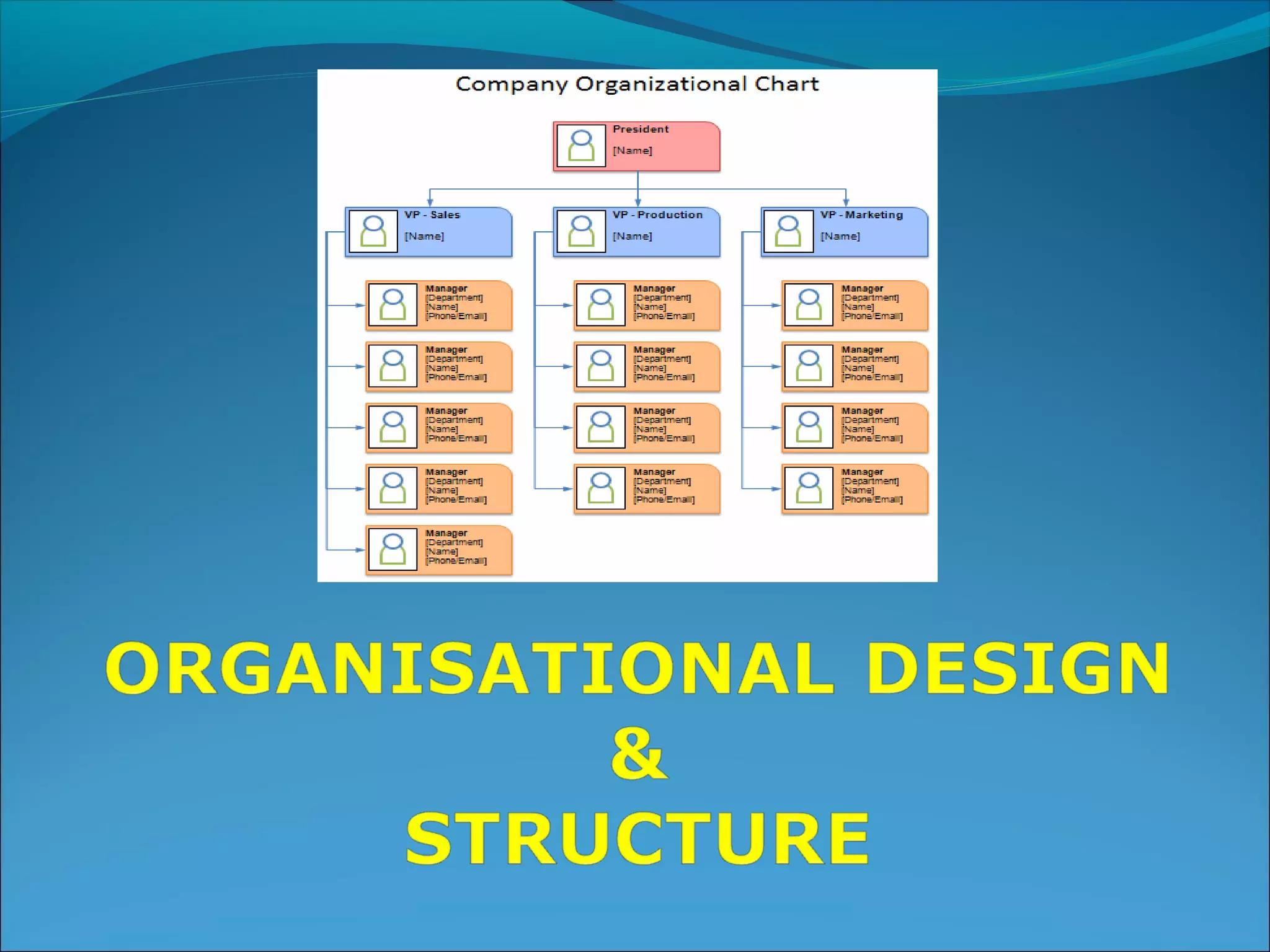
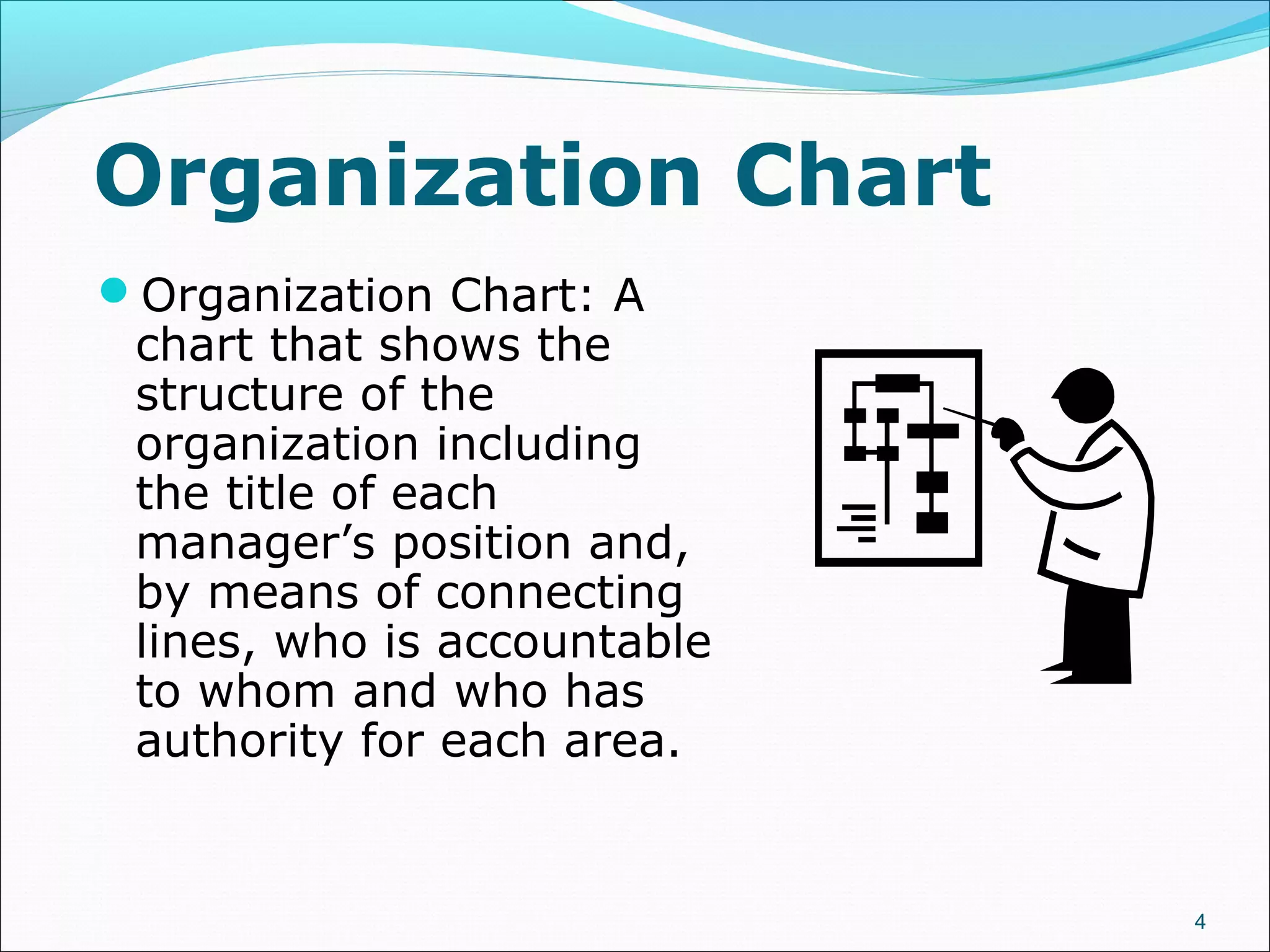
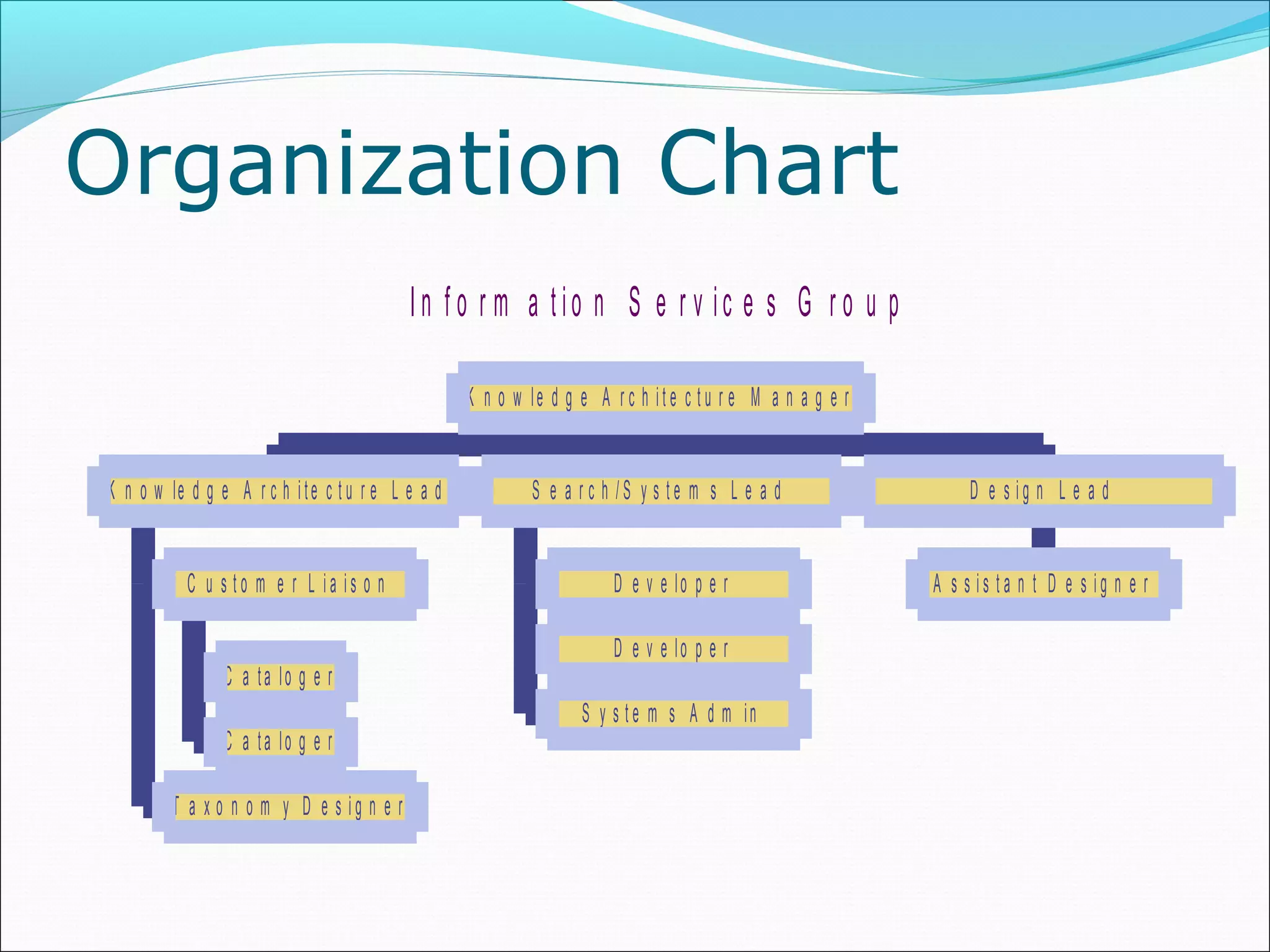
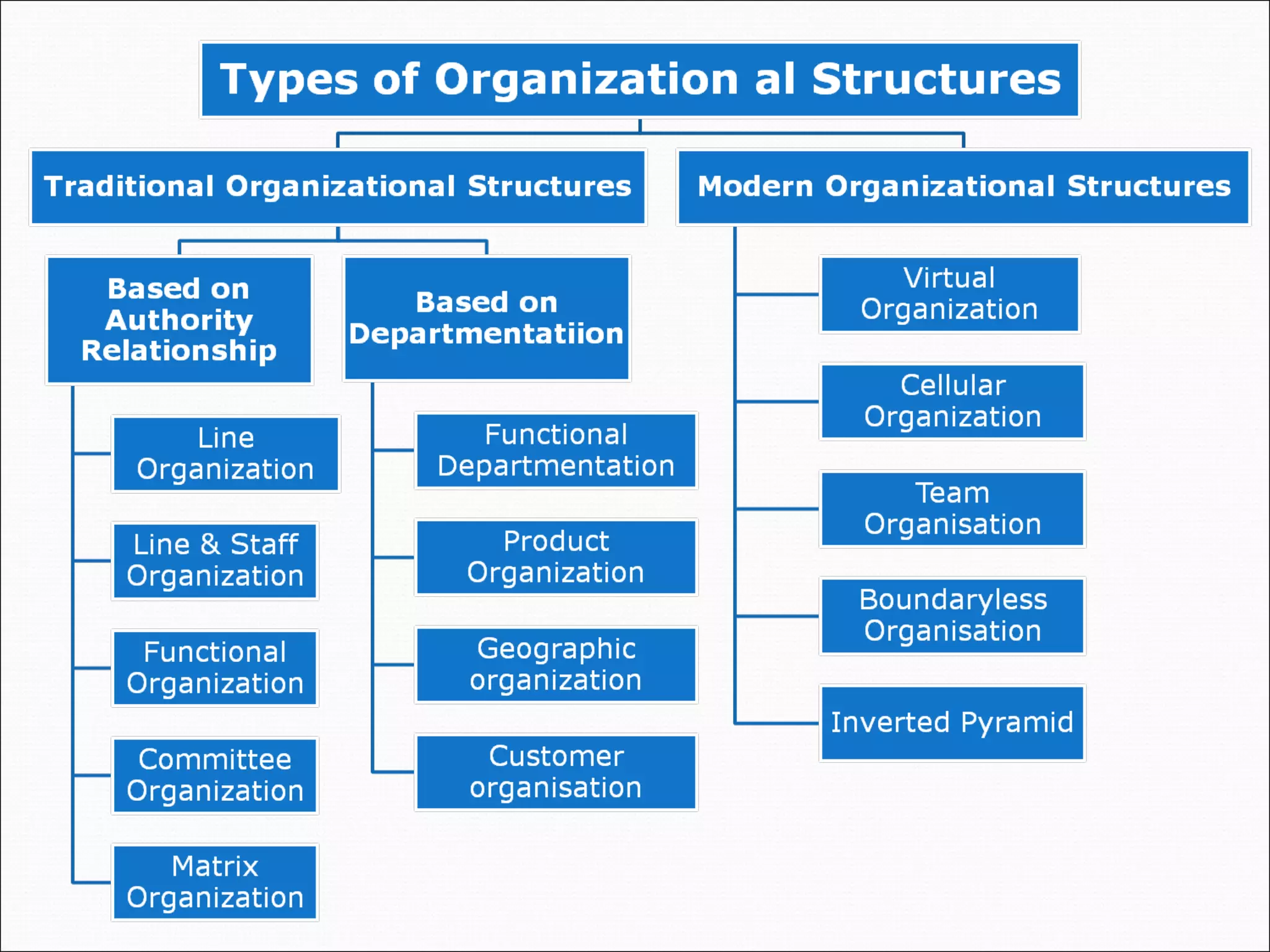
