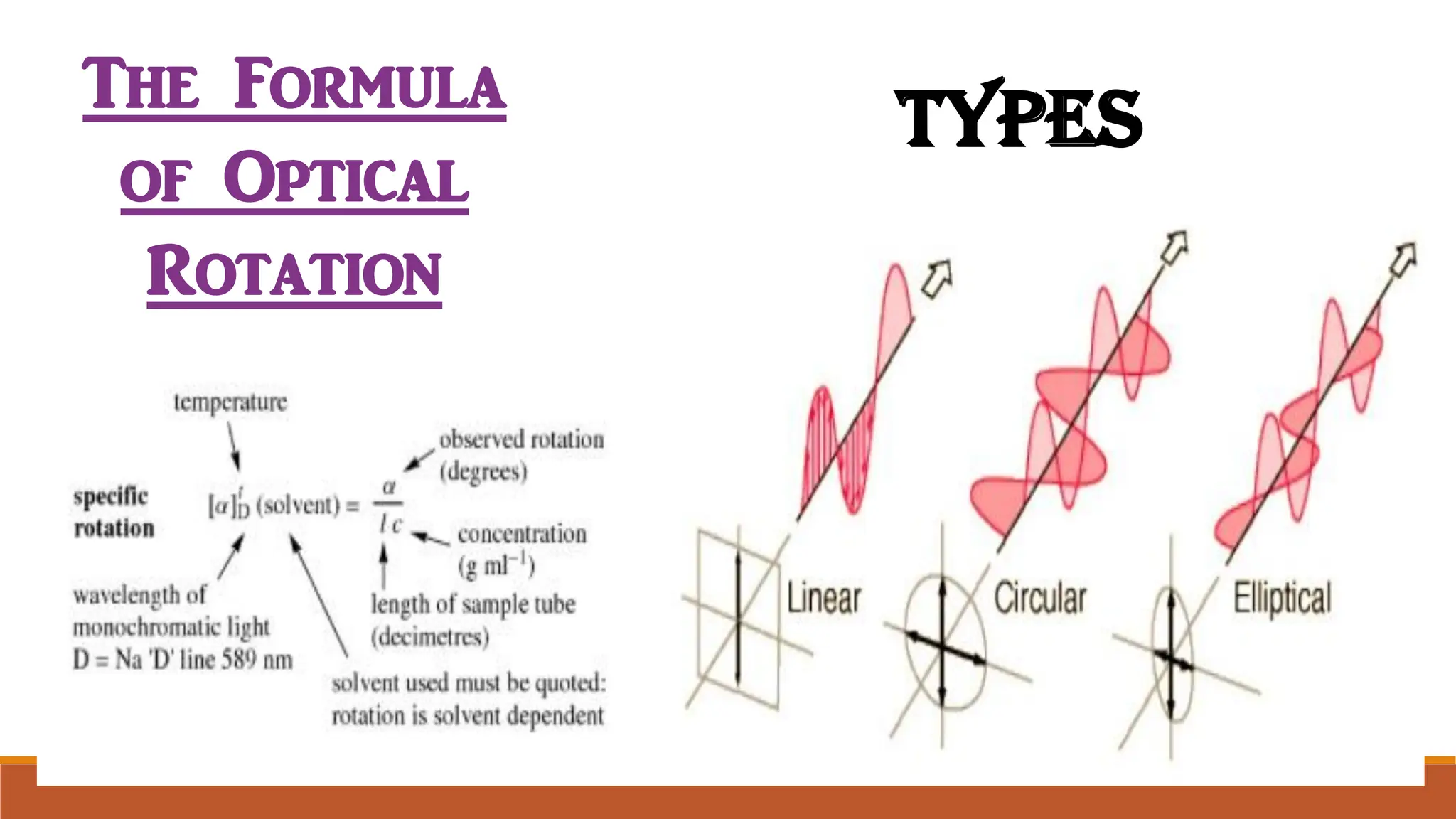
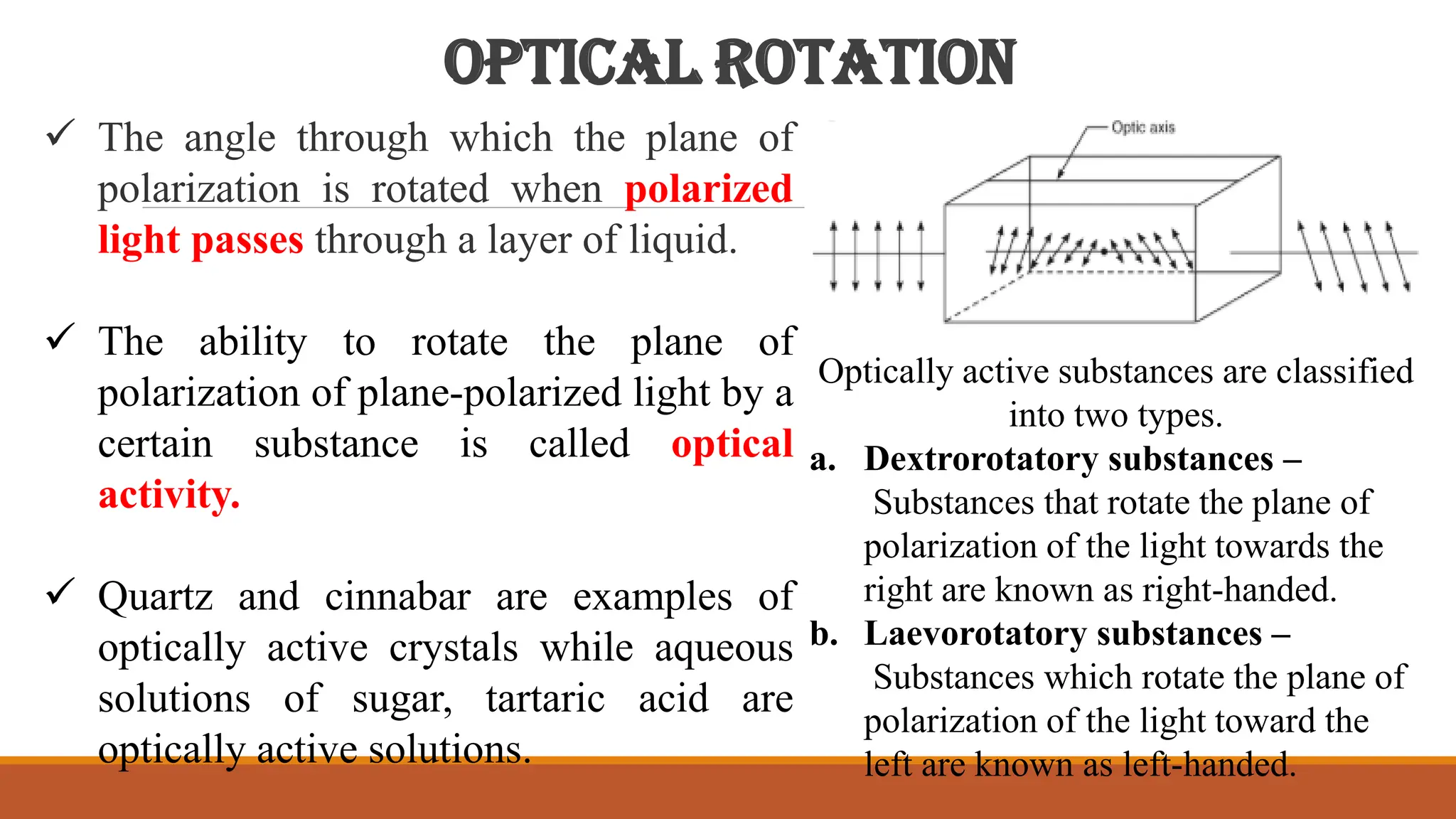
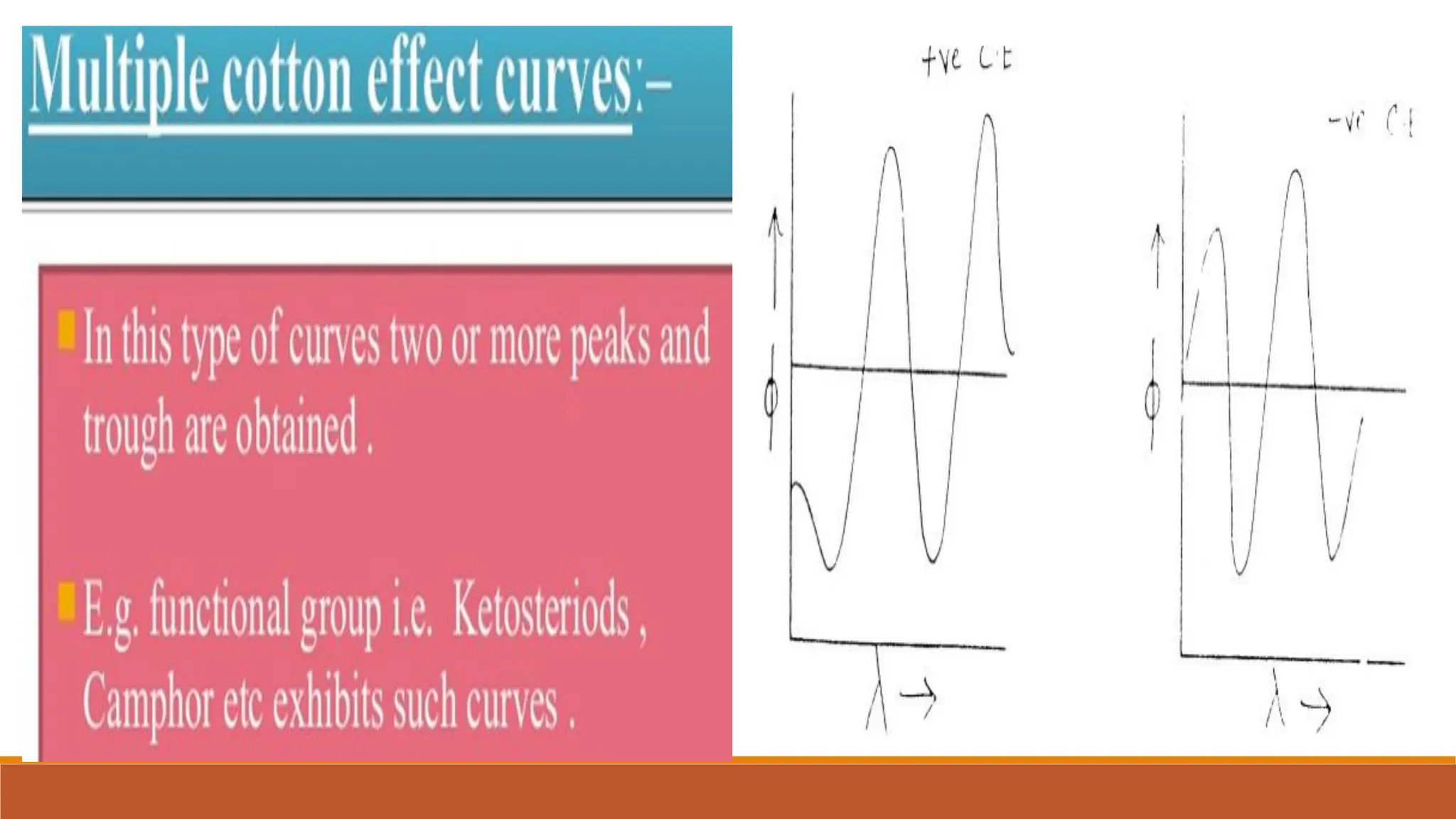
This document discusses optical rotatory dispersion (ORD), which refers to the variation in optical rotation of a substance with changing light wavelengths and is useful for determining the absolute configuration of metal complexes. It explains the types of polarized light, the concept of optical rotation, and the classification of optically active substances into dextrorotatory and laevorotatory. Additionally, it highlights the applications of optical rotation in kinetic reaction determination and molecular structure analysis, along with circular dichroism (CD) in studying biomolecules.