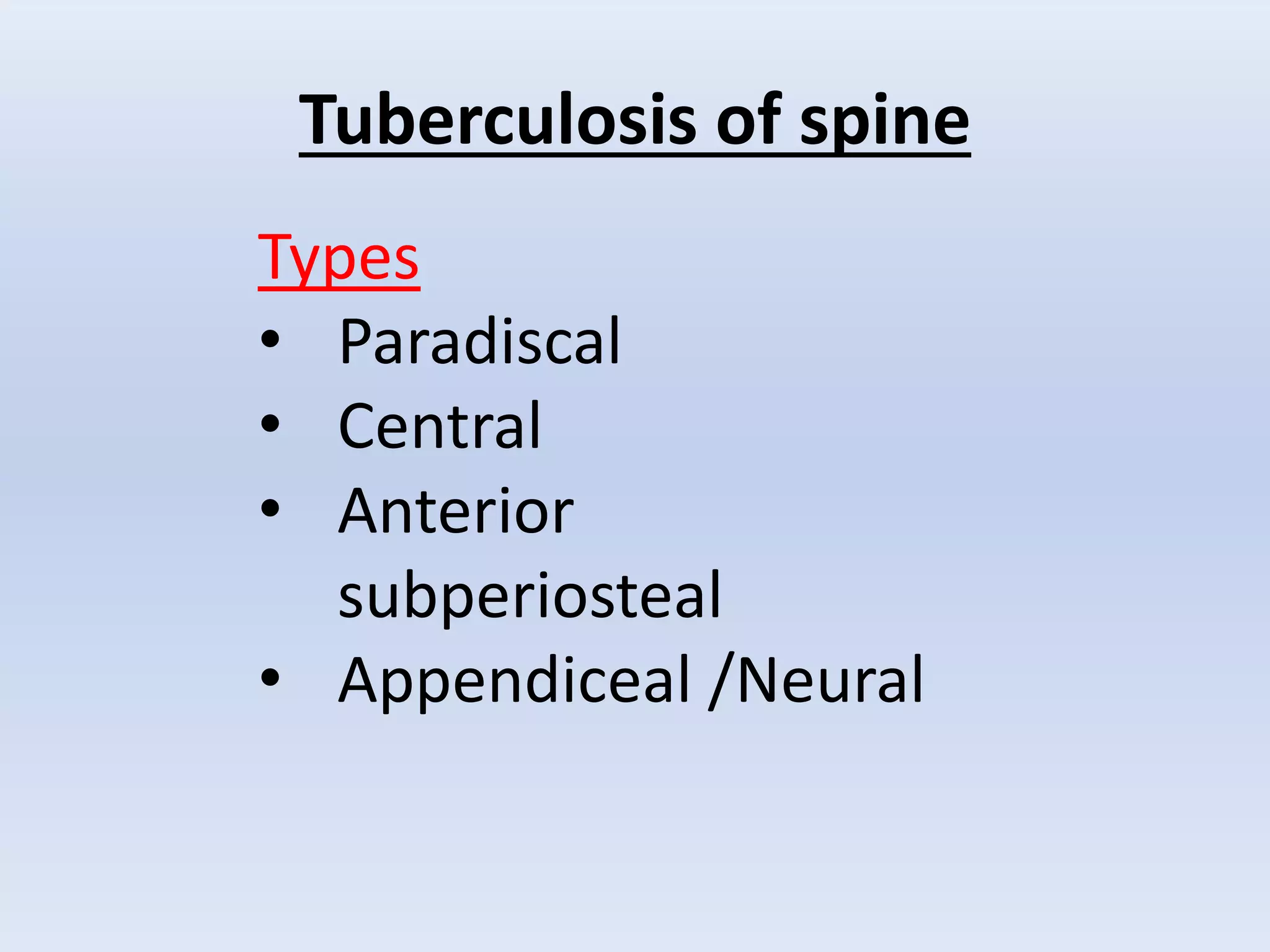
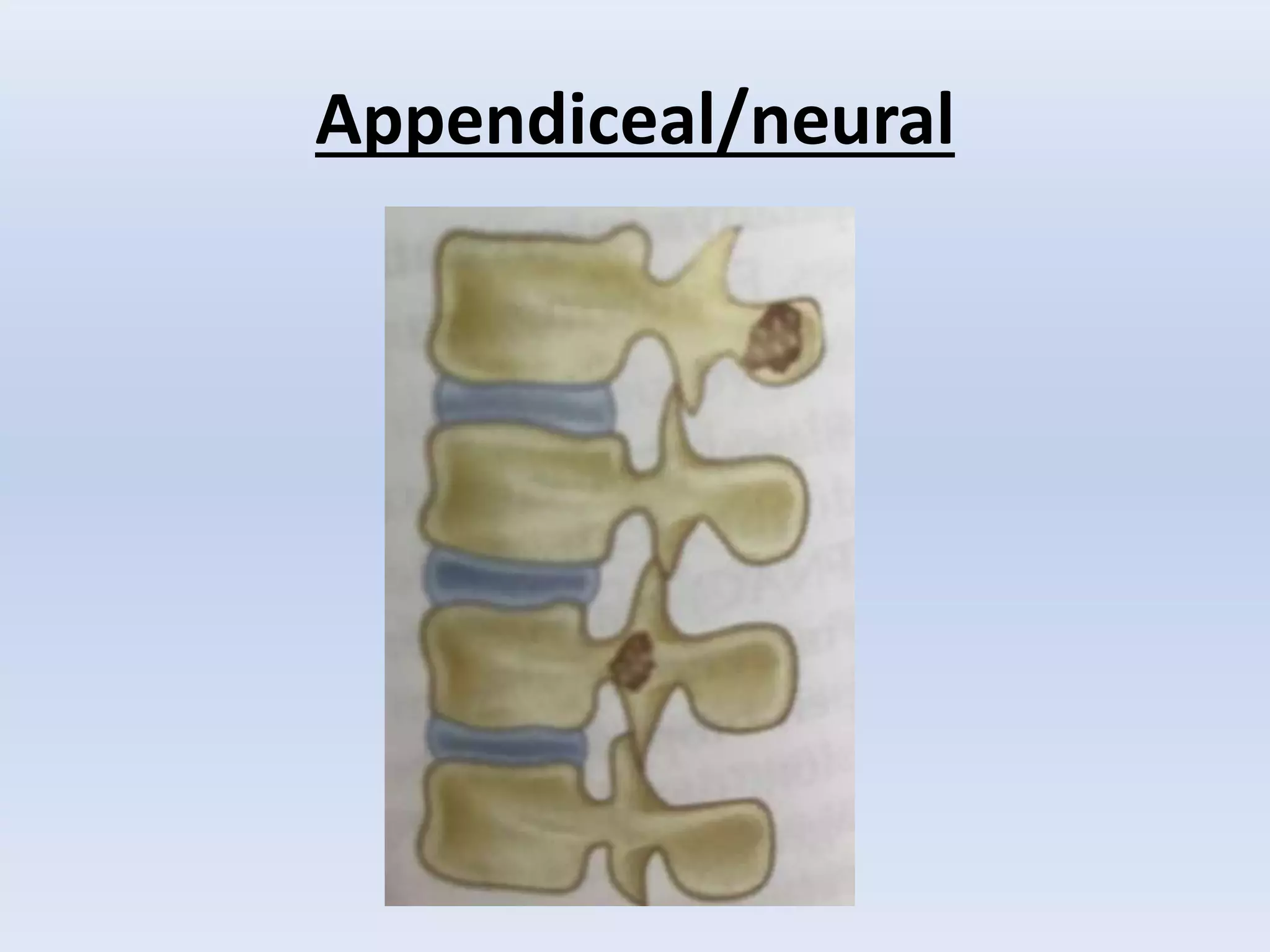
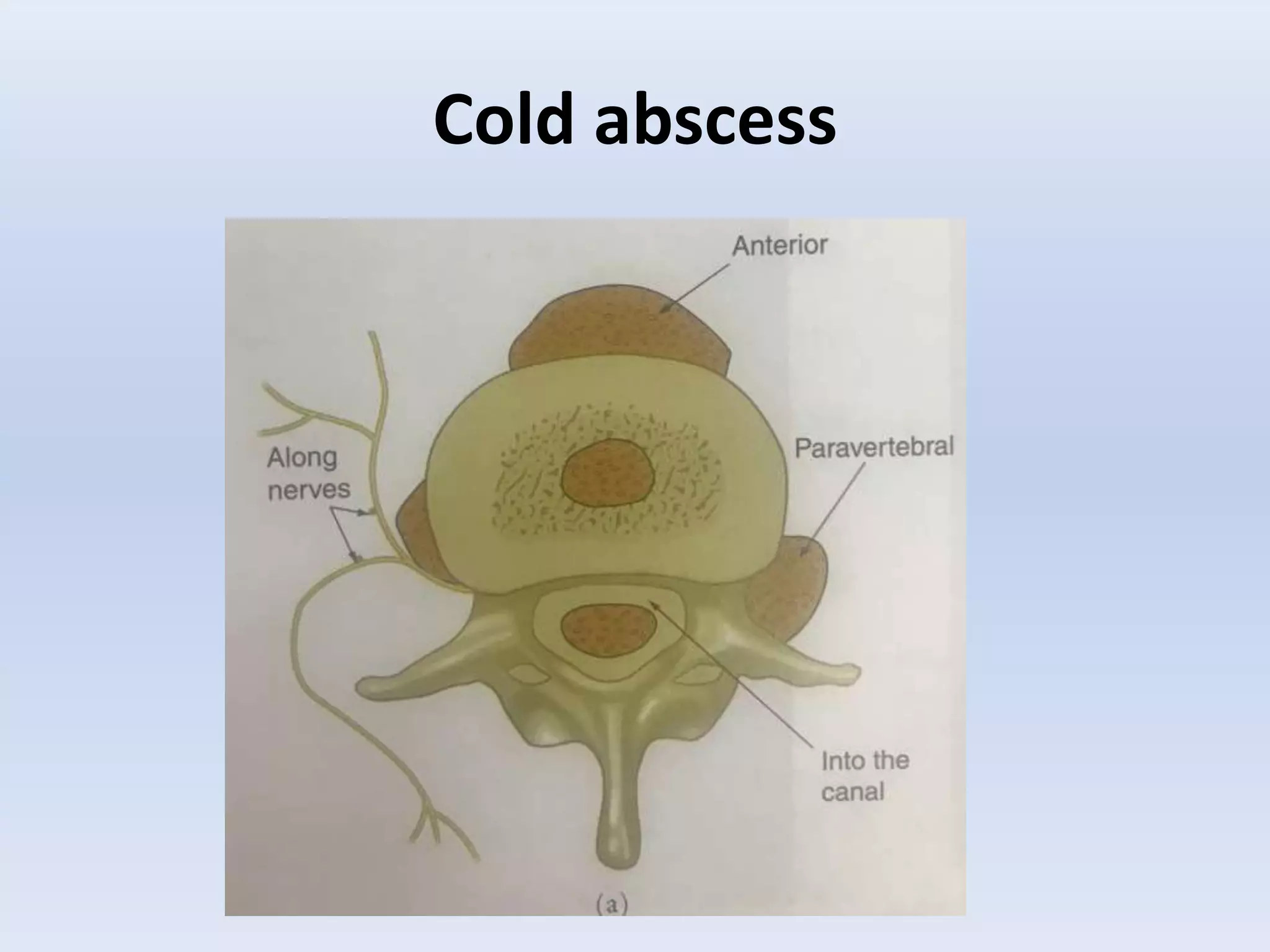
