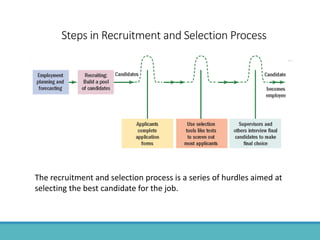
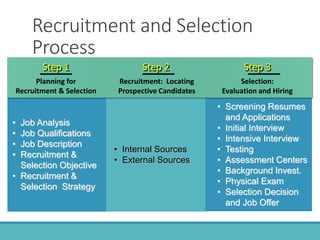
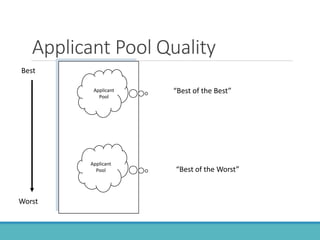
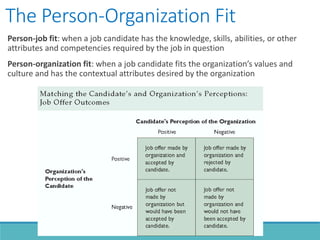
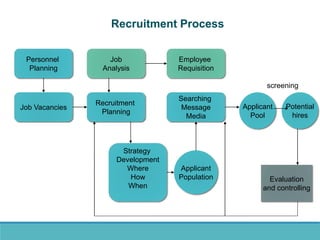
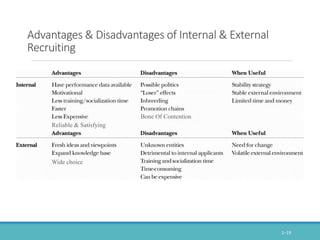
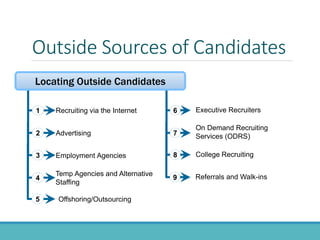
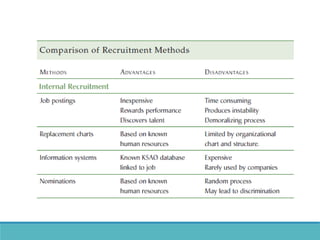
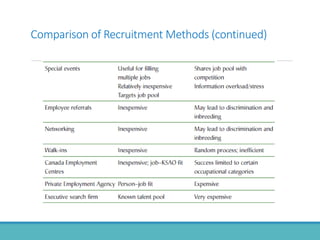
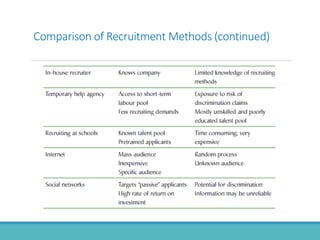
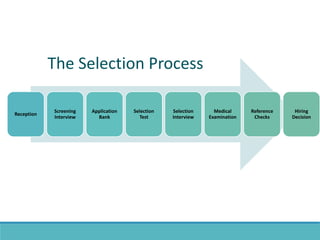
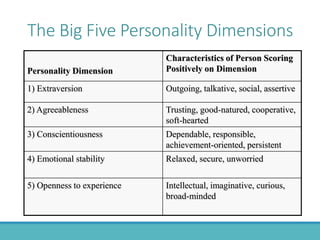
The document outlines the personnel planning and recruitment process, detailing steps from job analysis to selection. It emphasizes the importance of creating a robust applicant pool, utilizing various recruitment methods, and evaluating candidates to ensure a good fit with the organization. Additionally, it discusses metrics for assessing recruitment effectiveness and highlights potential challenges in attracting the best candidates.






























![Selection Testing
Intelligence Test
Aptitude Test
Personality Test (PIP) [Projective, Interest, Preference]
Achievement Test
Simulation Test
Assessment Centre [ In-basket, Leaderless Group Discussion, Business
Games]
Graphology Test [Handwriting Test]
Polygraph Test [Lie Detector Test]
Integrity Test](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit03b-160519044112/85/Staffing-Recruitment-and-Selection-42-320.jpg)









![Post Selection Strategies
-Making the Job Offer;
- An offer of employment may be made either verbally or in writing;
- Typically a verbal offer is made first, followed by a written offer once the
applicant accepts;
- The offer remains such until such time as the applicants [unconditionally]
accepts (either verbally or in writing);
- Note that the job advertisement is not a job offer, rather an invitation to
apply for employment;
- Employment offers should not be made during or immediately after the
employment interview;
- When making offers, employers should ensure they do not make any
statements that are misleading or deceptive (possible breaches of s31 of Sch 2 of the
Competition & Consumer Act 2010);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/unit03b-160519044112/85/Staffing-Recruitment-and-Selection-53-320.jpg)


