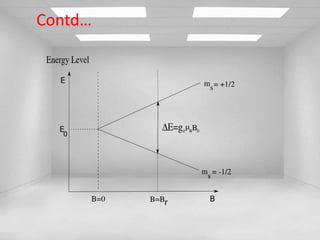
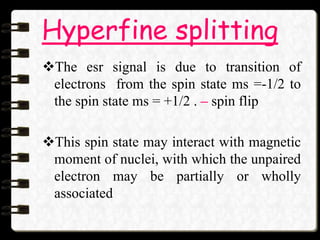
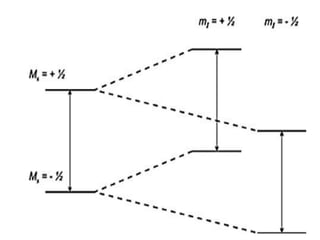
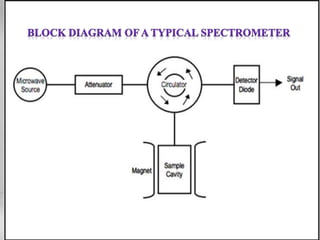
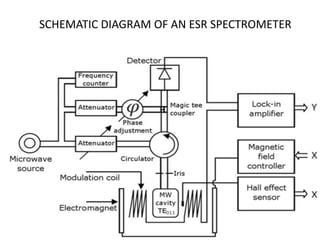
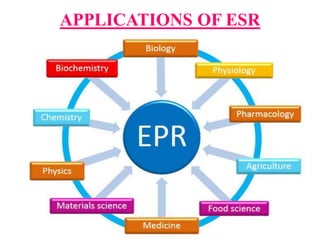
Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) spectroscopy, also known as Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR), utilizes microwaves to study molecules with unpaired electrons in a magnetic field. The technique reveals energy differences between electron spin states and allows for applications such as investigating molecular structure, dynamic processes, and the presence of free radicals. Key components of an ESR spectrometer include klystrons, wave guides, and sample cavities, with specific mechanisms for signal detection and modulation.