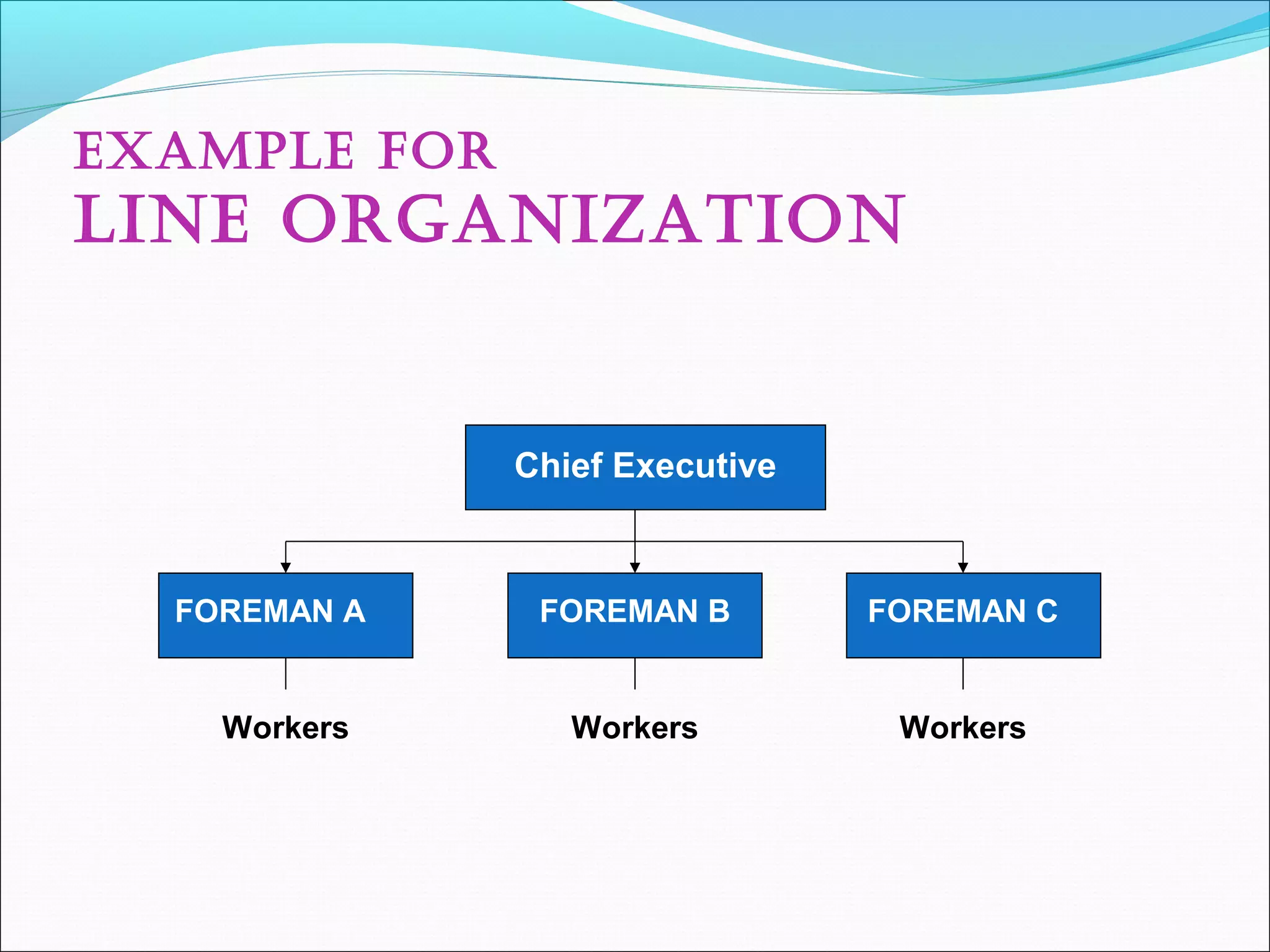
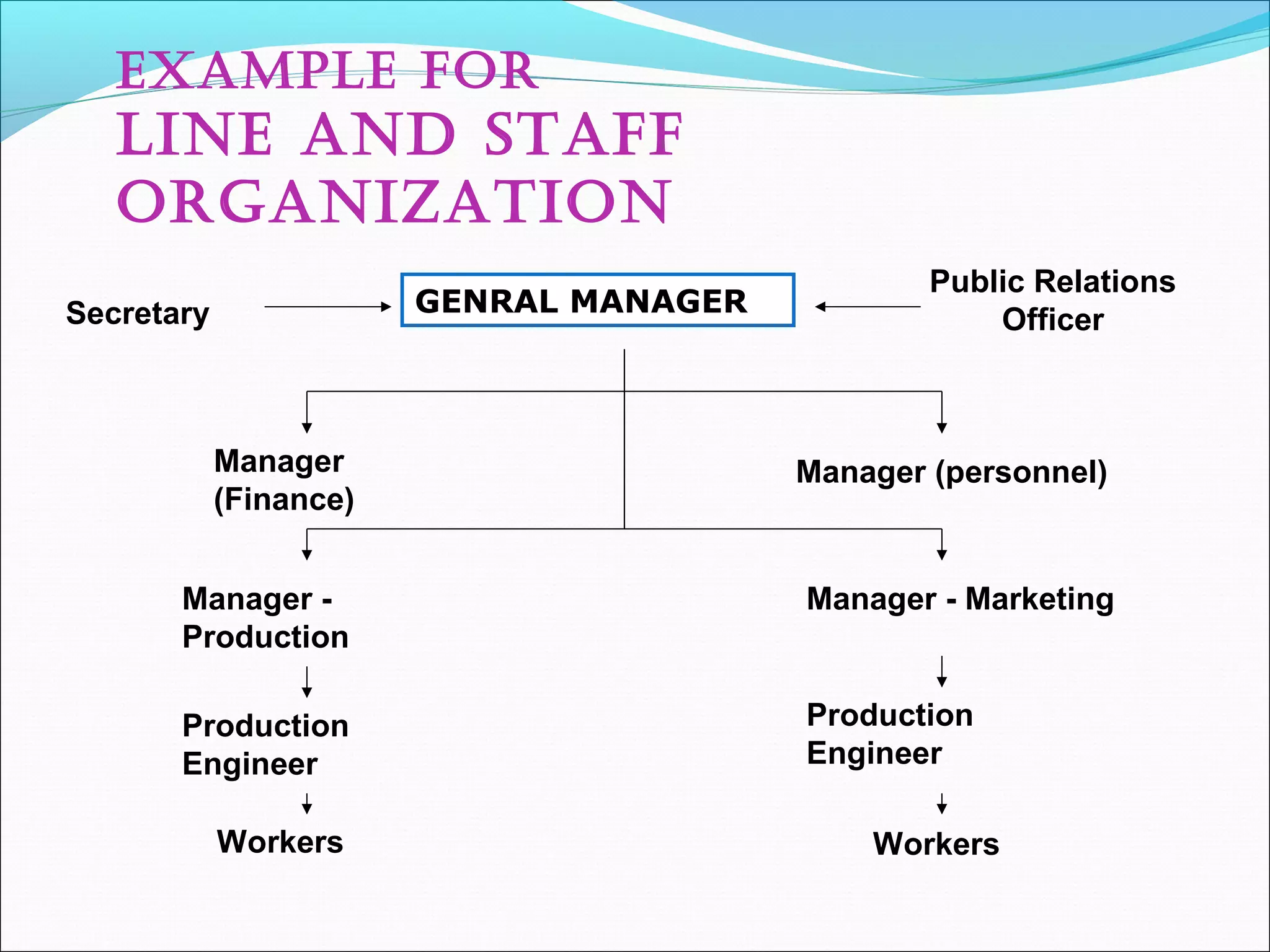
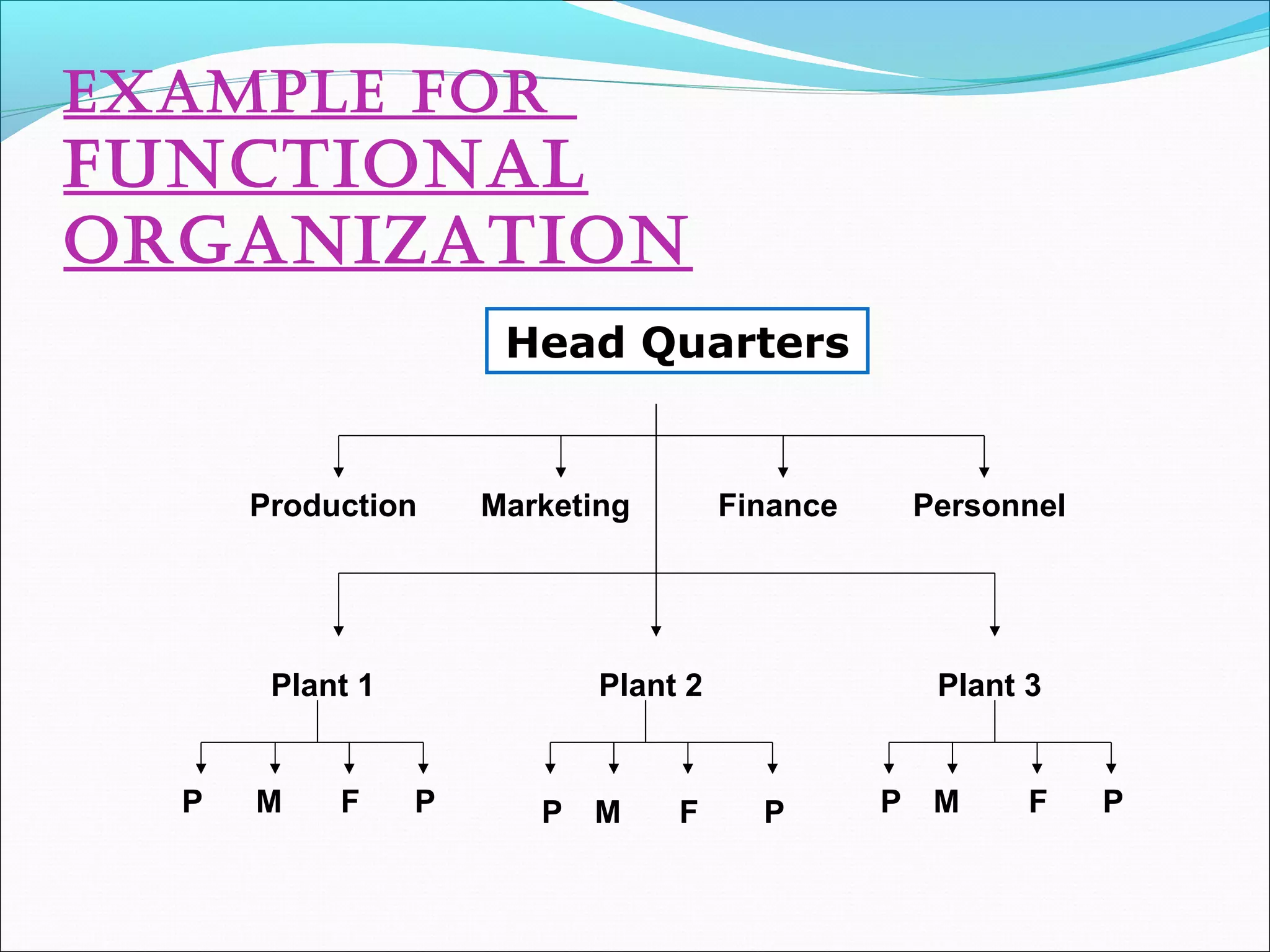
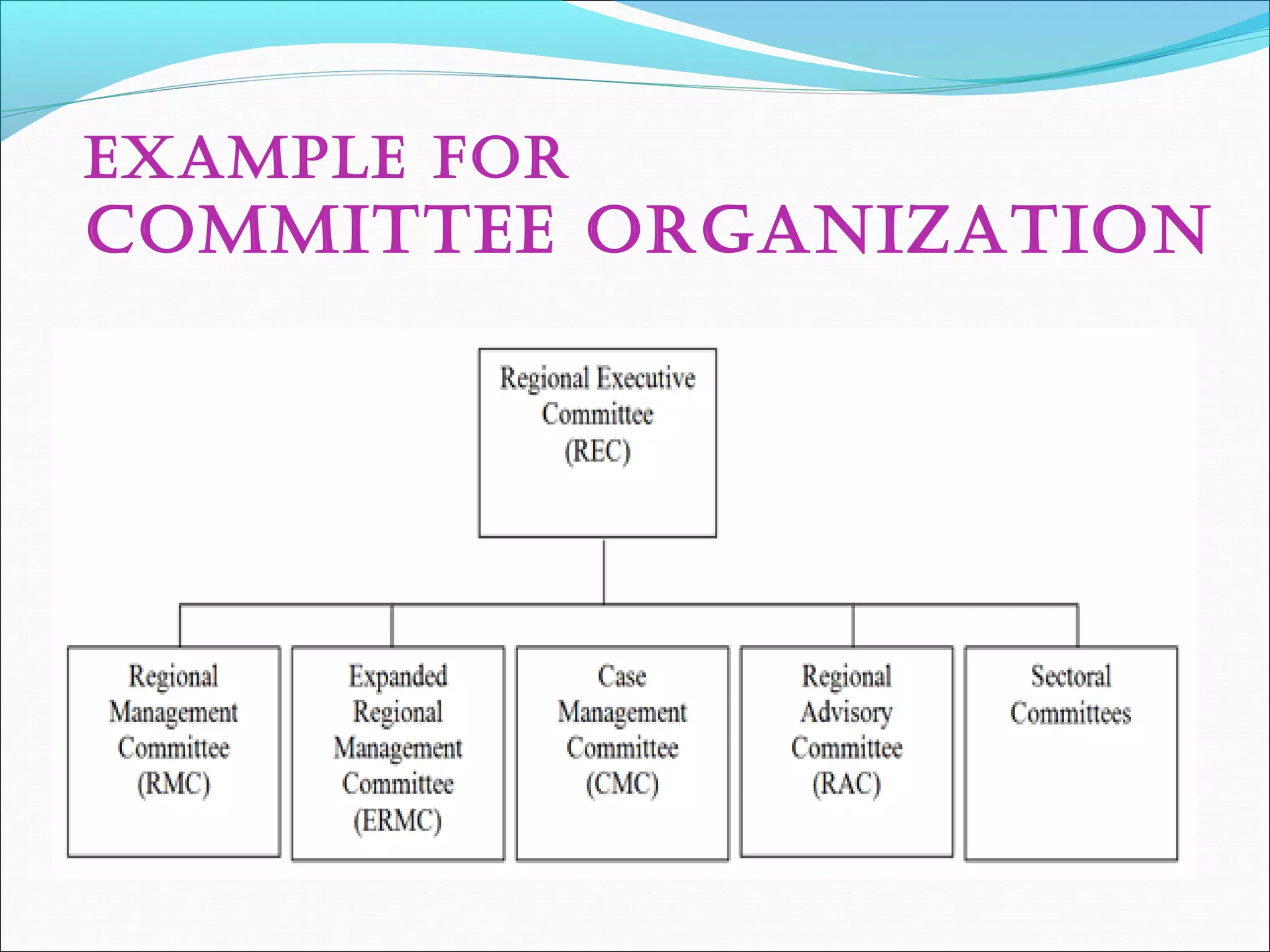
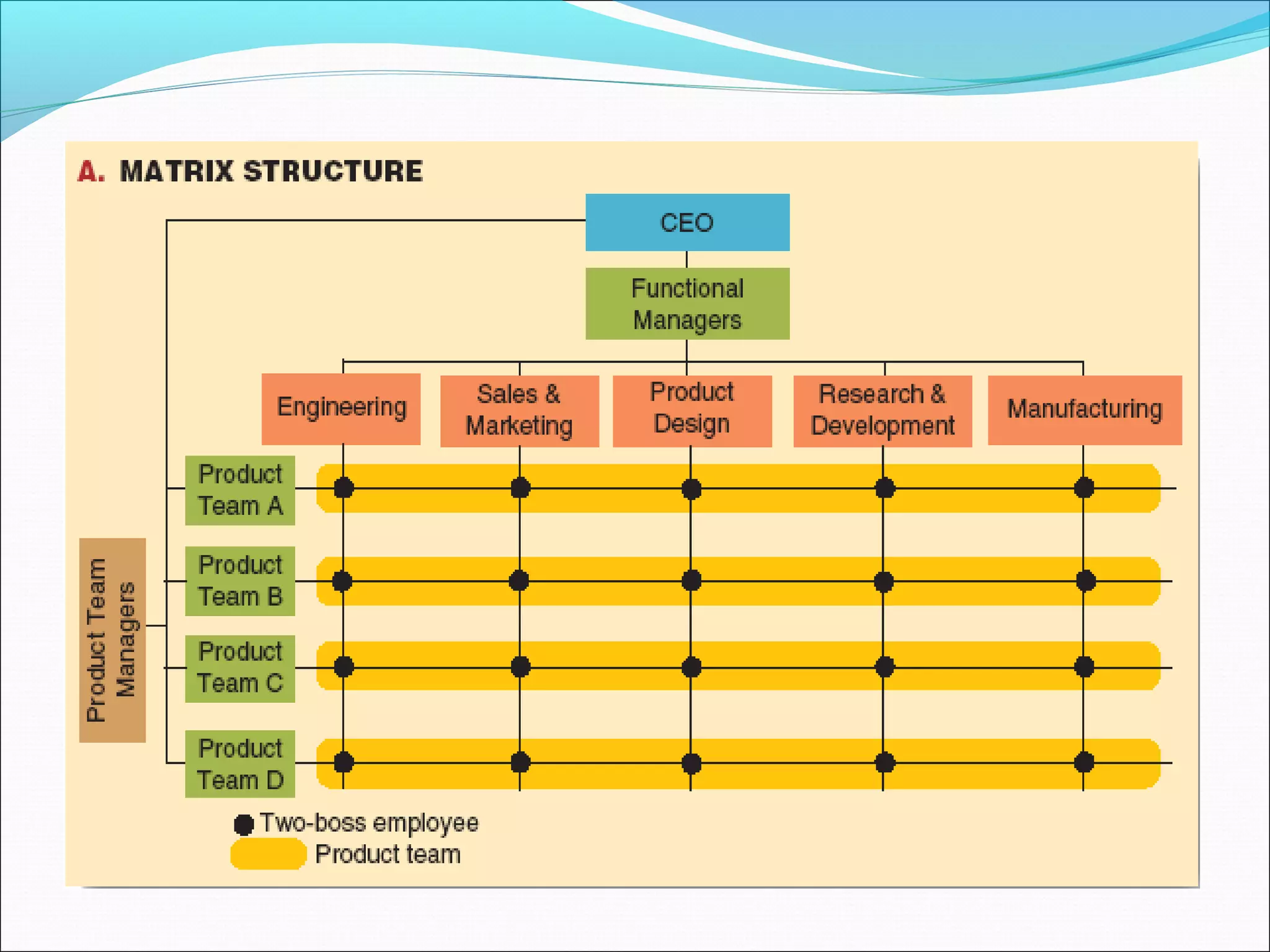