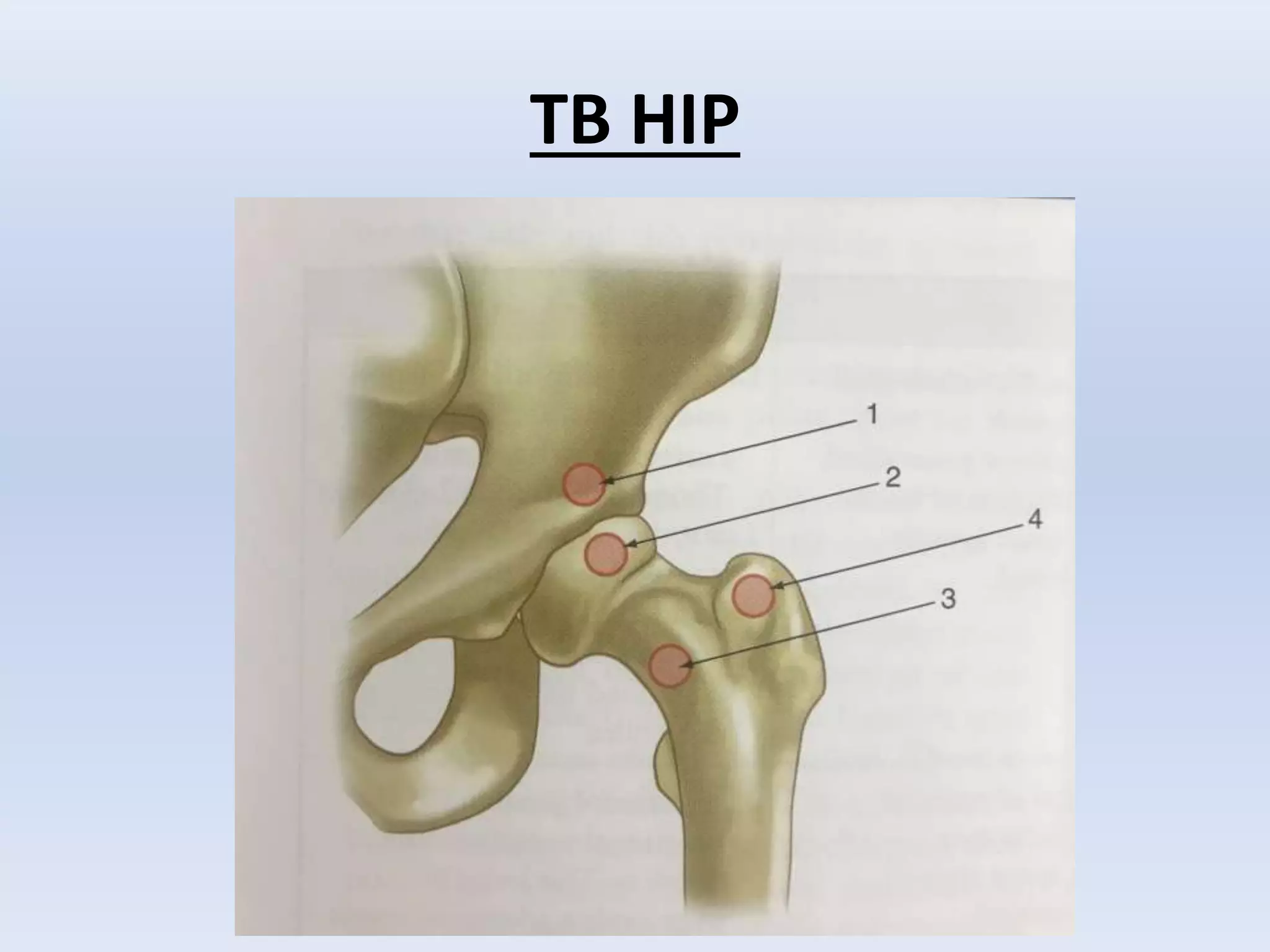
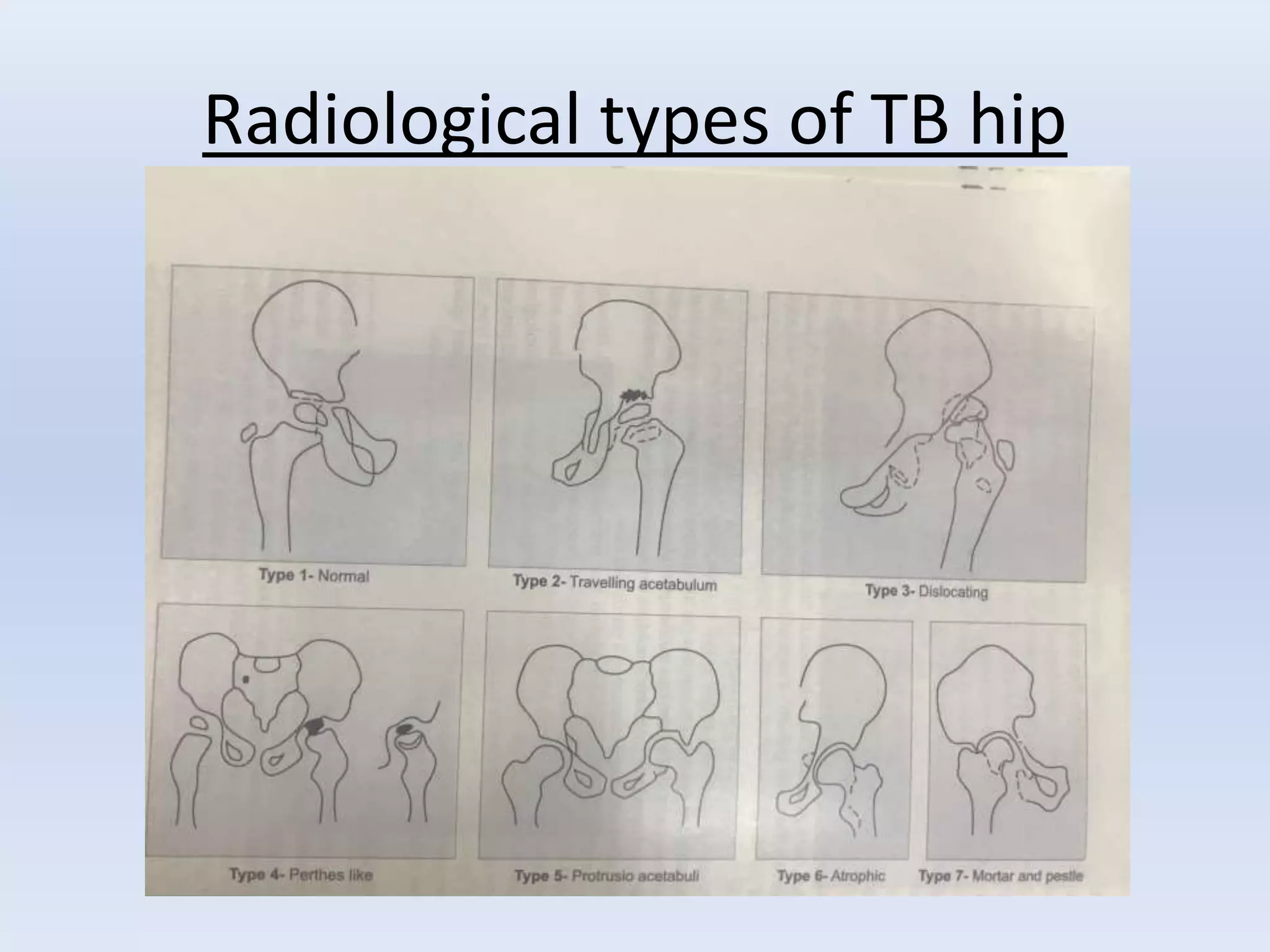
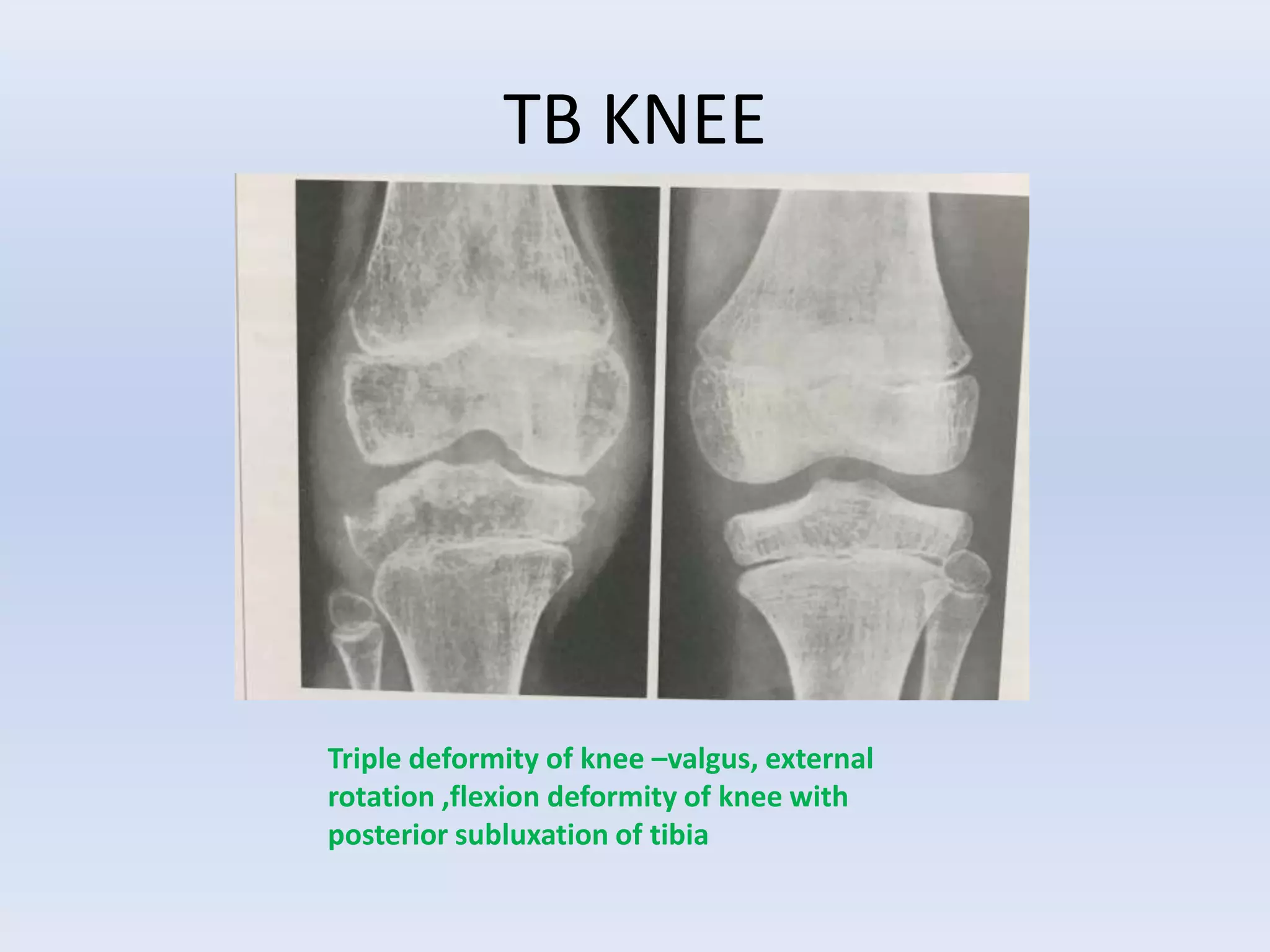
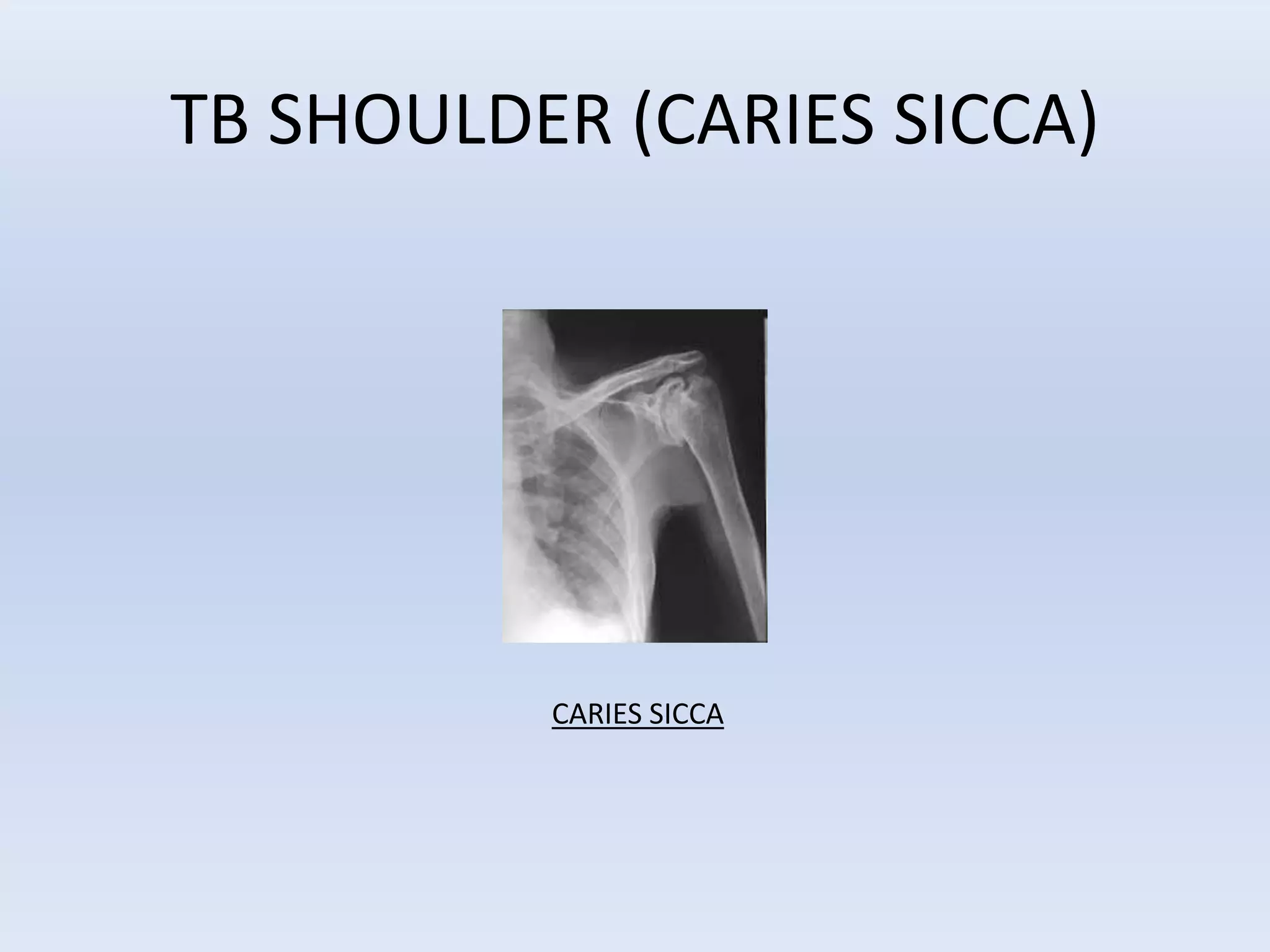
