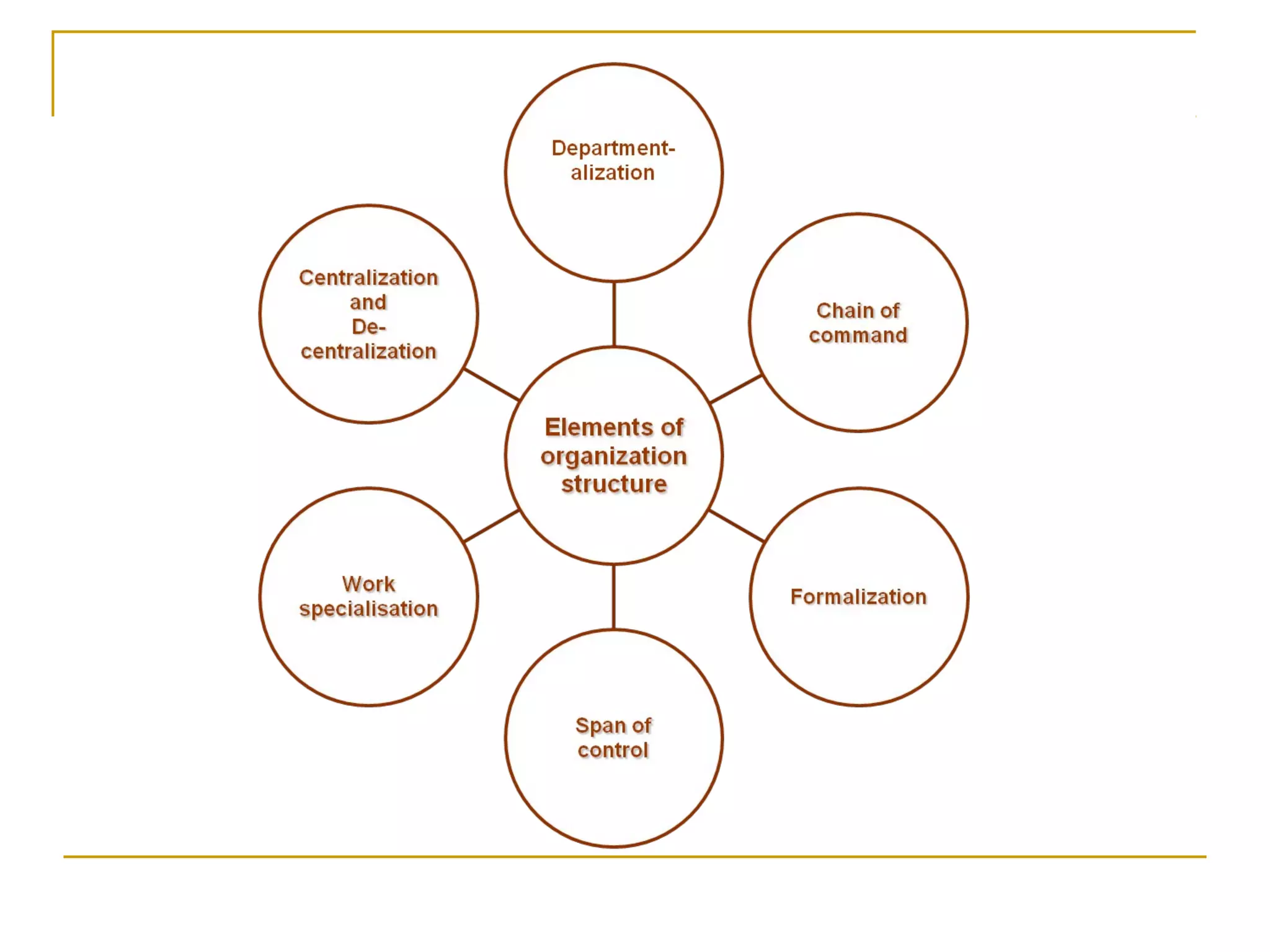
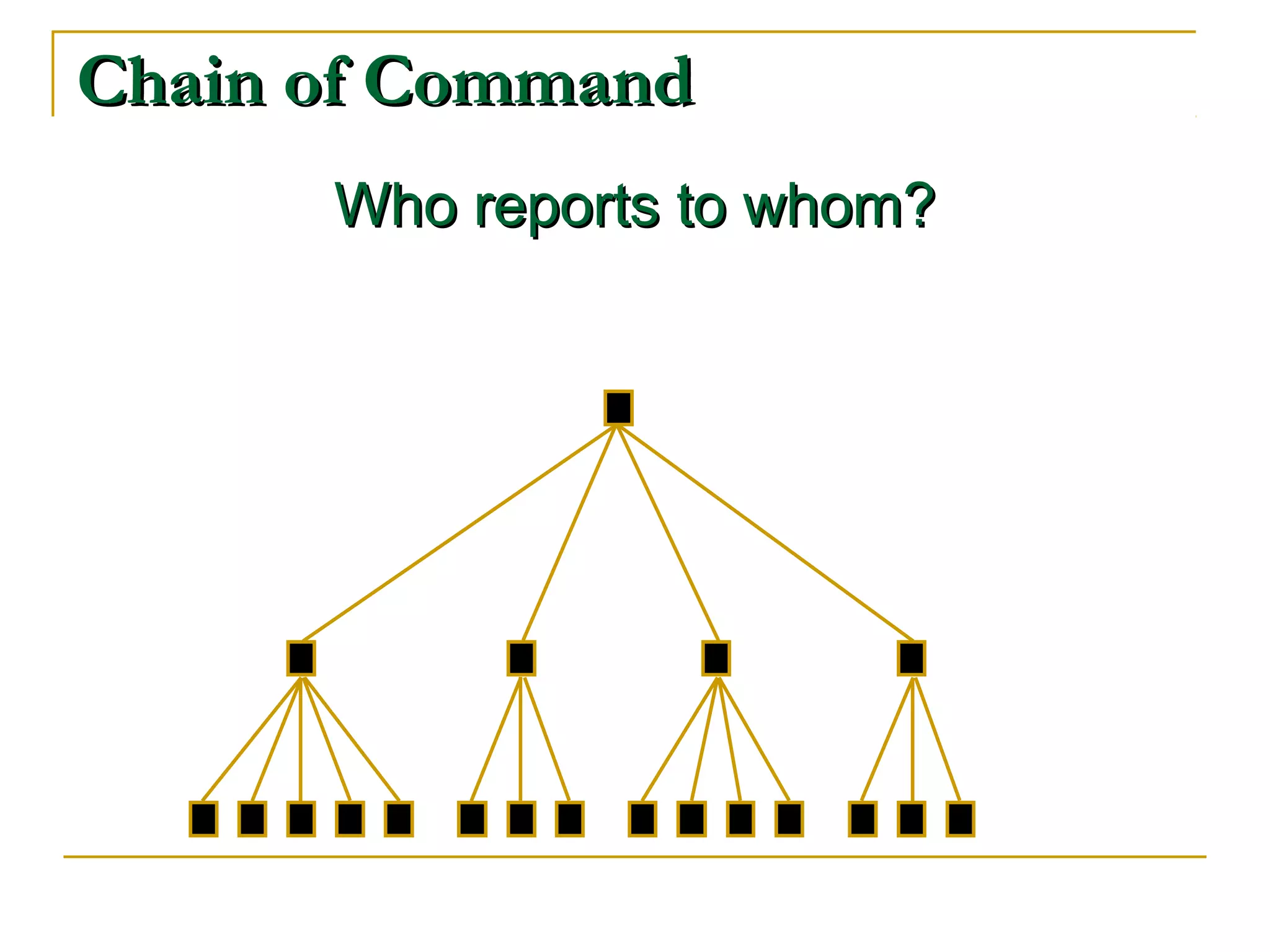
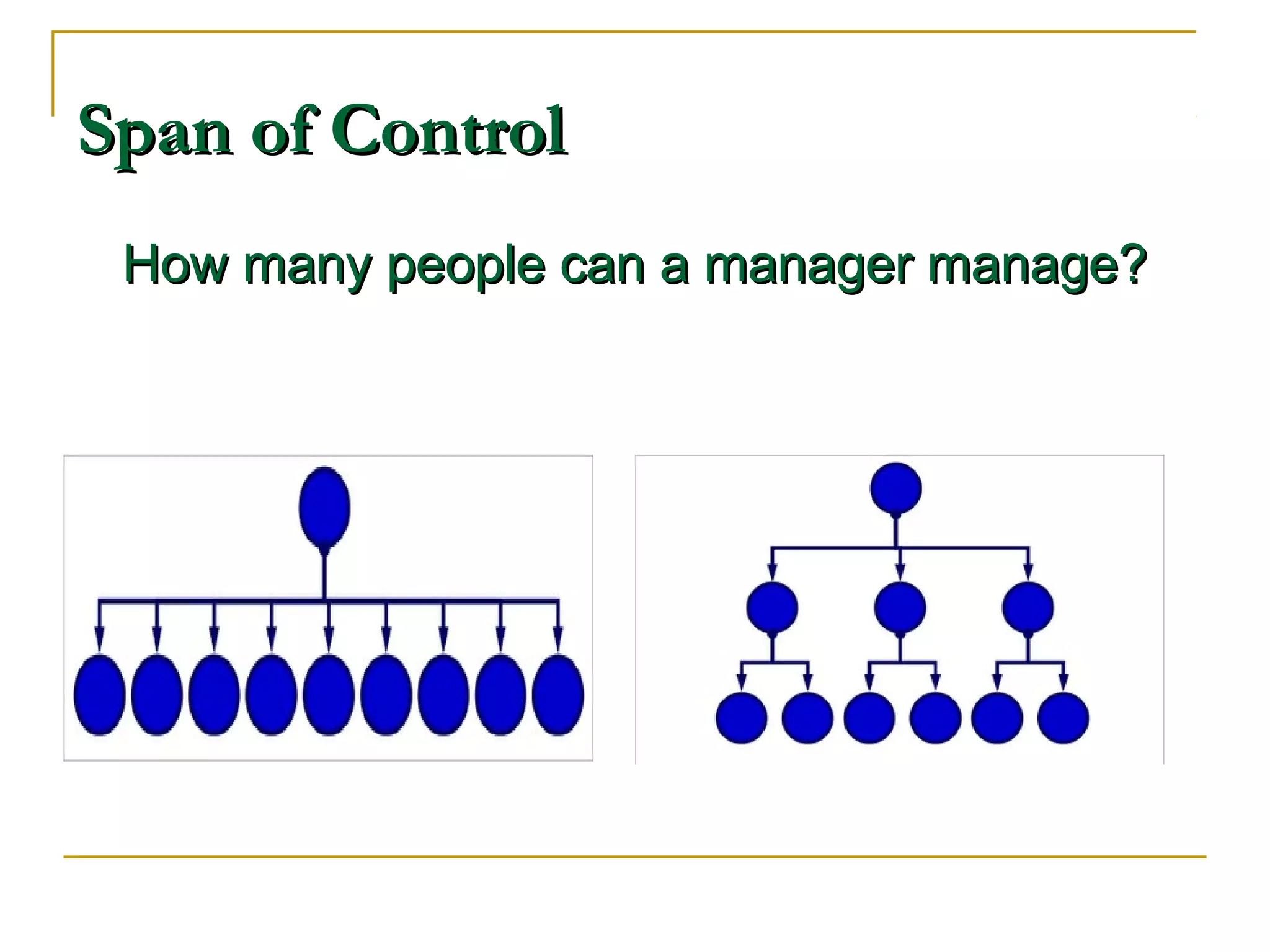