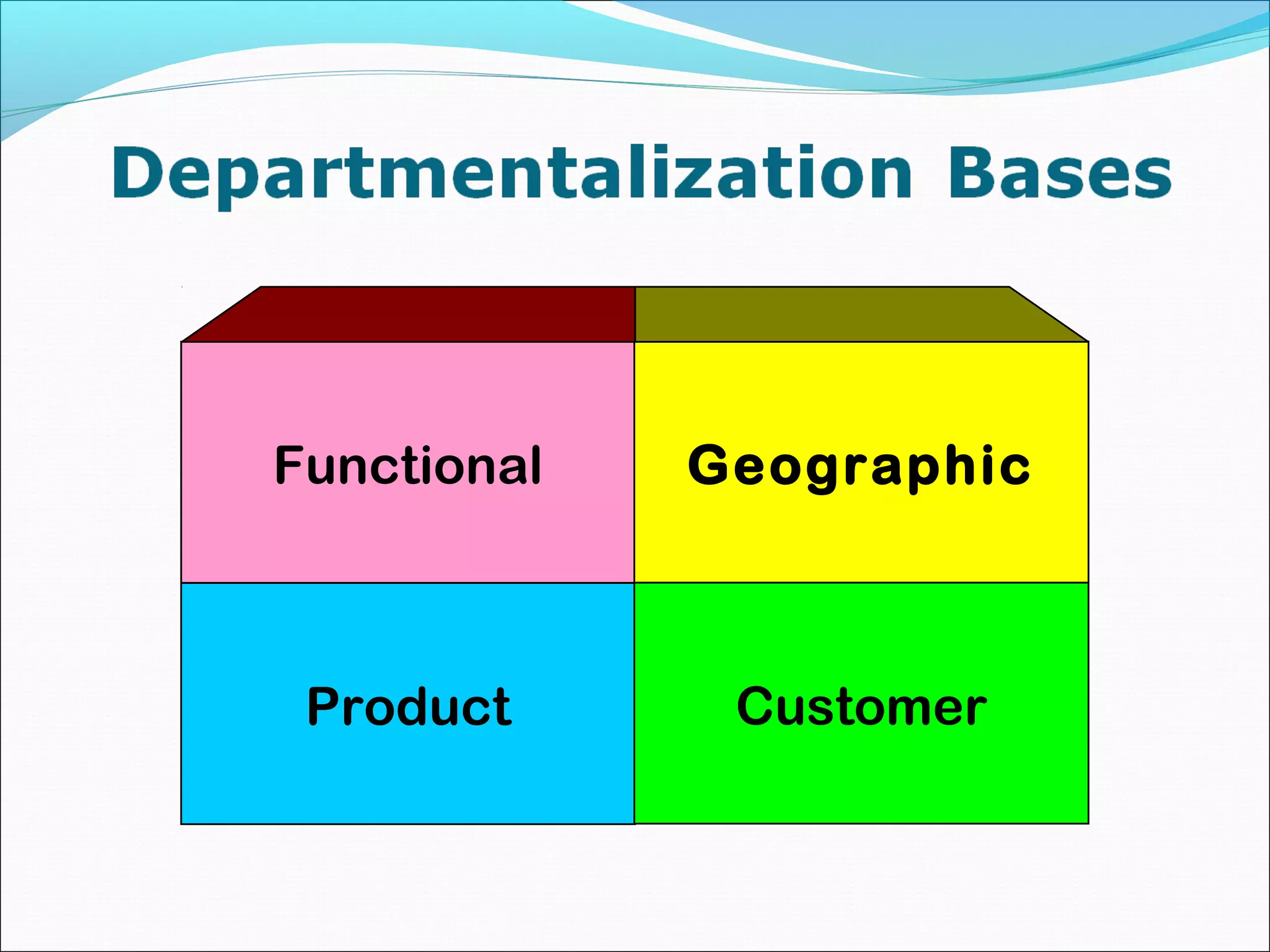
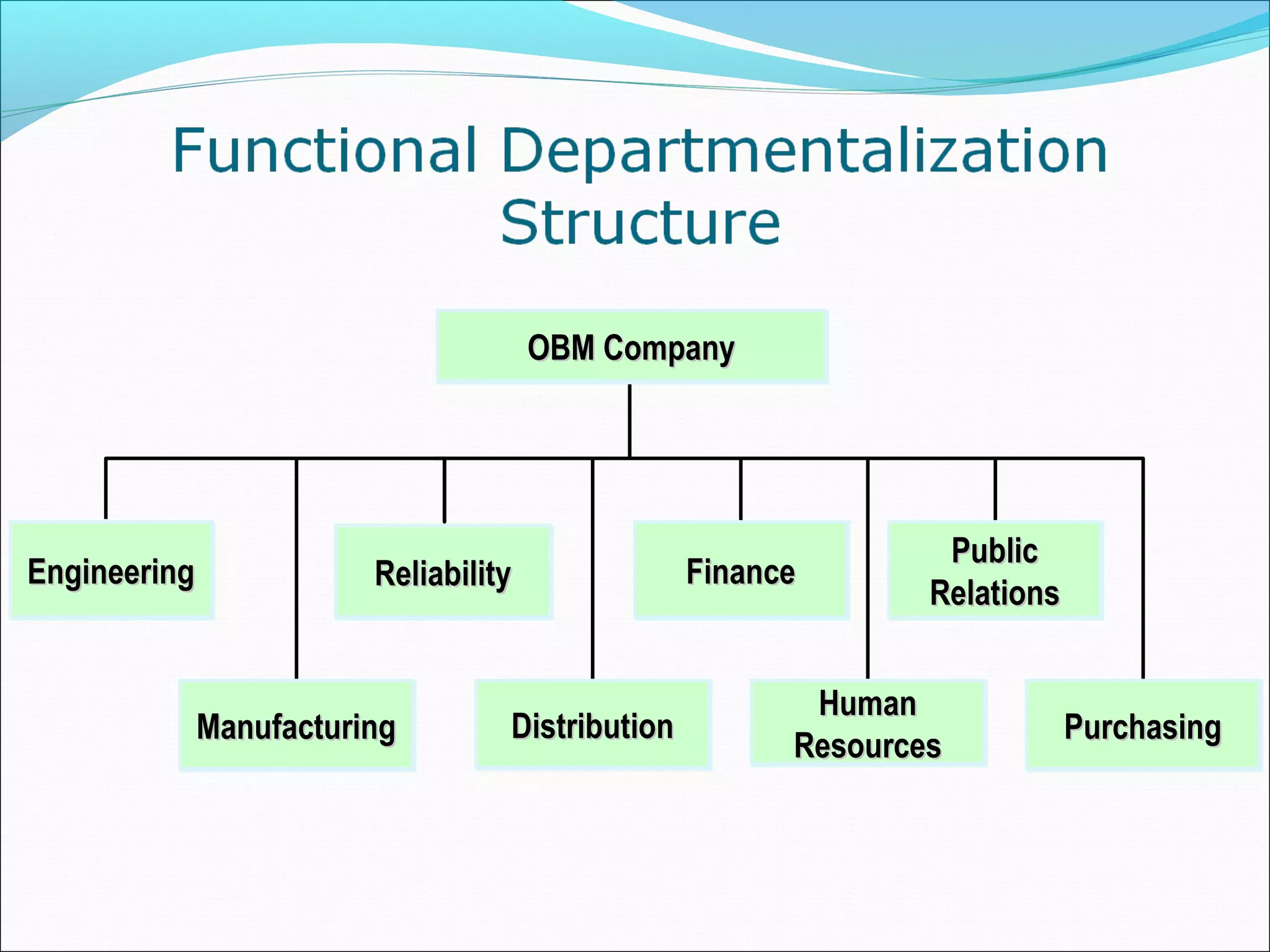
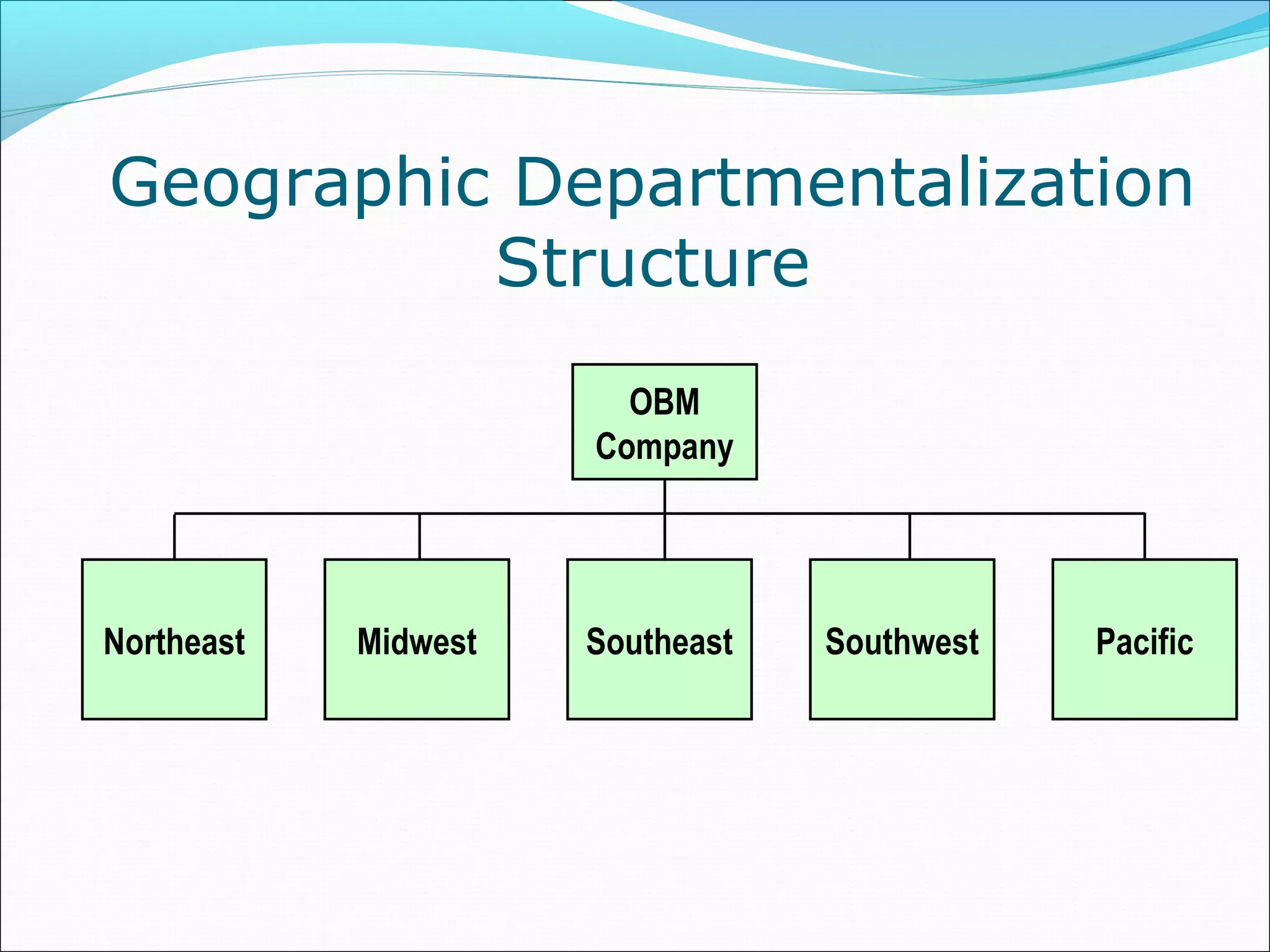
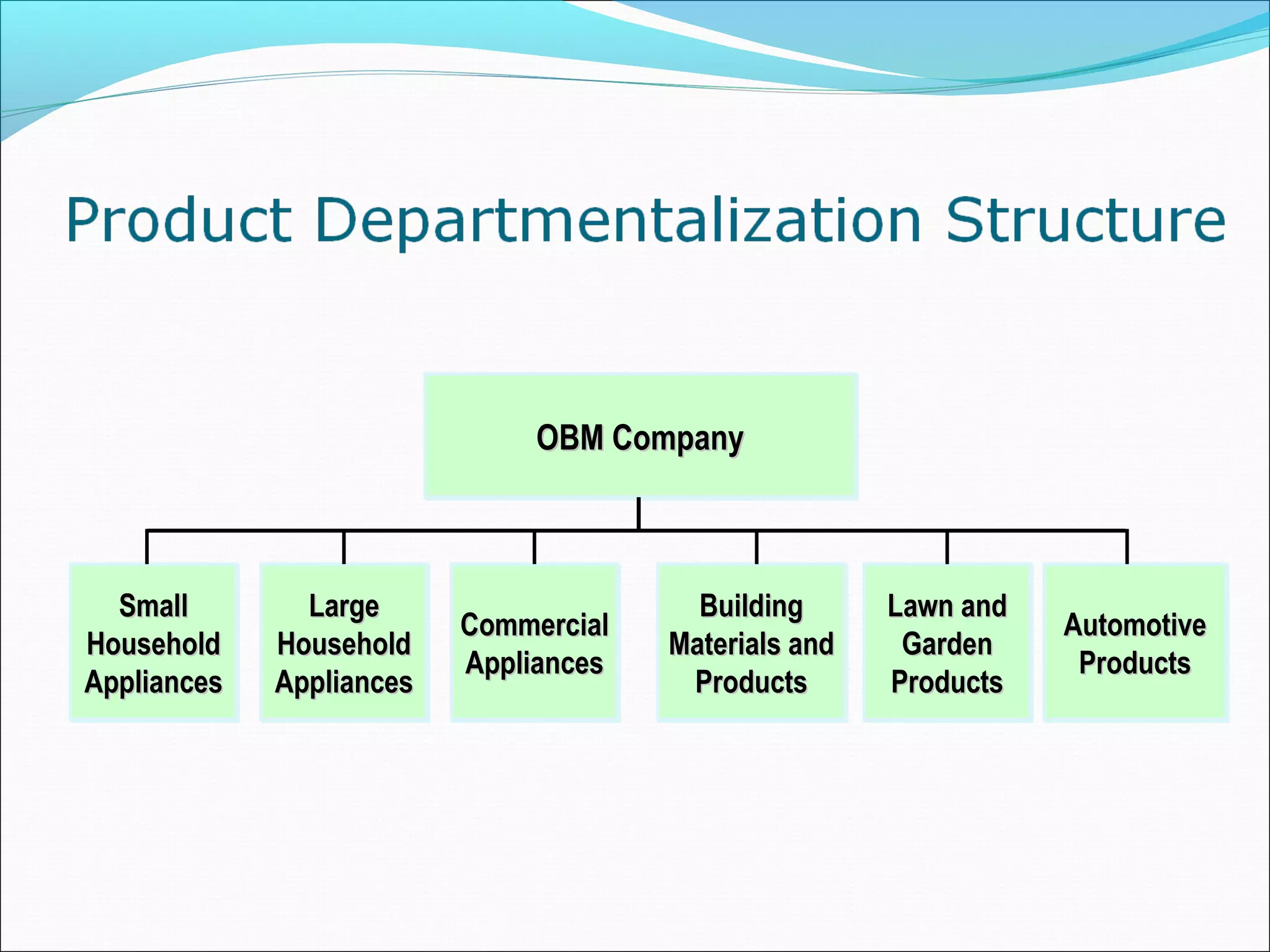