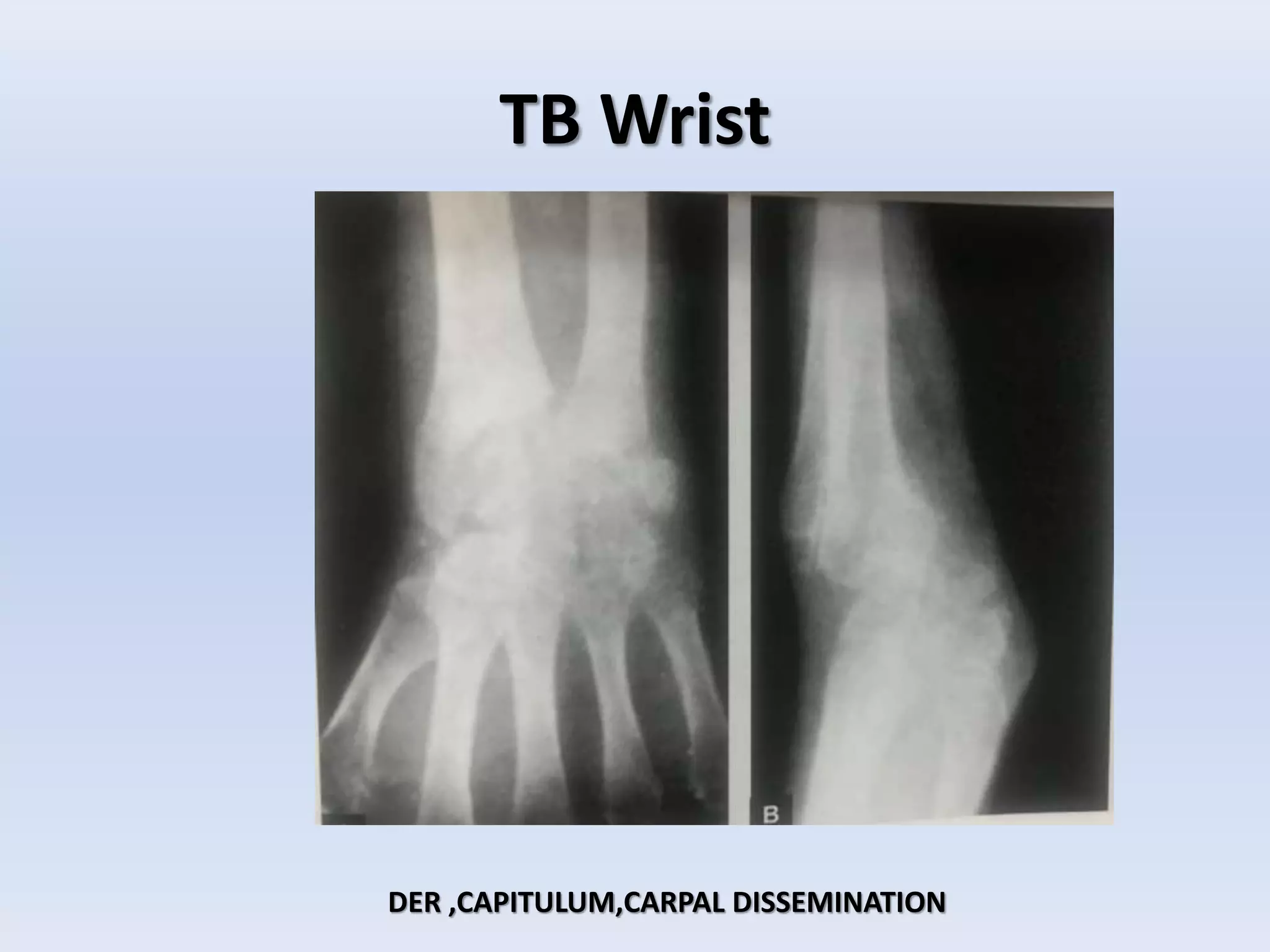
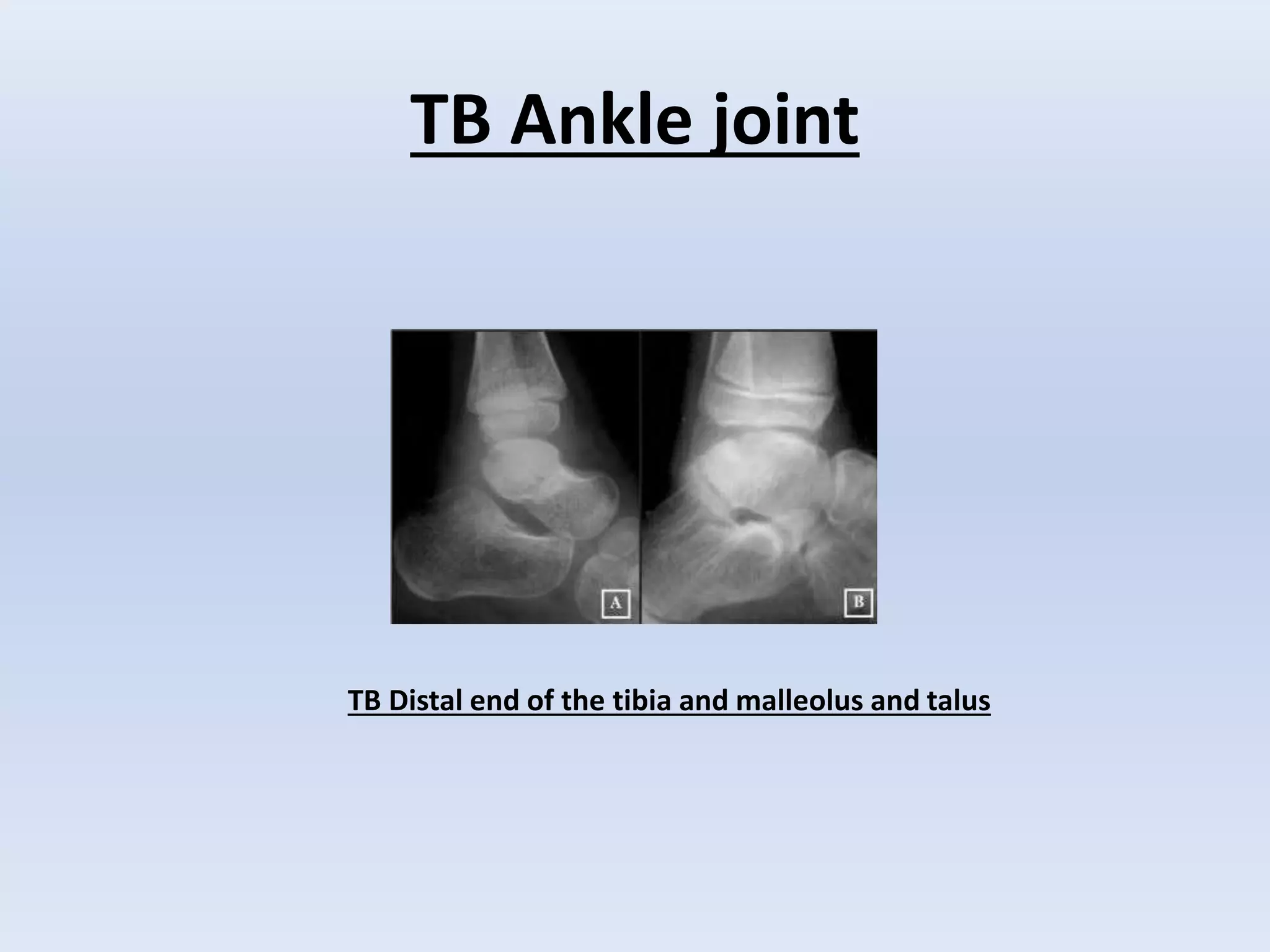
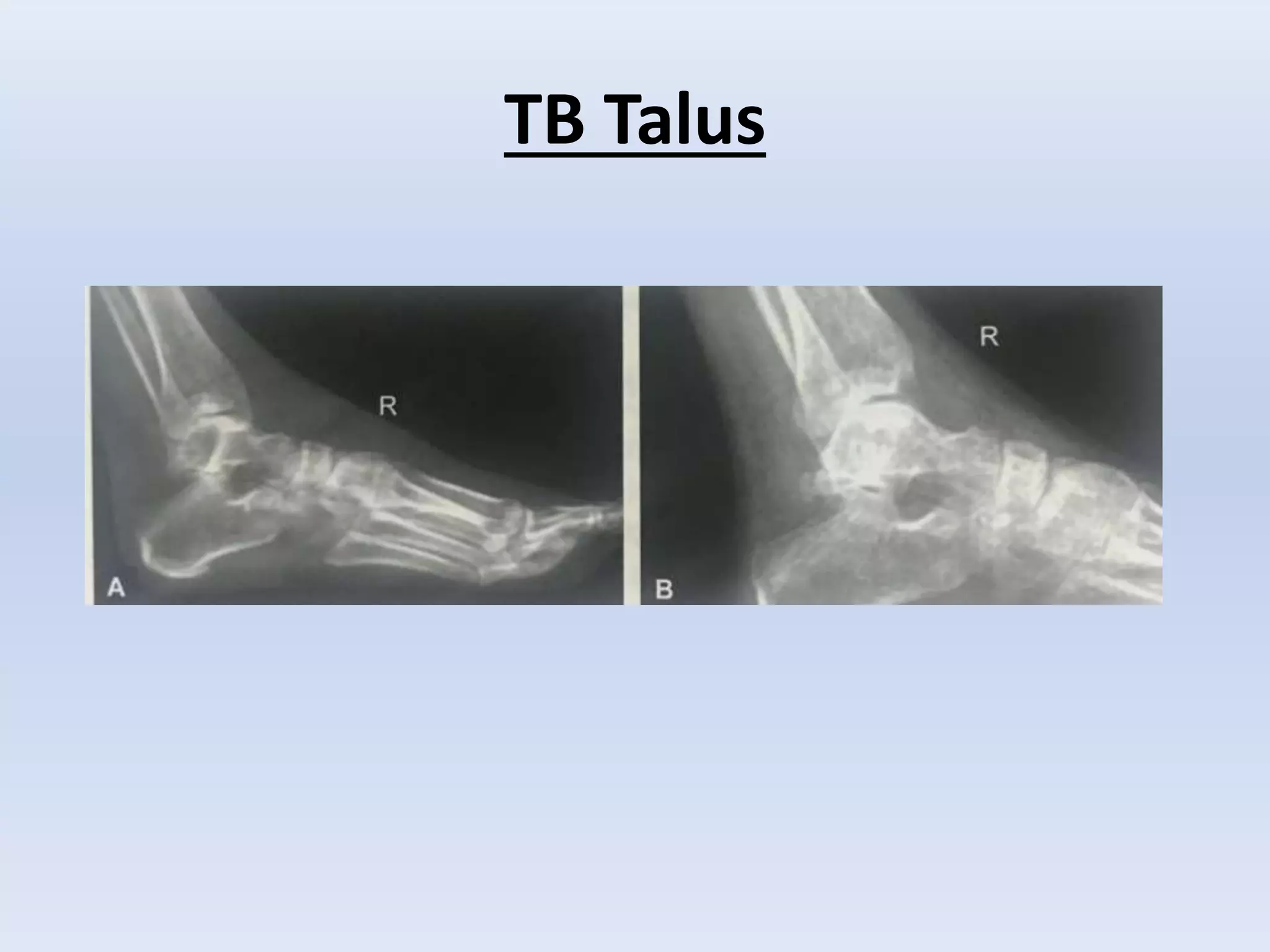
