Embed presentation


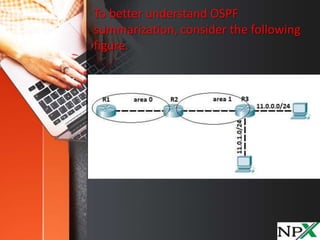
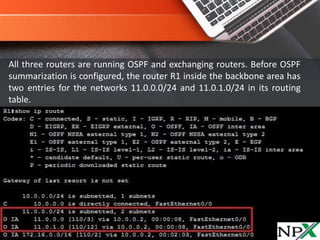
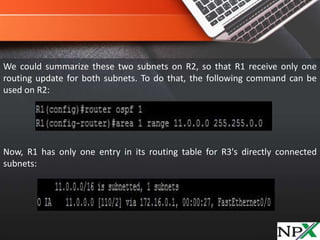


OSPF does not support automatic summarization like EIGRP, and route summarization can only be configured on Area Border Routers (ABRs) and Autonomous System Boundary Routers (ASBRs). Route summarization helps reduce OSPF traffic and route computation by combining multiple specific routes into a single, generic route. The "area AREA_ID range IP_ADDRESS MASK" command is used to configure OSPF summarization, allowing an ABR to advertise a single summary route for multiple subnets. Care must be taken with summarization to avoid overgeneralizing reachable networks.





