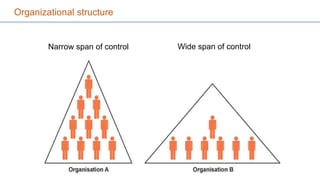
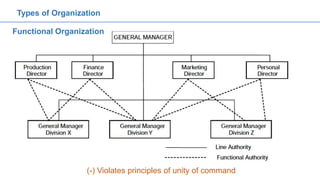
The document provides an overview of organizing and staffing concepts in management. It defines organizing as arranging work to accomplish goals and includes principles of organization like objectives and specialization. It also discusses types of organization structures like functional, line and staff. Staffing involves acquiring and retaining qualified employees and its elements include recruitment, selection, training and performance appraisal. Recruitment is the process of attracting job candidates while selection involves evaluating candidates and hiring.