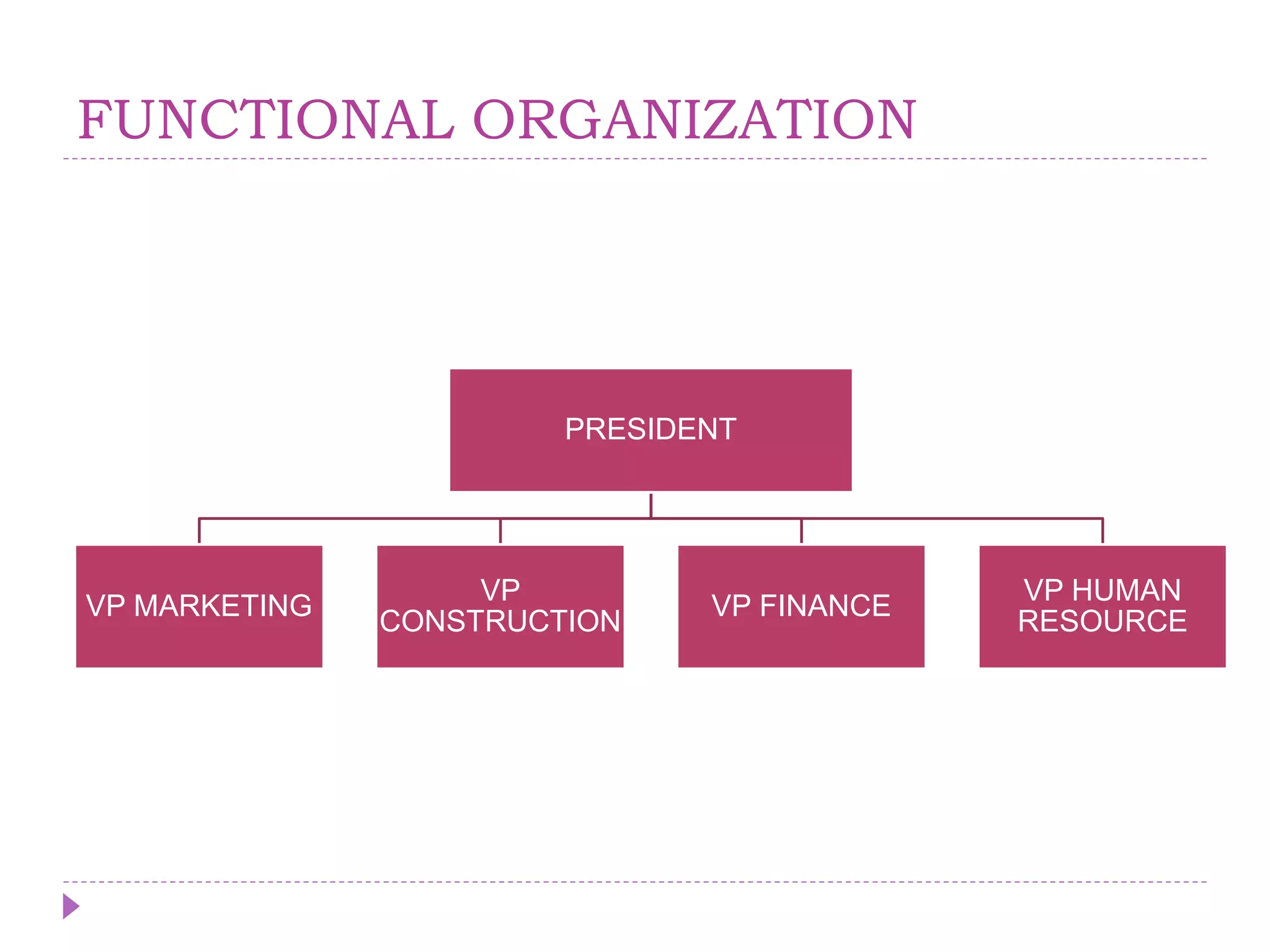
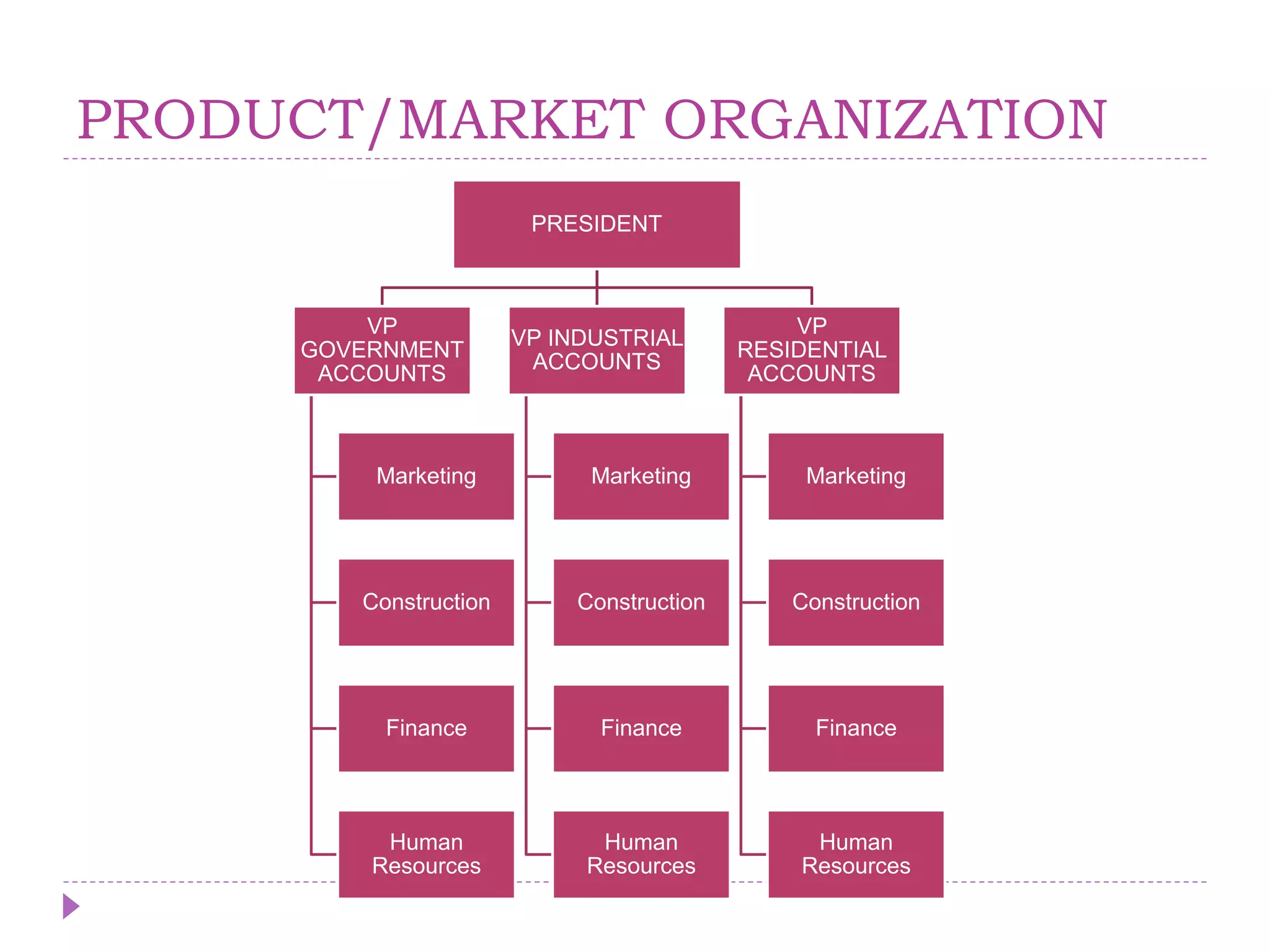
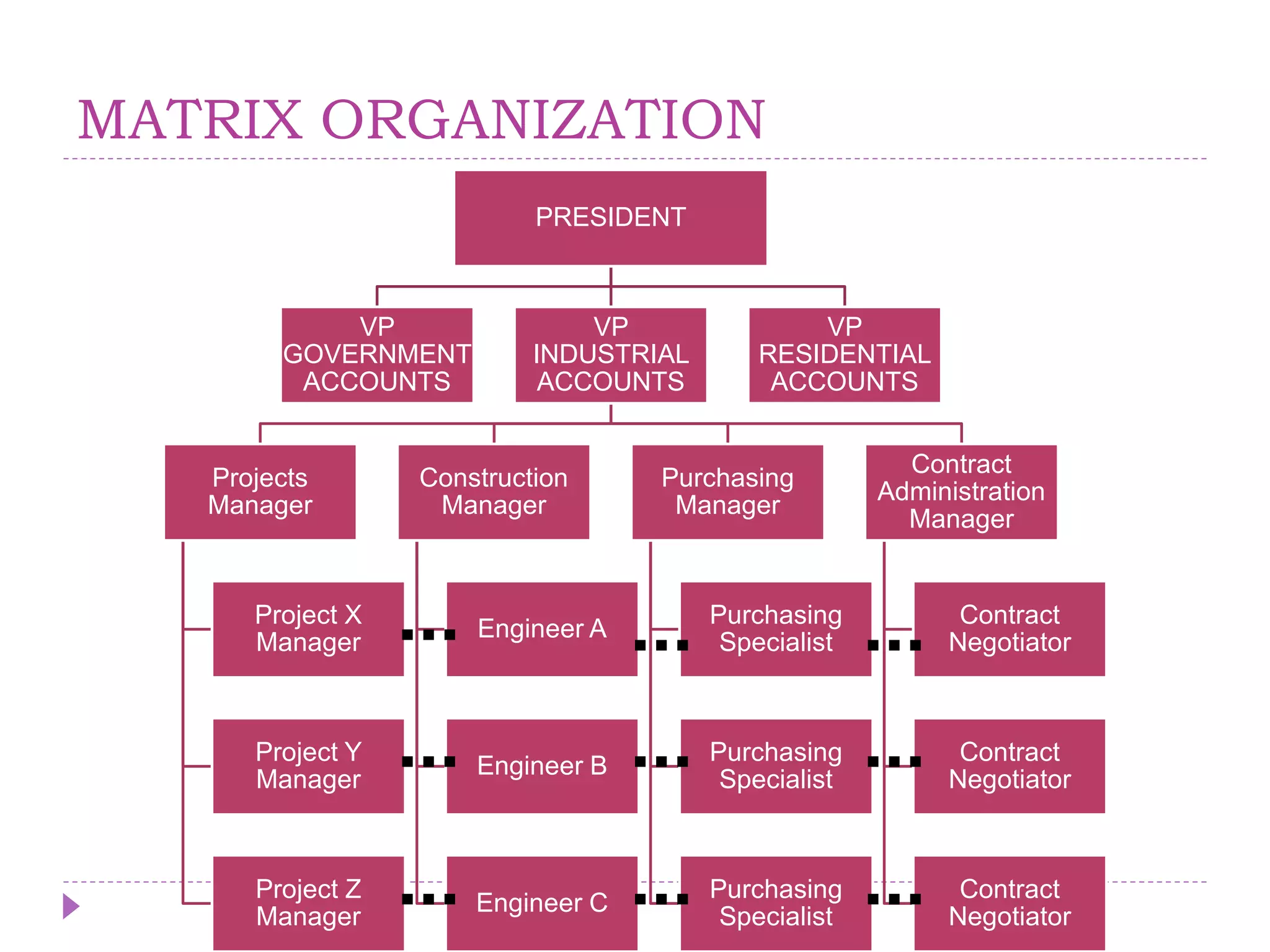
The document describes key concepts related to organizing processes in management. It defines organizing as structuring resources and activities to accomplish objectives efficiently and effectively. The document outlines different types of organizational structures like functional, product/market, and matrix structures. It also discusses delegation of authority and different types of authority like line, staff, and functional authority. Committees are described as formal groups used to achieve organizational goals.