Embed presentation
Downloaded 87 times









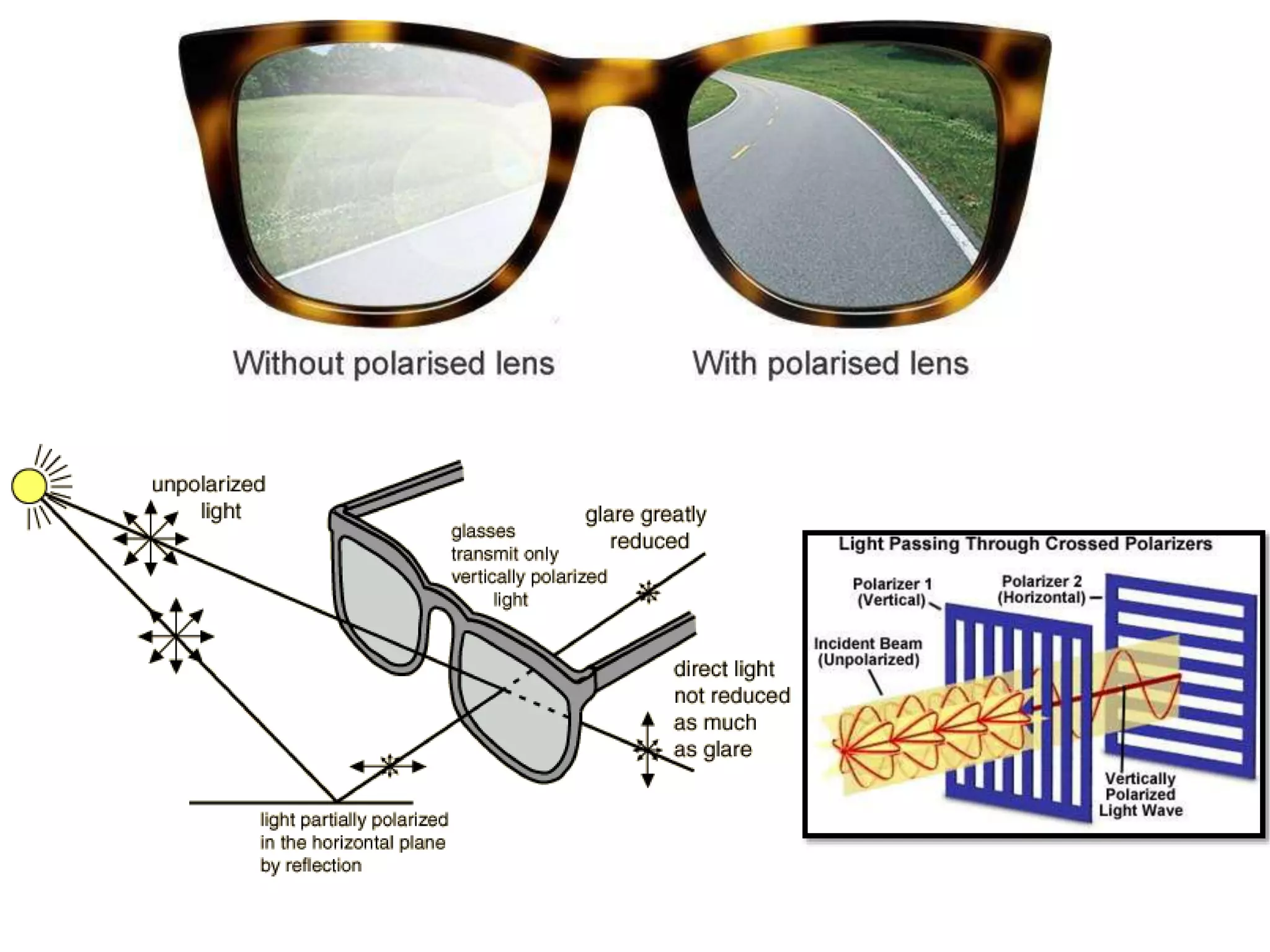

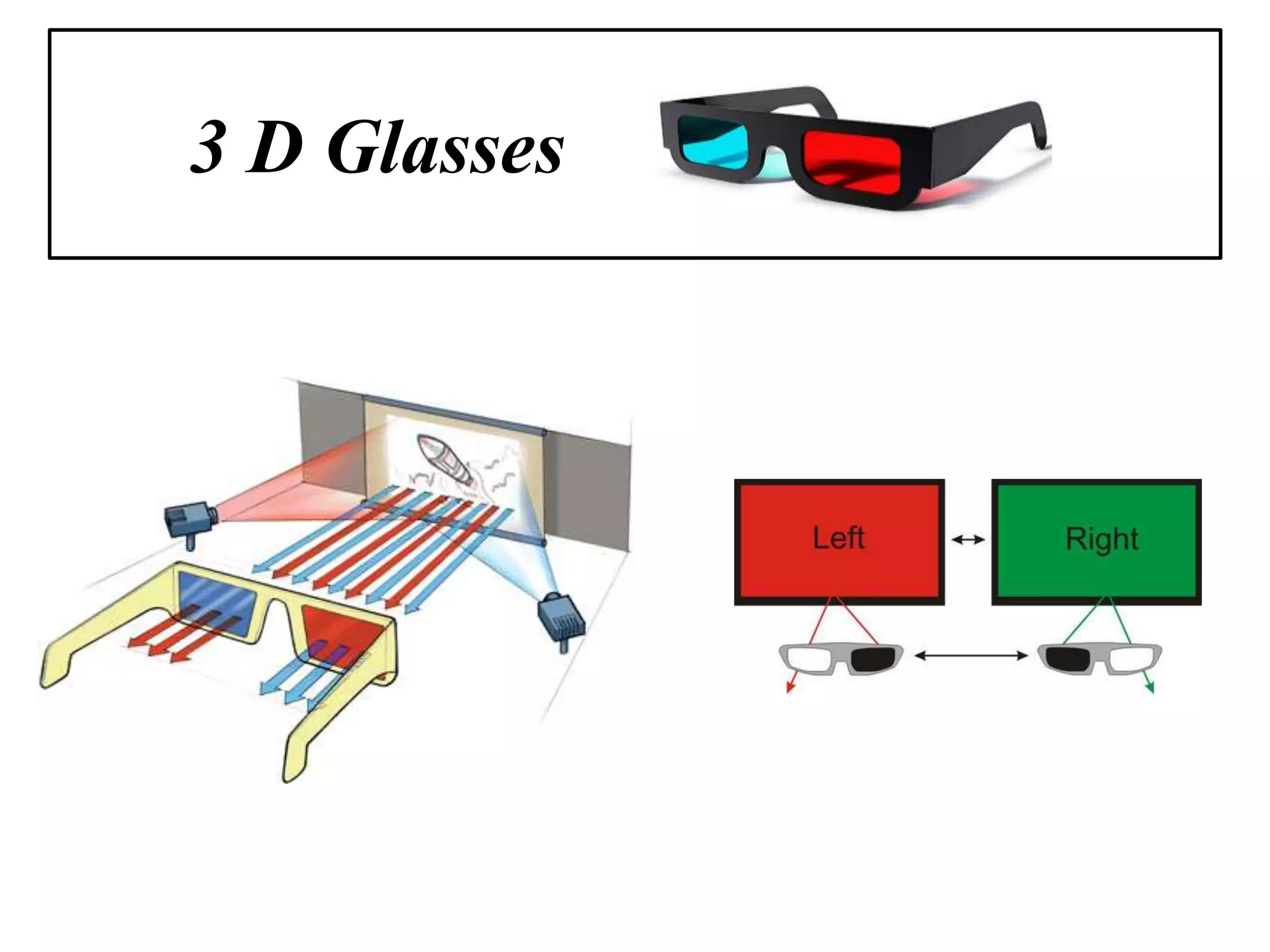


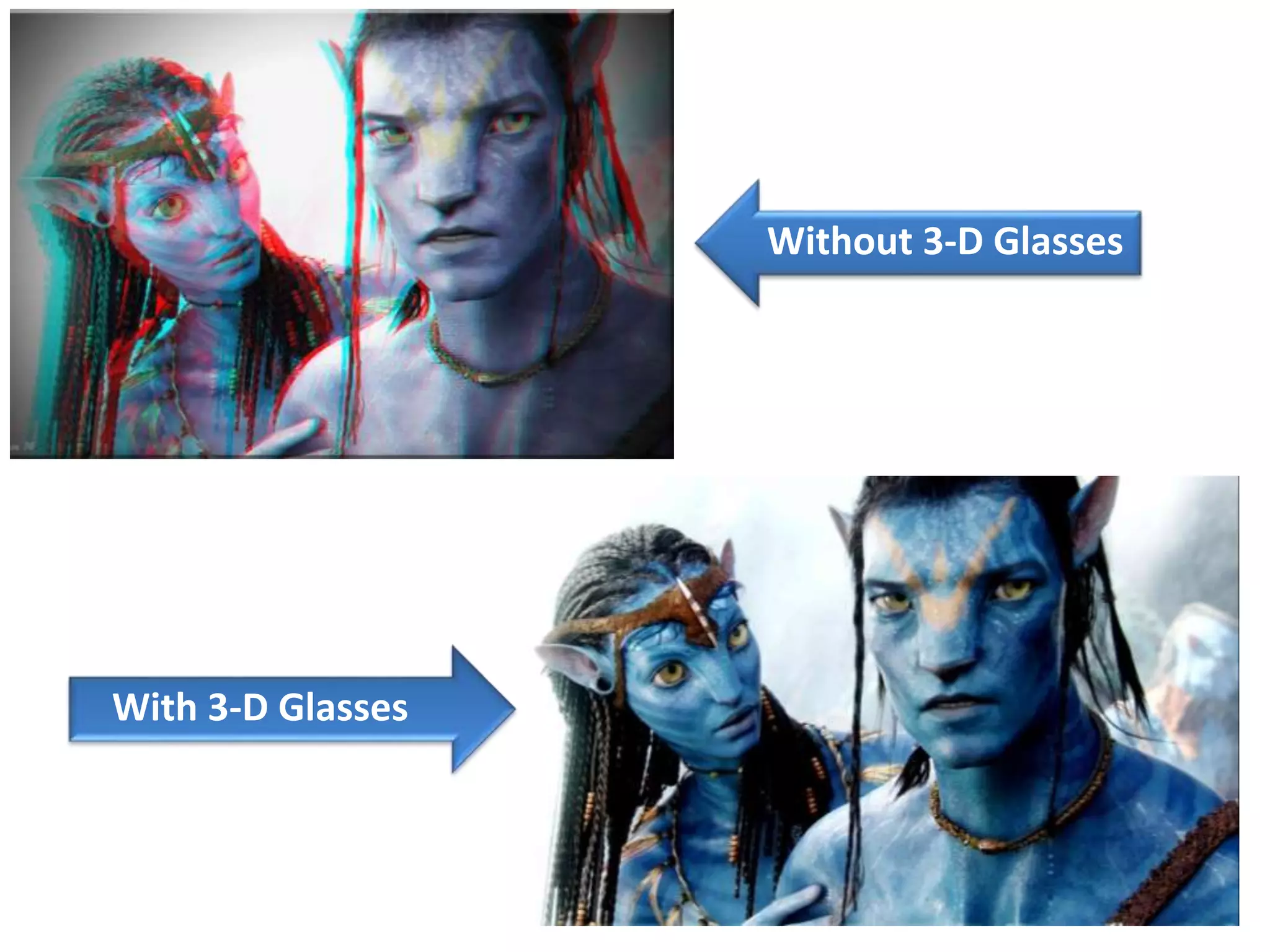

Optical rotatory dispersion (ORD) measures the angle of rotation of plane-polarized light after it passes through a chiral substance. Circular dichroism (CD) measures the differential absorption of left and right circularly polarized light by some materials. ORD spectra are dispersive and show the specific rotation versus wavelength, while CD spectra are absorptive and plot molar ellipticity versus wavelength. Both techniques exploit the fact that chiral molecules interact differently with left and right circularly polarized light.
