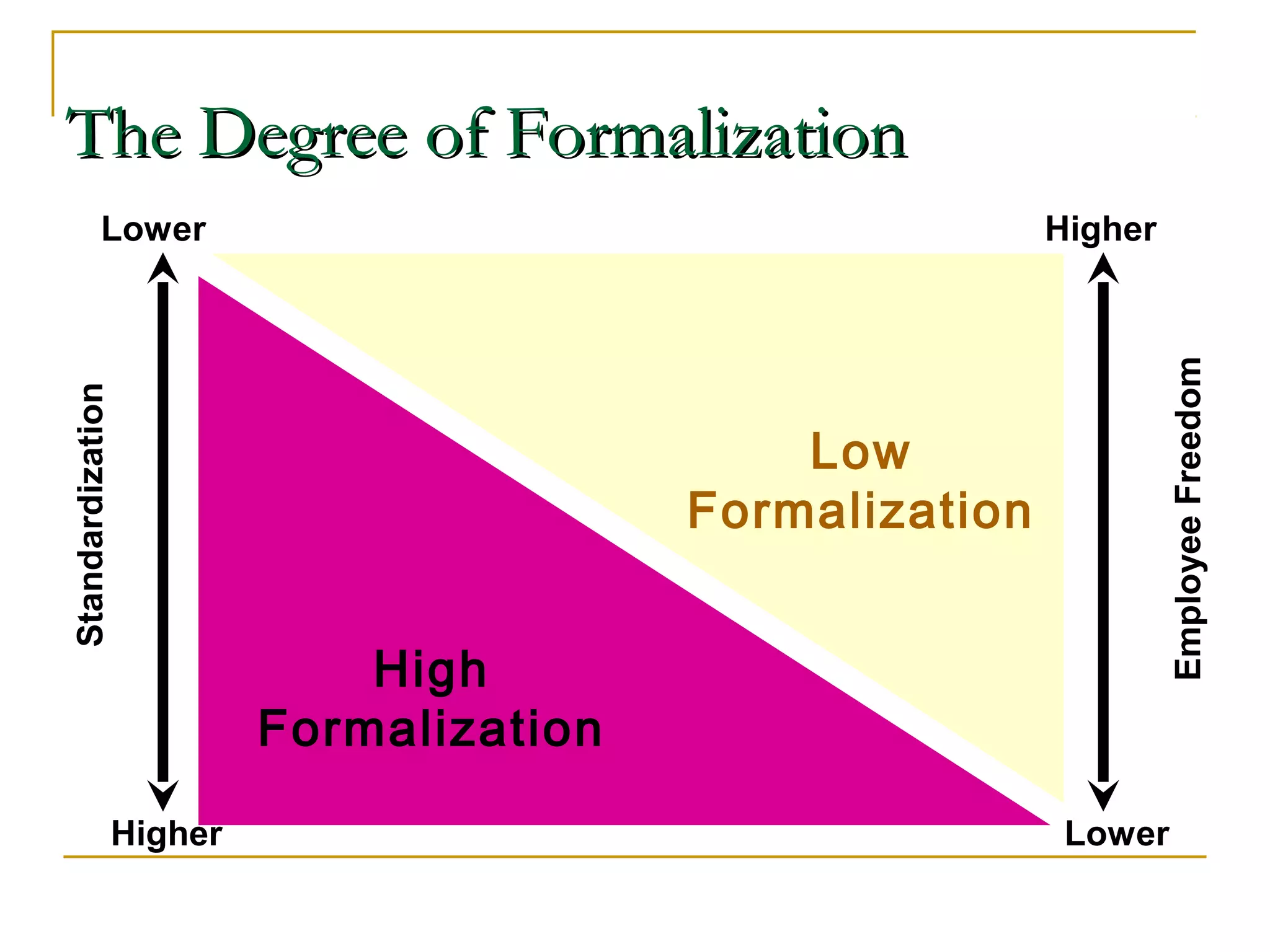
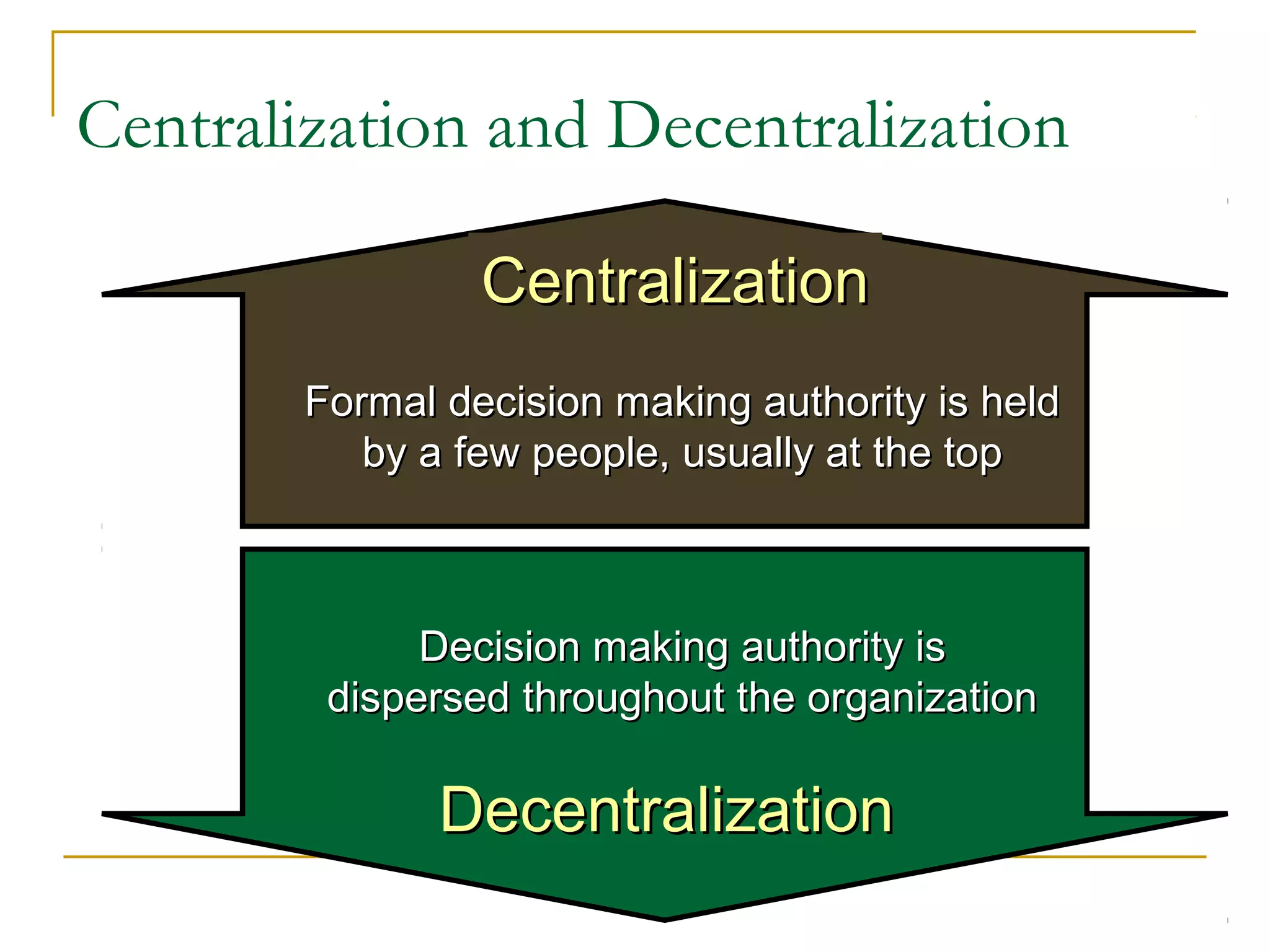
