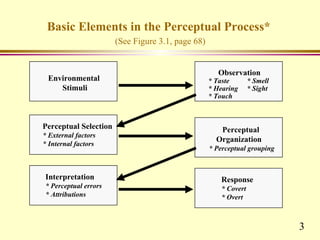
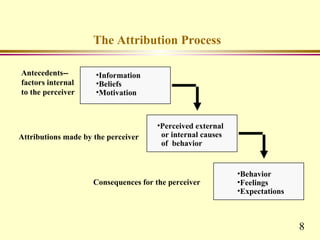
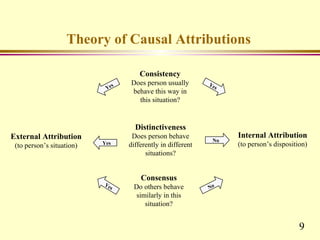
This chapter discusses key concepts related to perception and attribution. It defines perception as how people select, organize and respond to information. Perception involves observation, selection, organization, interpretation and response. Common perceptual errors include stereotyping, halo effect, and projection. The chapter also defines attribution as how people understand the causes of behaviors. Attributions can be internal or external. Frequent attribution errors include the fundamental attribution error and self-serving bias.