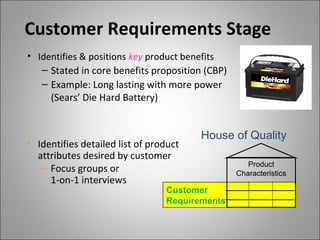
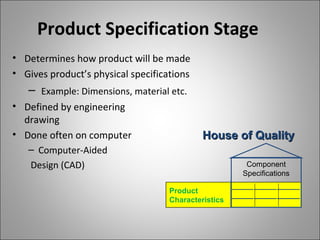
QFD (Quality Function Deployment) is a method for developing products and services by translating customer needs and requirements into technical specifications. It involves cross-functional teams who create a series of "houses" or matrices to break down the product design into increasing levels of detail from customer needs to component specifications. Implementing QFD leads to benefits like reduced time to market, lower costs, improved quality, and increased customer satisfaction.