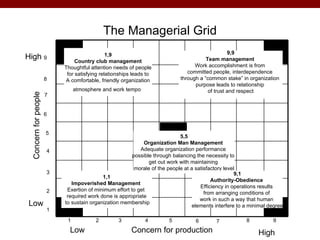
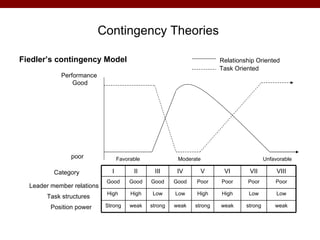
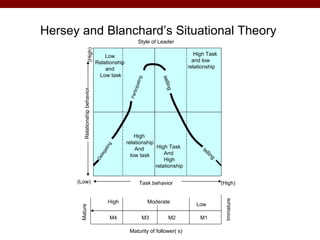
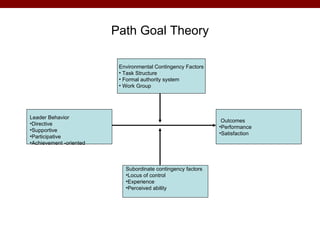
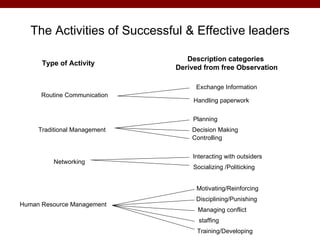
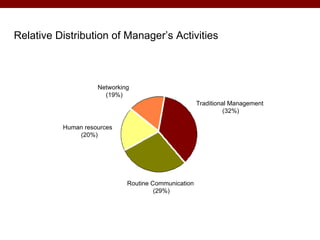
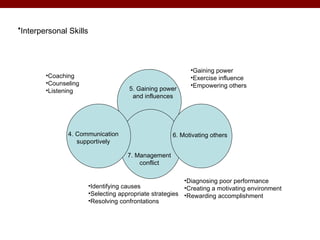
The document discusses various theories and frameworks of leadership including trait theories, behavioral theories, contingency models, and contemporary approaches like charismatic, transformational, and transactional leadership. It also identifies important skills for effective leadership such as self-awareness, communication, problem solving, influence and empowerment, conflict management, and motivation. Theories indicate that leadership style should match the demands of the particular situation to achieve optimal performance.