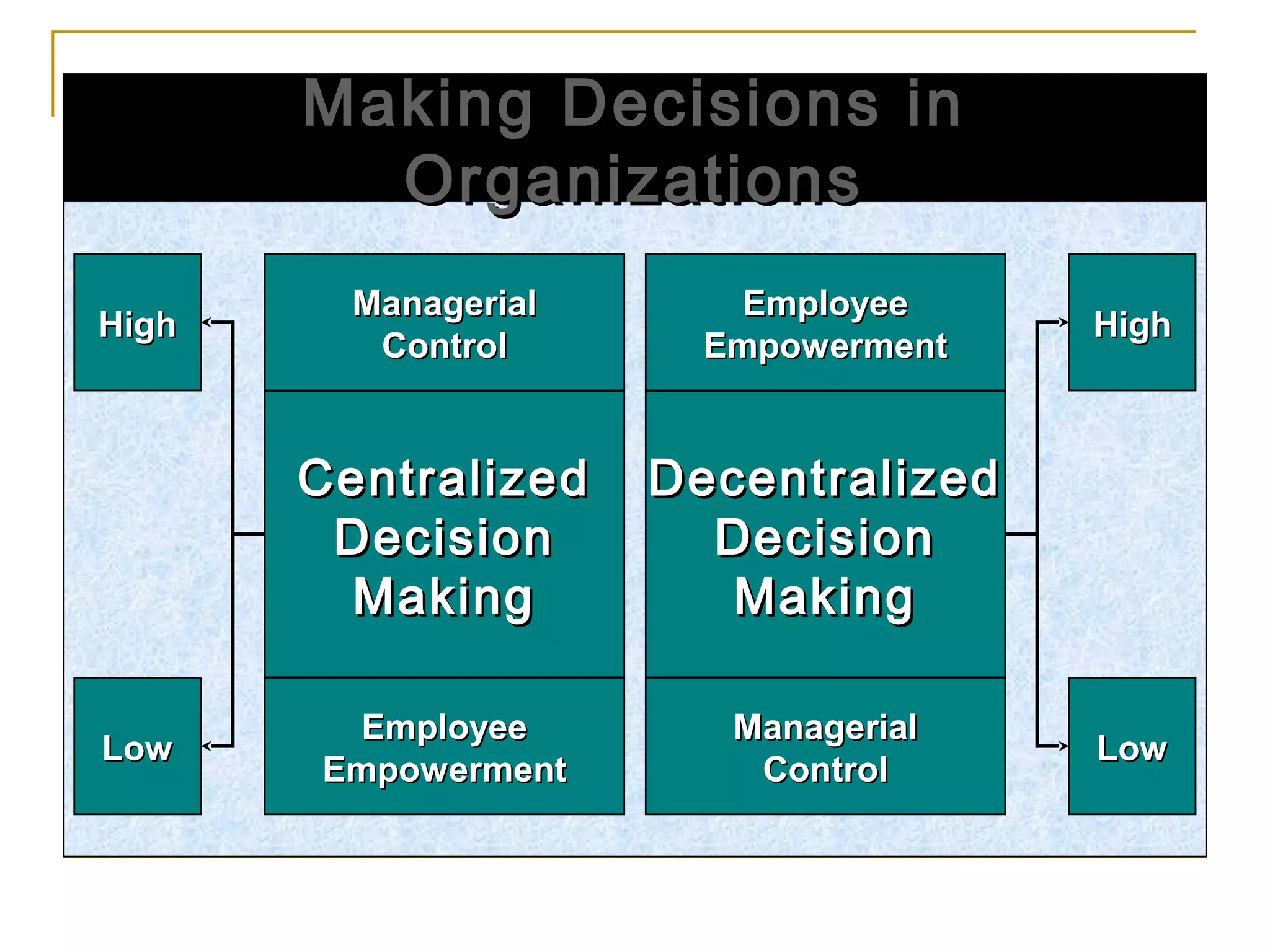
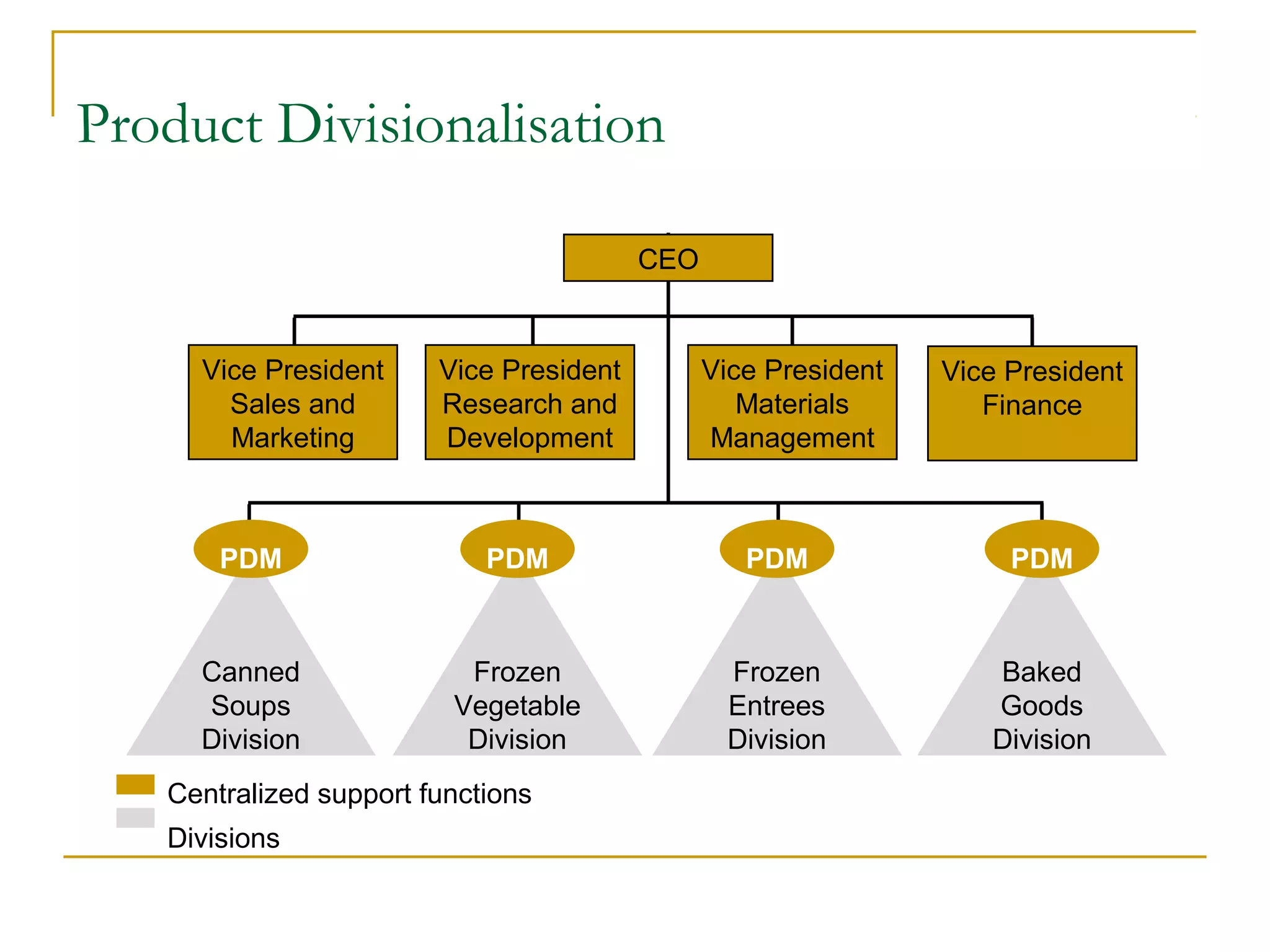
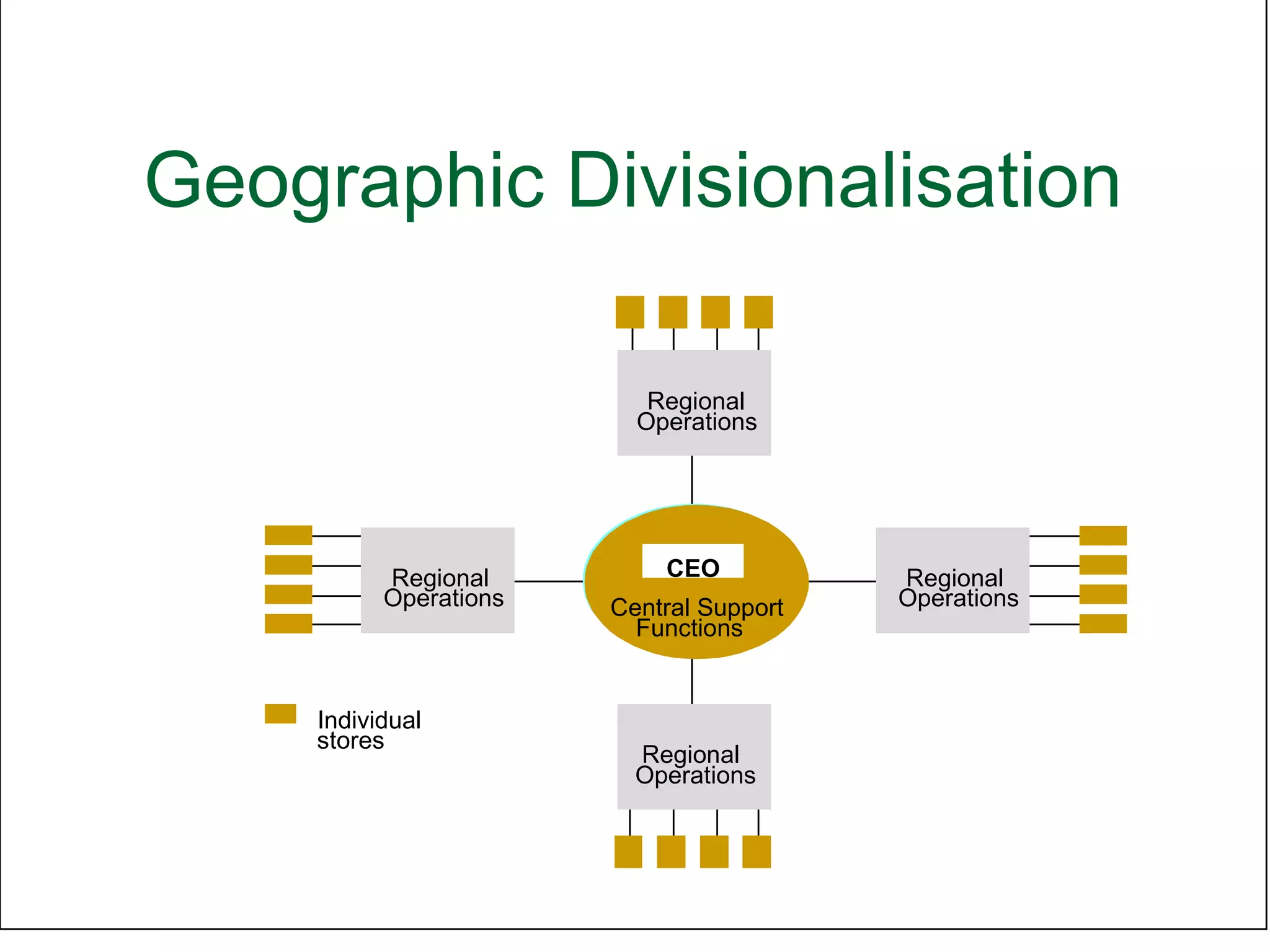
