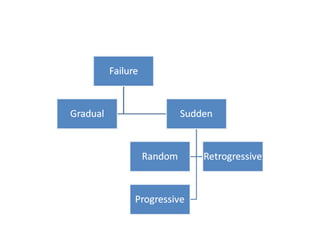
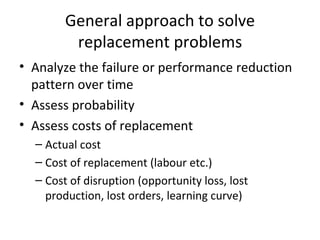
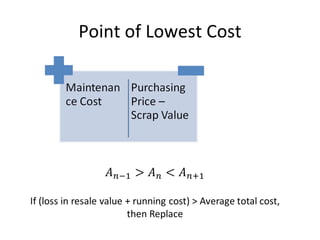
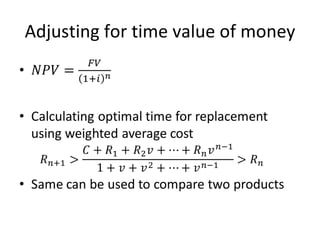
This document discusses replacement theory and models for determining when to replace products or services. It examines factors like maintenance costs increasing over time, probabilities of failure, and costs of failure or disruption. Common replacement scenarios explored include replacing when maintenance costs exceed replacement costs, replacing after a set number of failures, or periodically over time. The general approach is to analyze failure and performance patterns over time and assess costs and probabilities to determine the optimal replacement strategy.