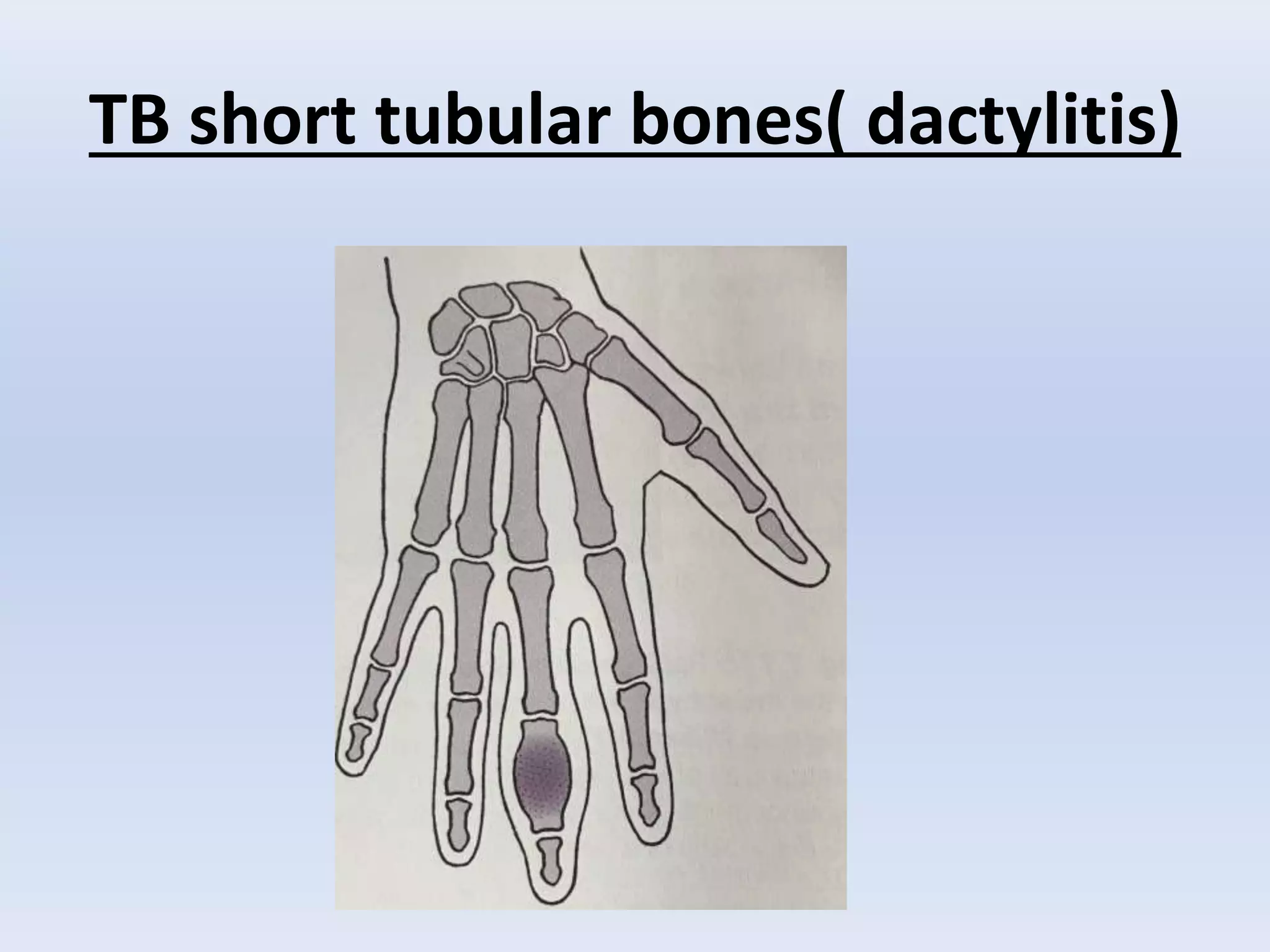
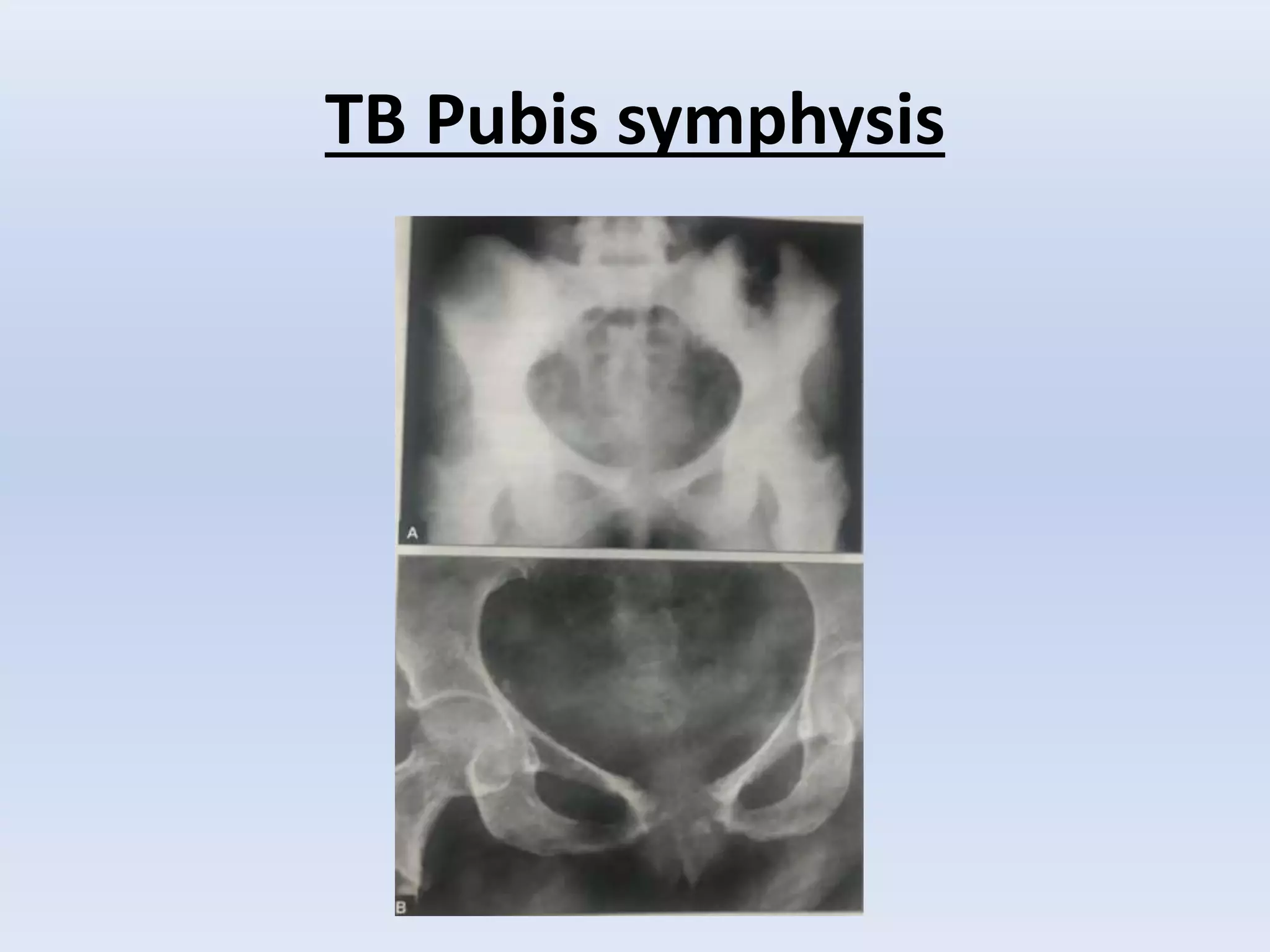
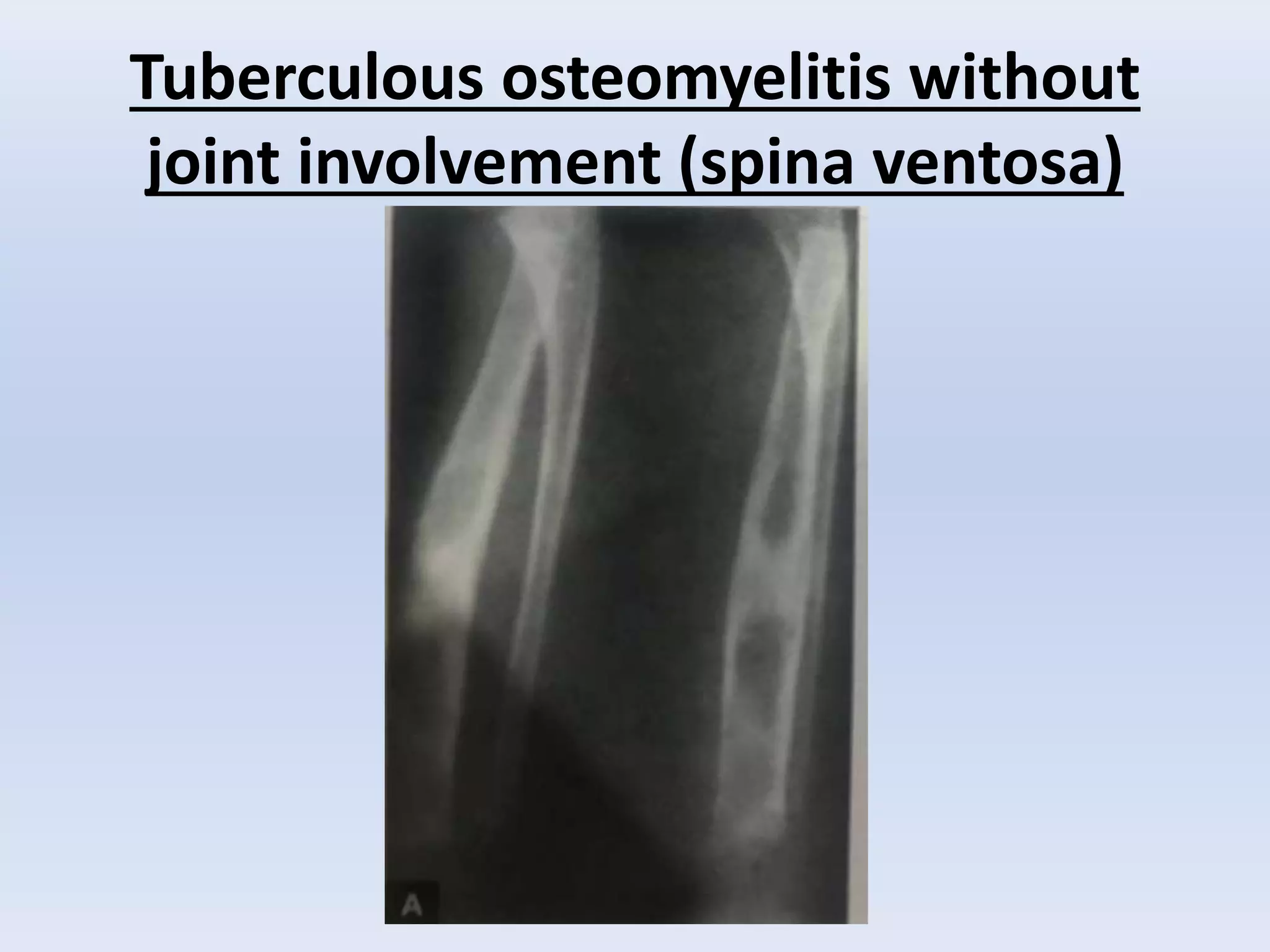
Tuberculosis is a common infection that can involve bones and joints. The spine is the most common site affected, accounting for about 50% of cases. Symptoms include constitutional symptoms like fever as well as localized pain, stiffness, and deformity. Diagnosis involves imaging like x-rays, CT, or MRI as well as tests like tuberculin skin tests or sputum/synovial fluid analysis. Treatment involves chemotherapy and sometimes surgery to treat deformities, abscesses, or neurological complications. The goal is to heal the infection and achieve a good functional outcome.