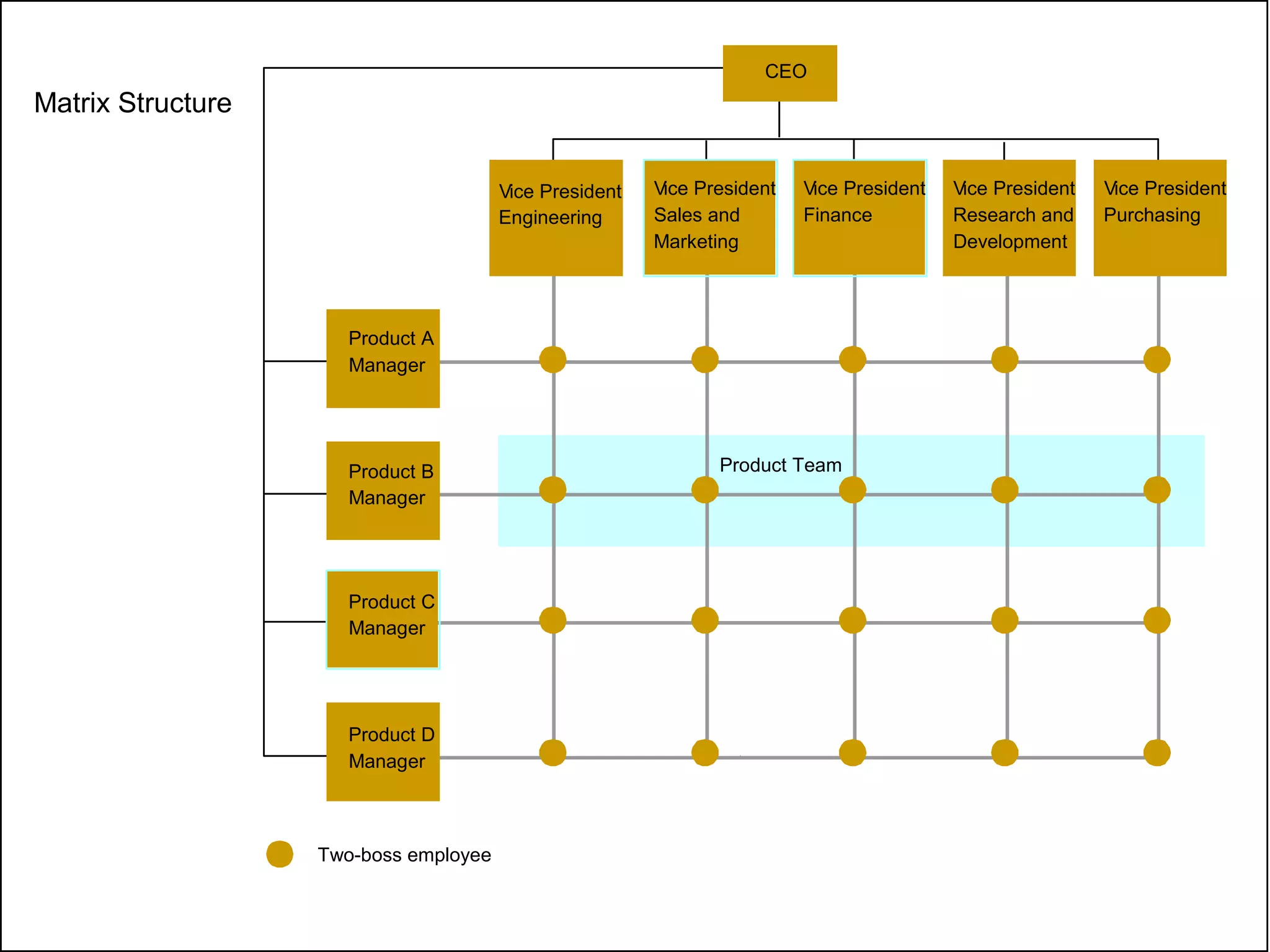
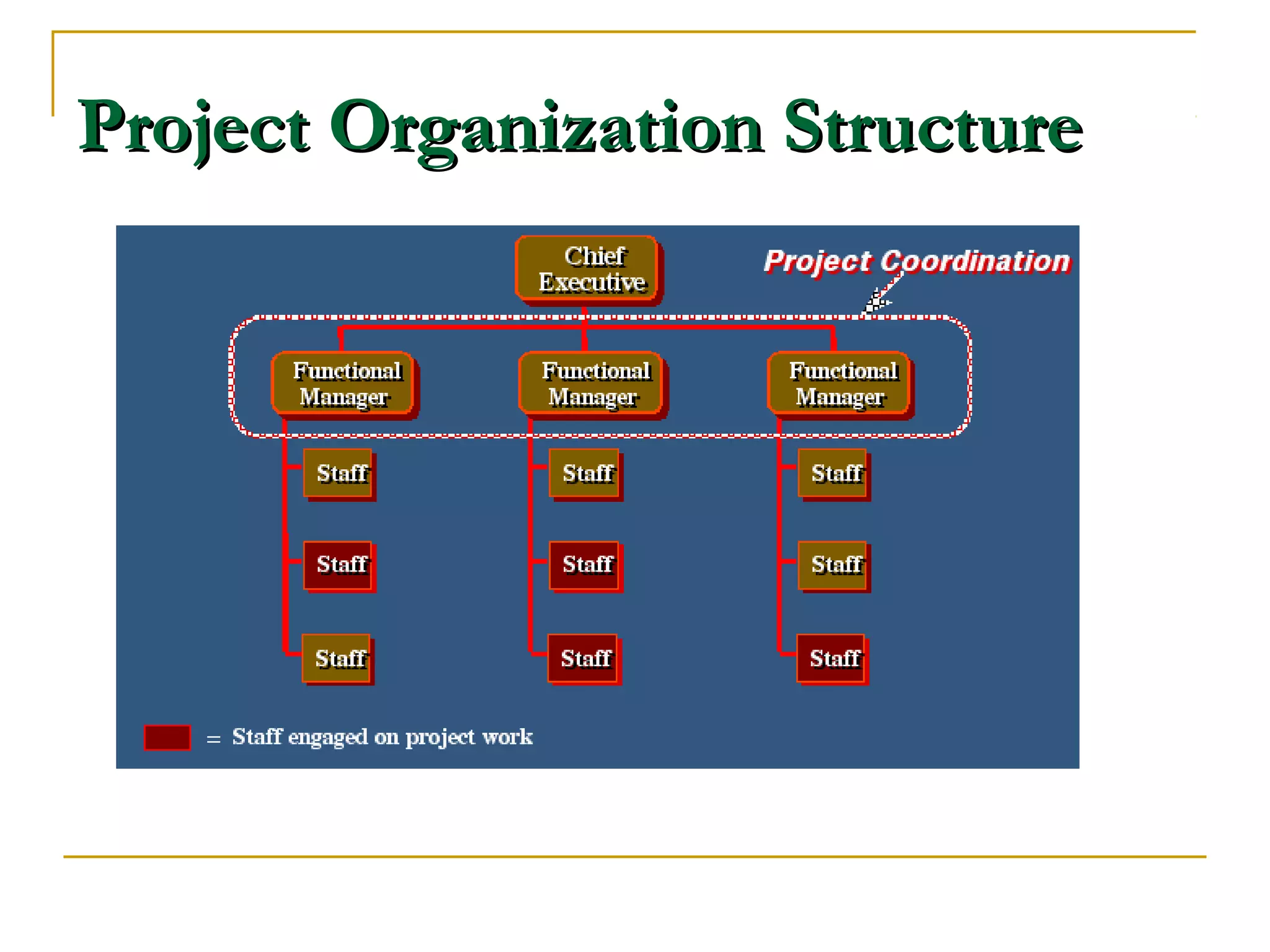
Organizational structure defines how tasks are divided and coordinated within a company. It establishes reporting relationships, decision making processes, and the degree of standardization and centralization. Common structures include functional, divisional, matrix, and network forms. Structure is important for facilitating management, encouraging growth and innovation, and optimizing human and technological resources.