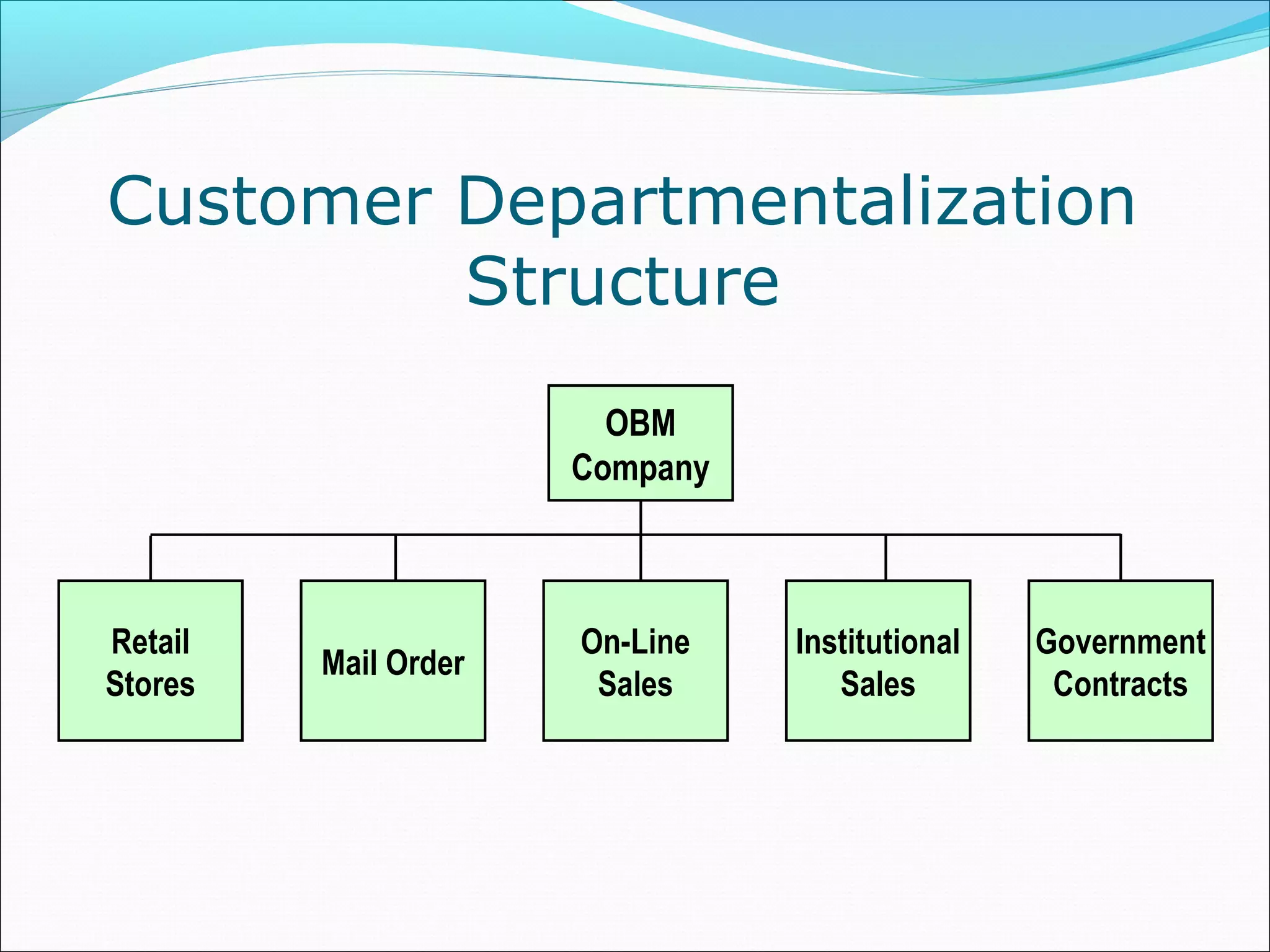
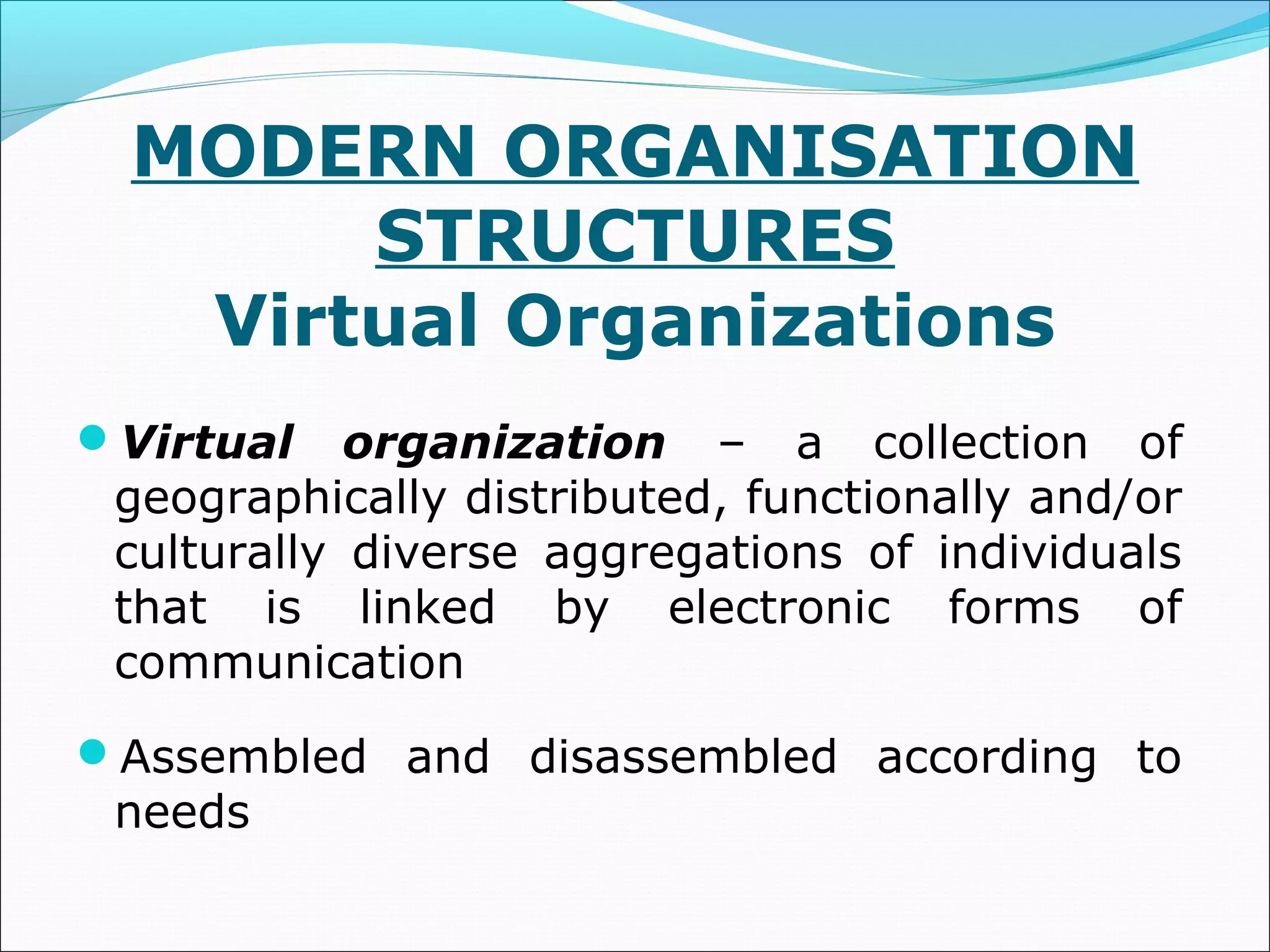
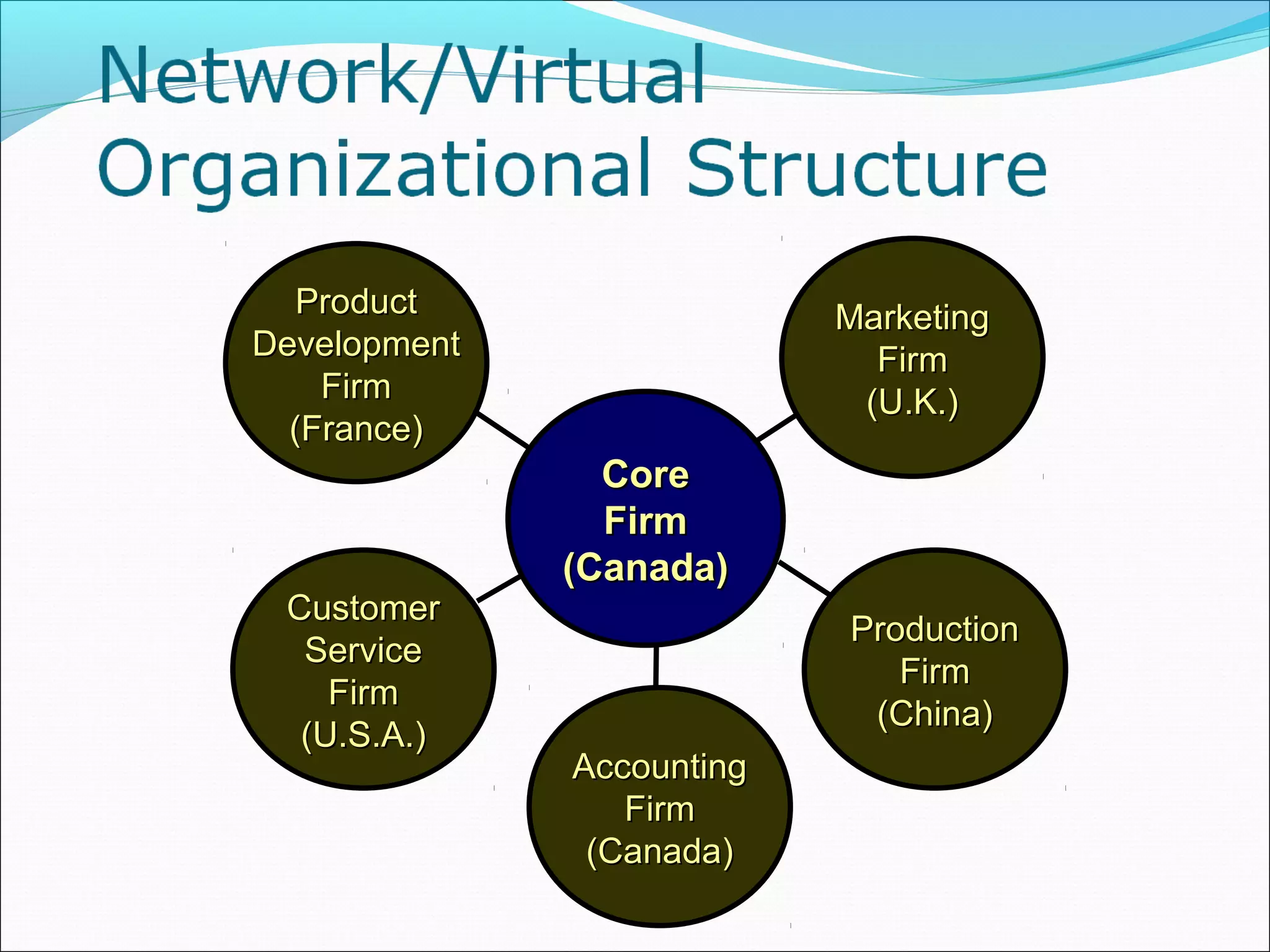
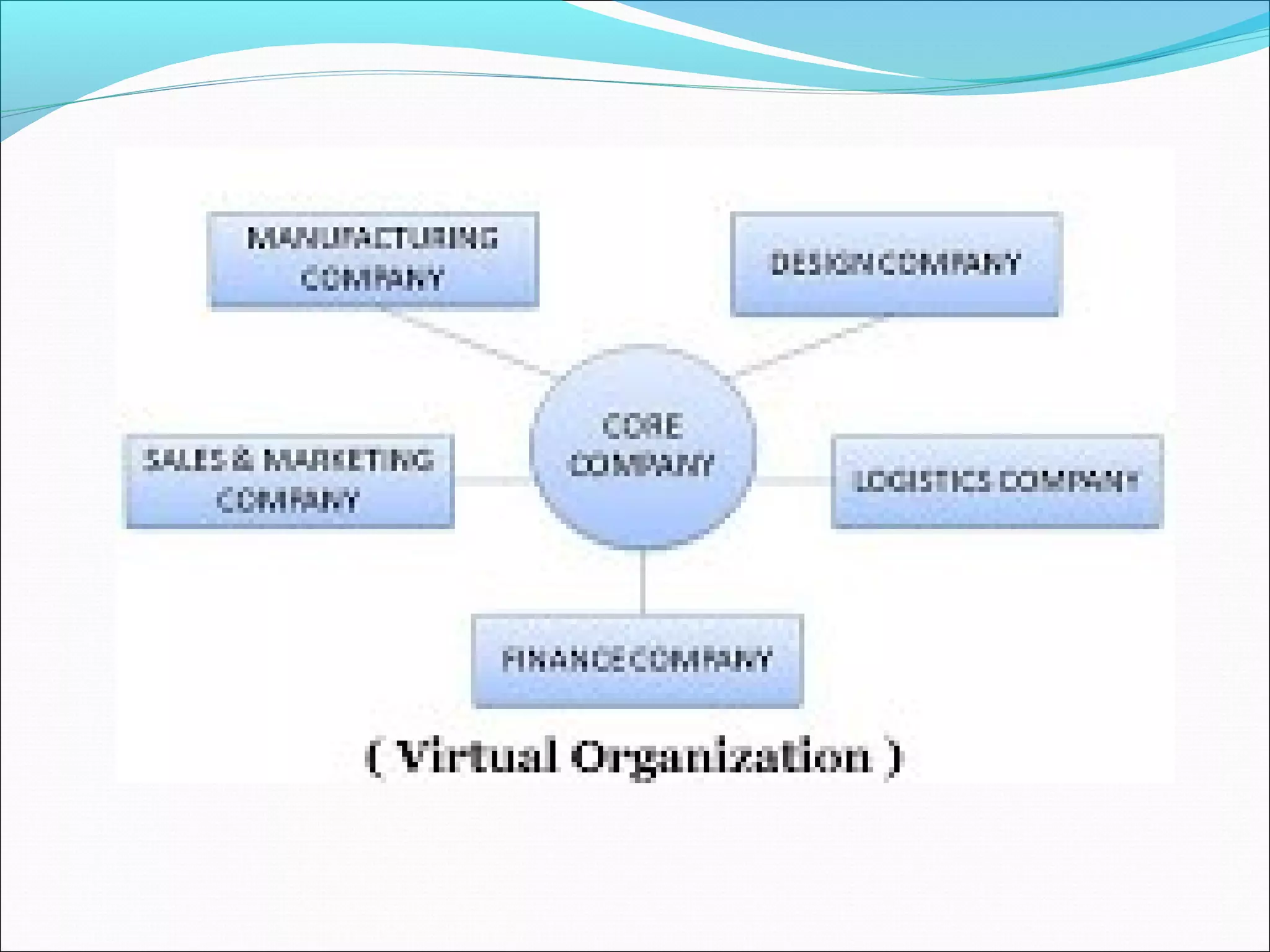
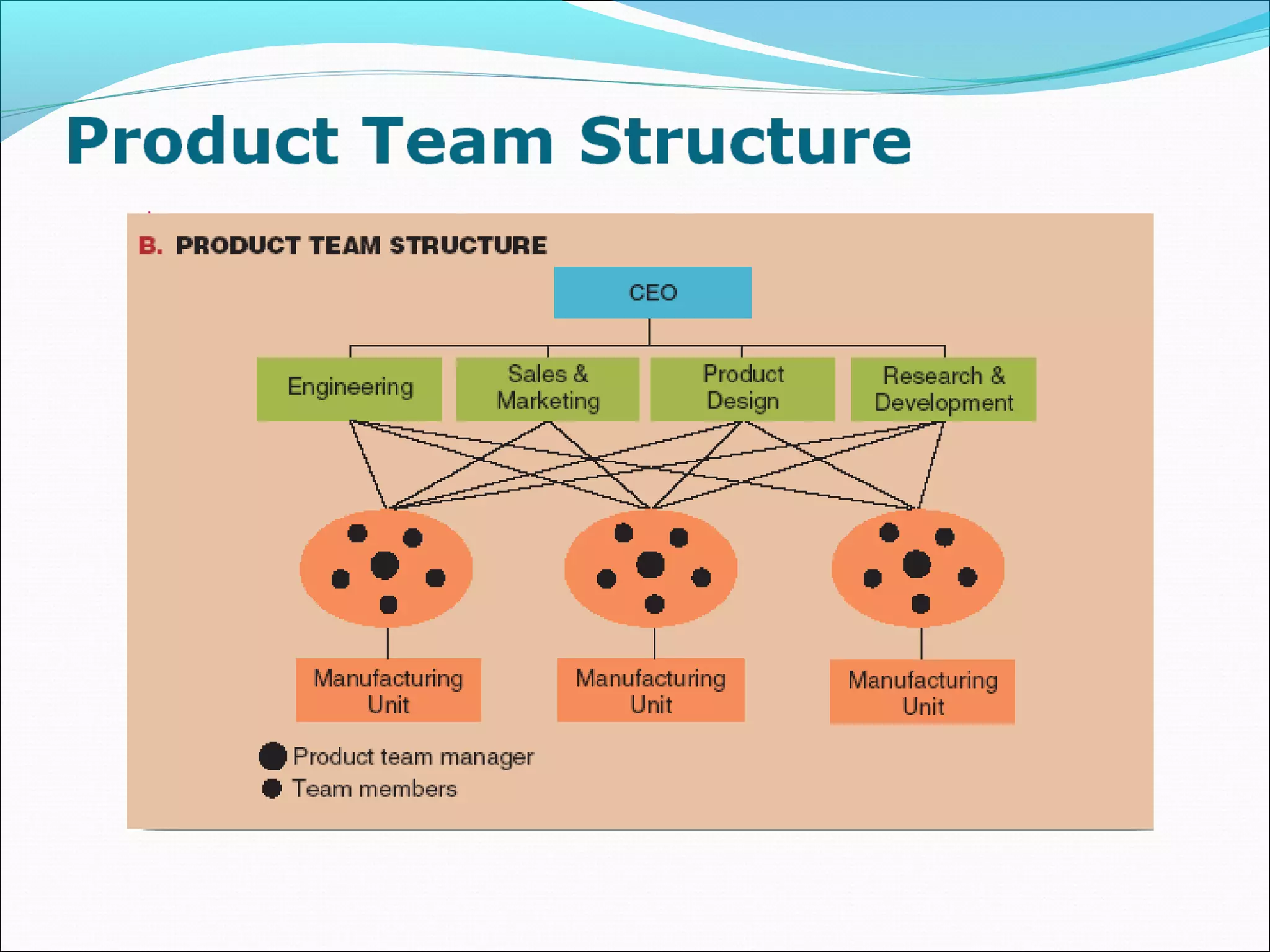
