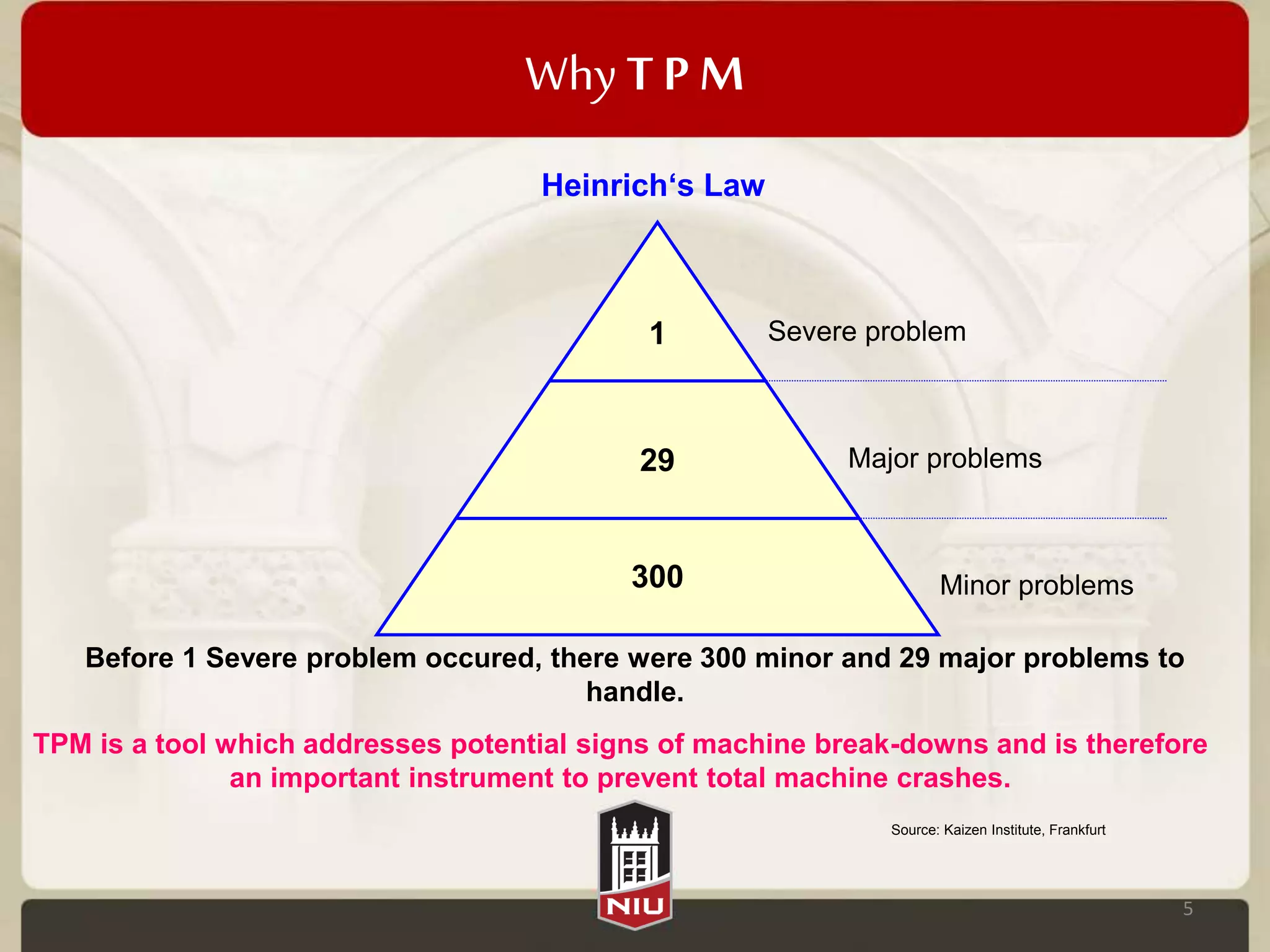
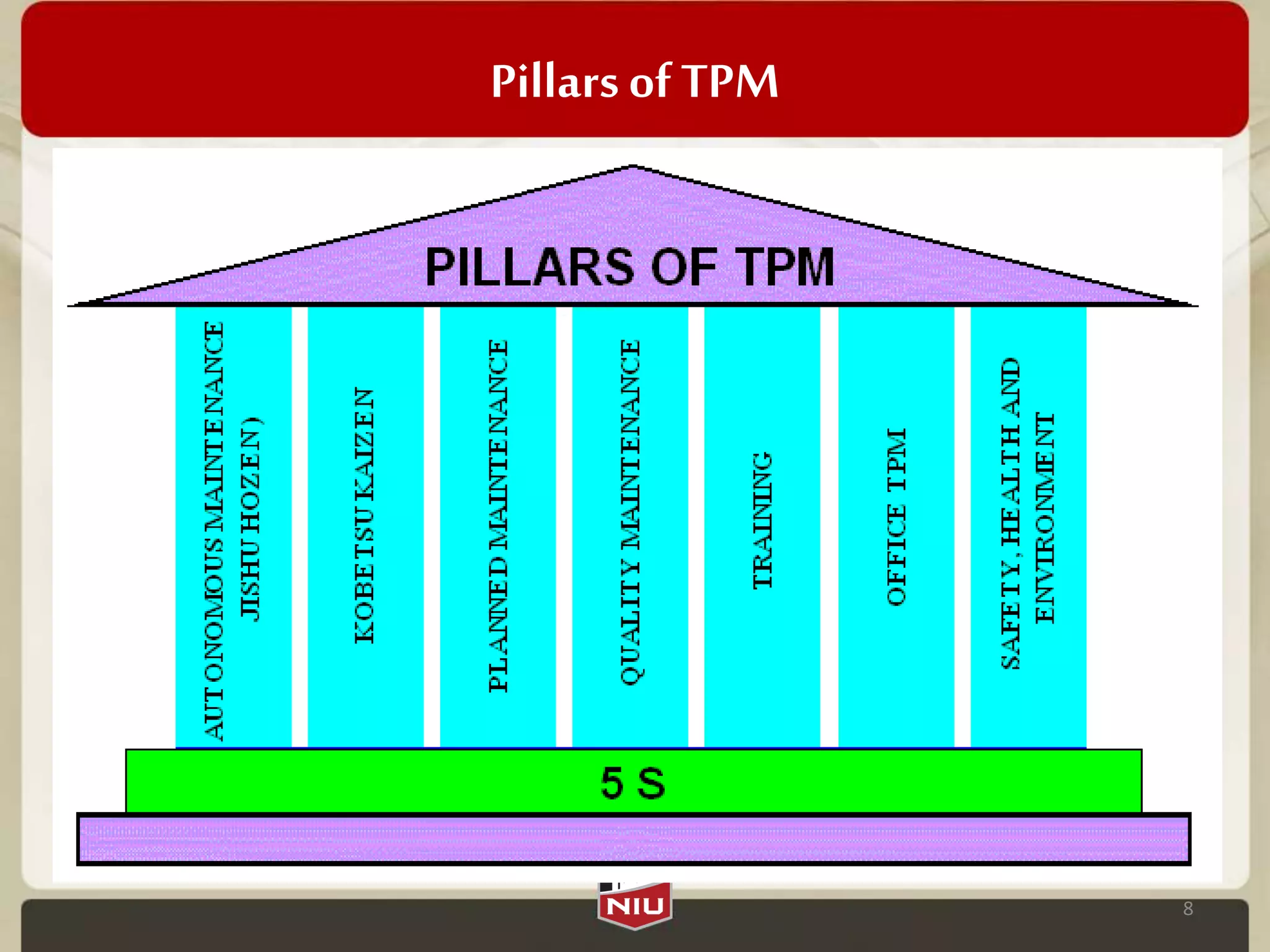
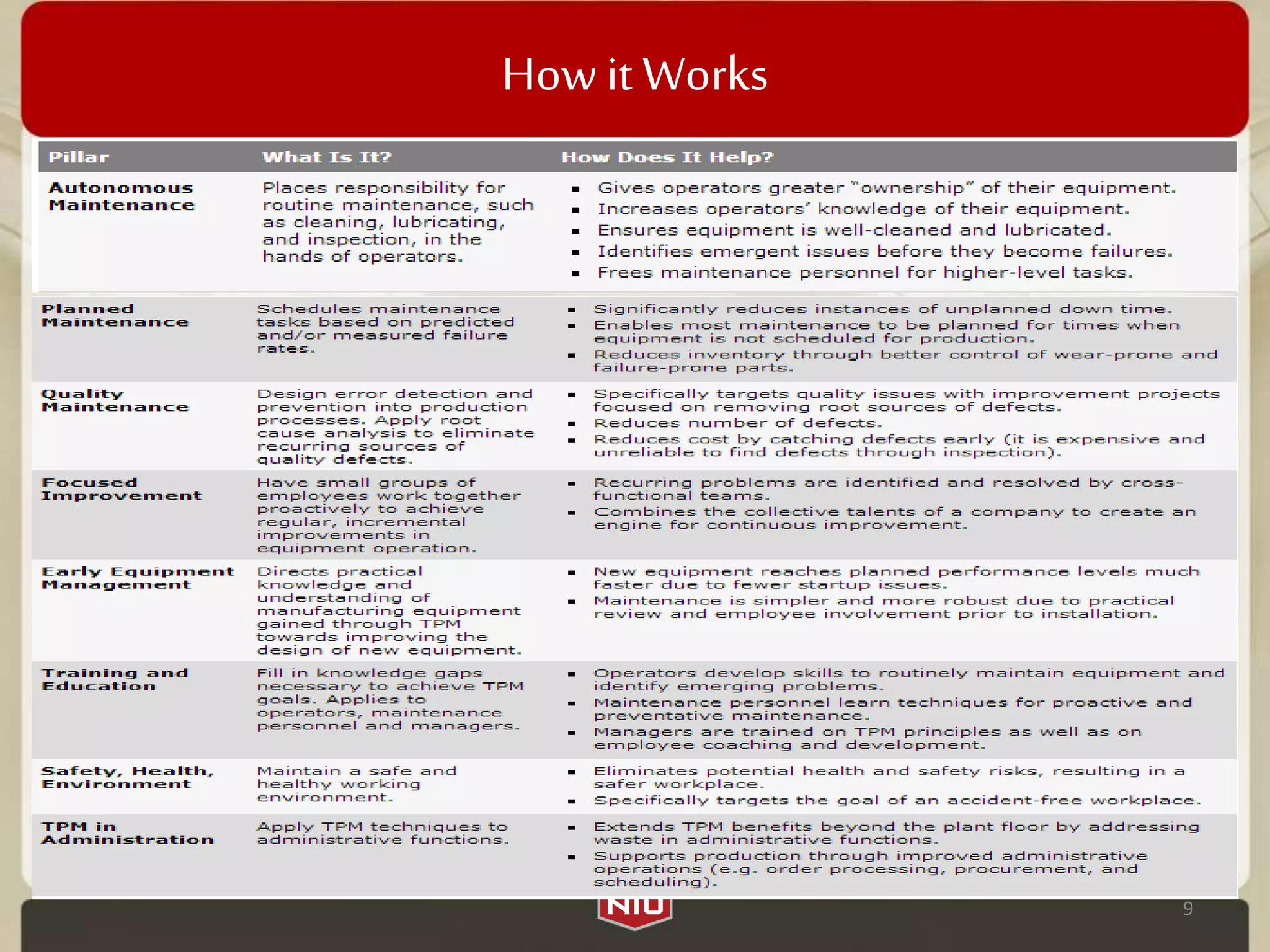
This document provides an overview of Total Productive Maintenance (TPM). TPM aims to eliminate losses like equipment downtime, defects, and accidents by involving machine operators in preventative maintenance. Its objectives are to create a safer work environment, improve quality, reliability, and financial performance. TPM measures effectiveness using Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and addresses six major losses: availability, performance, and quality losses. It works by establishing pillars like autonomous, planned, and quality maintenance.