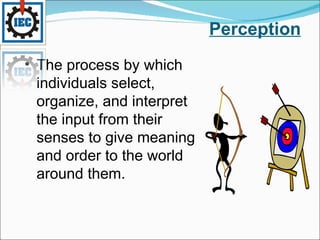
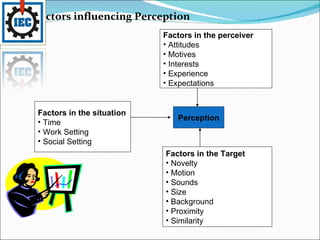
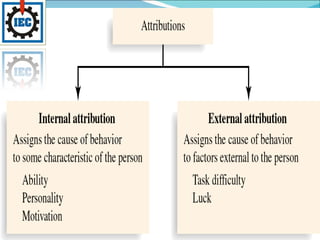
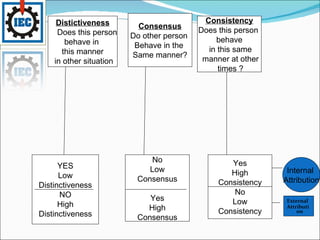
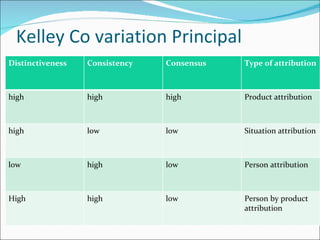
Perception is the process by which individuals select, organize, and interpret sensory input to make sense of their environment. It involves sensation, selection, organization, and translation of stimuli, influenced by factors in the perceiver like attitudes and experience, and factors in the target like novelty and size. Person perception involves making judgments about others through attribution theory, considering the distinctiveness, consensus, and consistency of internal versus external causes of behavior. Shortcuts in judging others include selective perception, halo effects, contrast effects, and stereotyping, with specific applications in organizations like interviews, performance expectations, evaluations, and assessing employee effort.