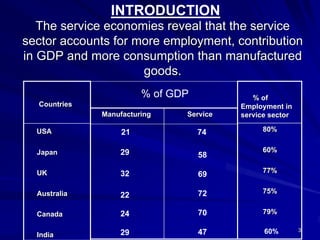
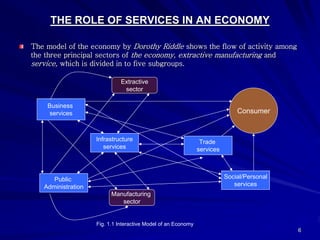
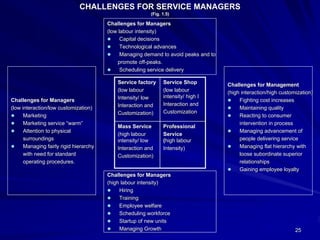
The document discusses the significance of the service sector in modern economies, highlighting its rapid growth and contribution to GDP and employment. It emphasizes the unique characteristics of services, such as intangibility and perishability, and the challenges faced in marketing them effectively. Additionally, it examines India’s position as a growing service economy and the importance of innovative marketing strategies tailored to consumer needs.