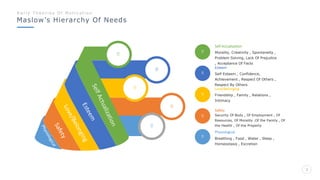
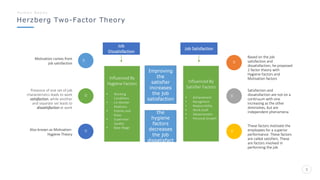
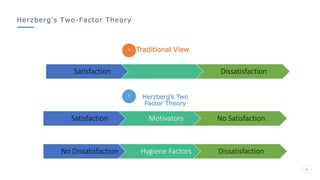
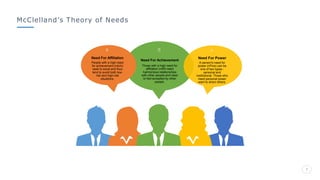
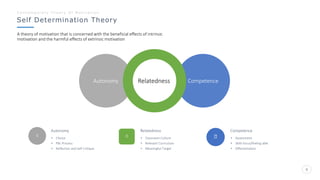
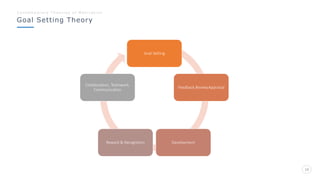
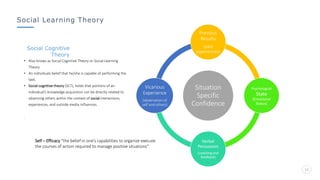
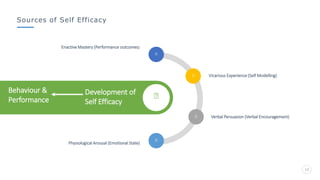
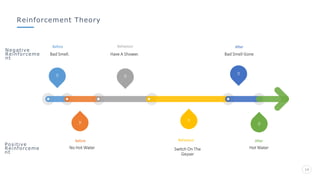
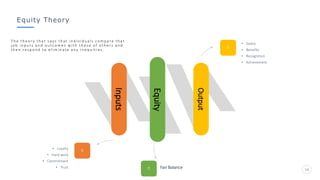
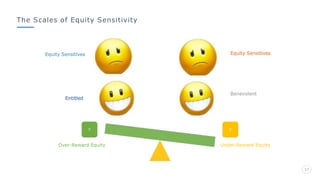
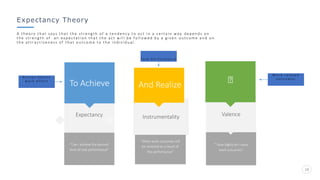
Bharati Airtel Ltd is an Indian telecommunications company that became the fifth largest telecom operator in the world. It uses motivation theories to drive employee performance. Specifically, it employs expectancy theory by linking employee performance to expected outcomes like rewards and recognition. It also uses goal setting theory by setting clear and challenging goals for employees. This helps improve employee performance and drives the company's success.