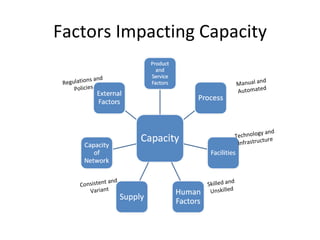
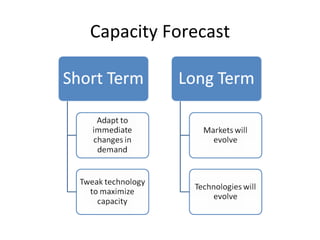
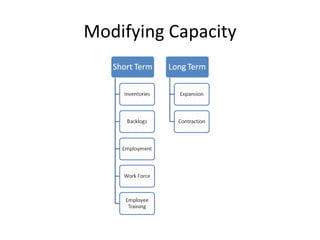
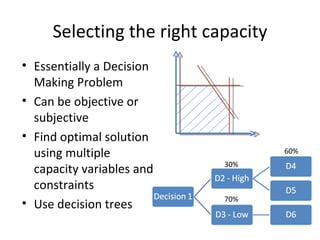
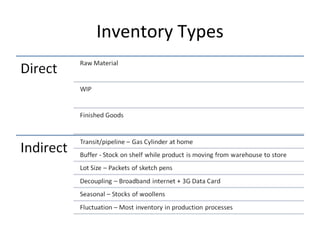
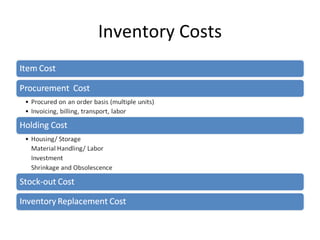
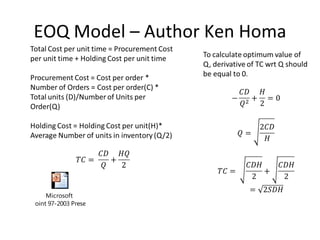
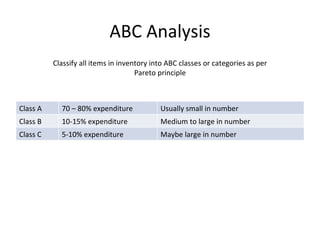
This document discusses capacity and inventory management. It covers topics like capacity management, factors that impact capacity, capacity forecasting, modifying capacity, selecting capacity. It also discusses inventory management, reasons for inventory, inventory types, costs, EOQ model, reorder point/level, and ABC analysis for classifying inventory items. The key aspects of managing both capacity and inventory effectively are identified.