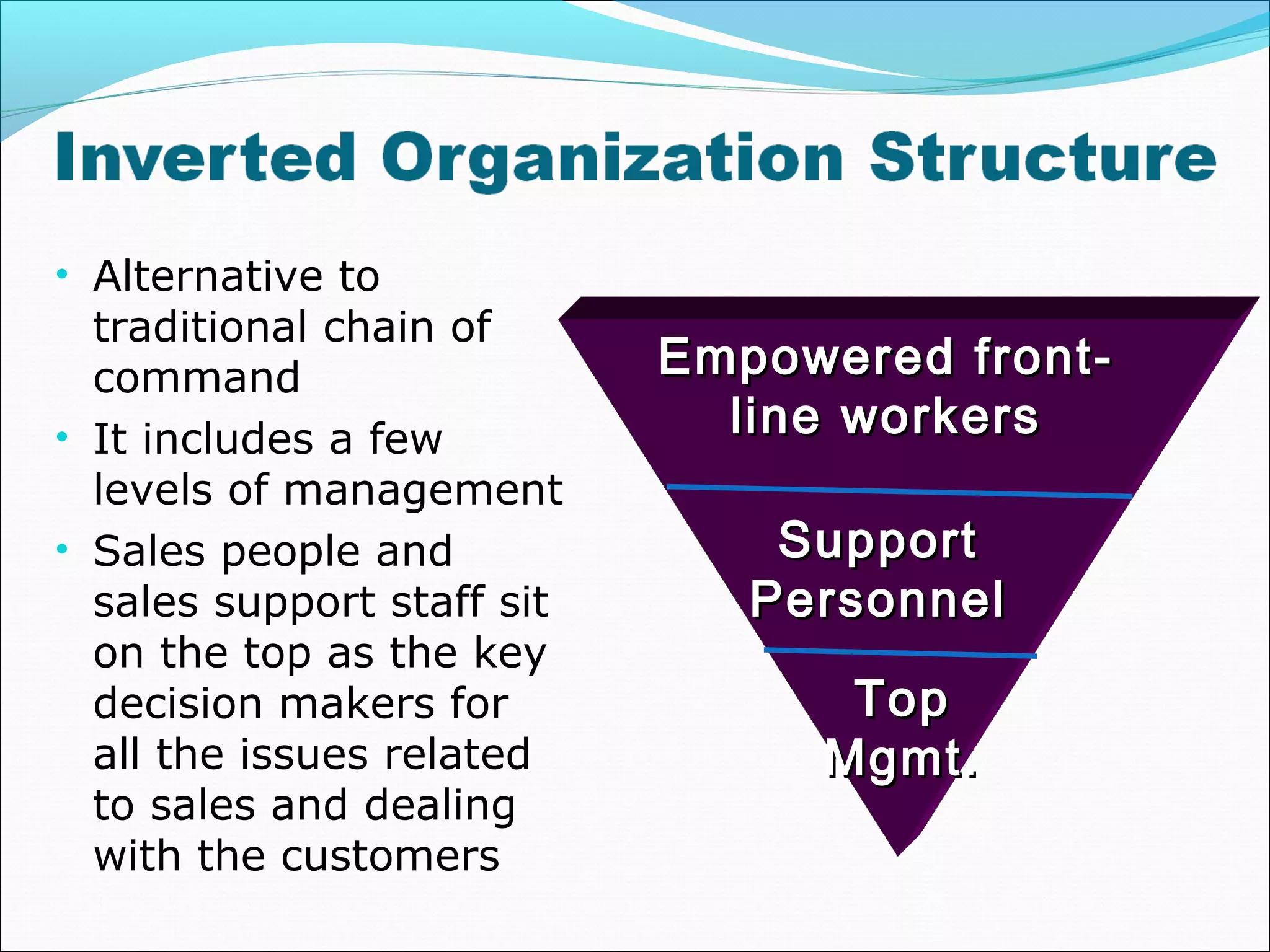
This document discusses various concepts related to organizational structure and design. It begins by defining organizing and organization design as management decisions that result in a specific organizational structure. An organization structure consists of the pattern of jobs and job groups in an organization. Common organization structures discussed include line, line and staff, functional, committee, matrix, and modern structures like virtual organizations, cellular organizations, team structures, and boundaryless organizations. The document also covers organization charts, departmentalization based on functions, geography, products, and customers, and principles of organization.