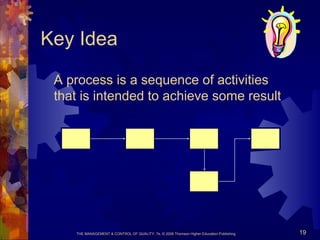
The document discusses key concepts in quality management. It explains that building quality into an organization's products, services, and infrastructure is challenging but important. Quality assurance aims to provide customers with goods and services that meet their needs. An organization needs different perspectives on quality from different business functions to truly satisfy customers. Total quality focuses on customer satisfaction, reducing costs, and continuous improvement through a systems approach. It is based on customer focus, participation, process management, and learning. Quality begins at the personal level and is important for organizational success.