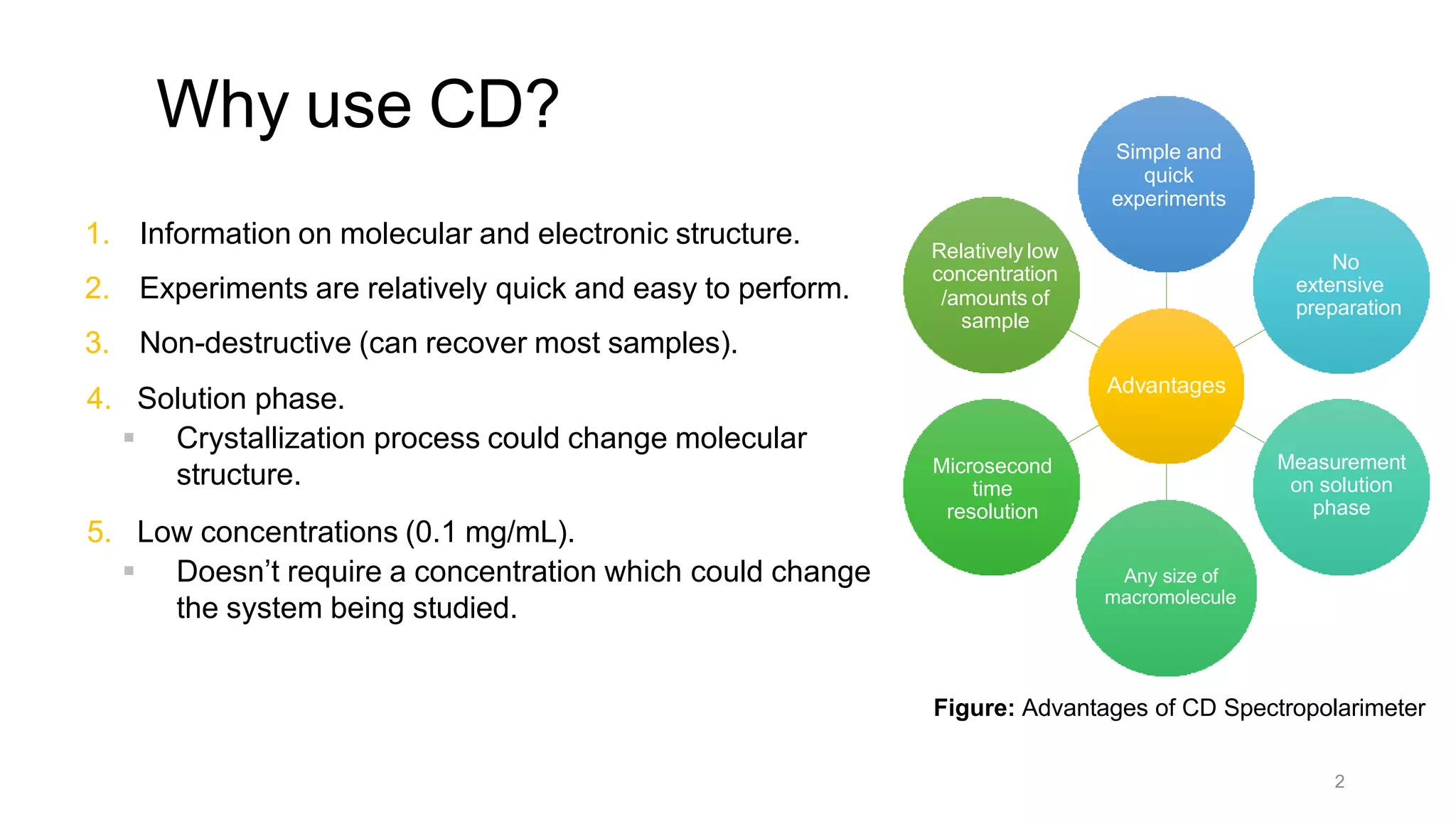
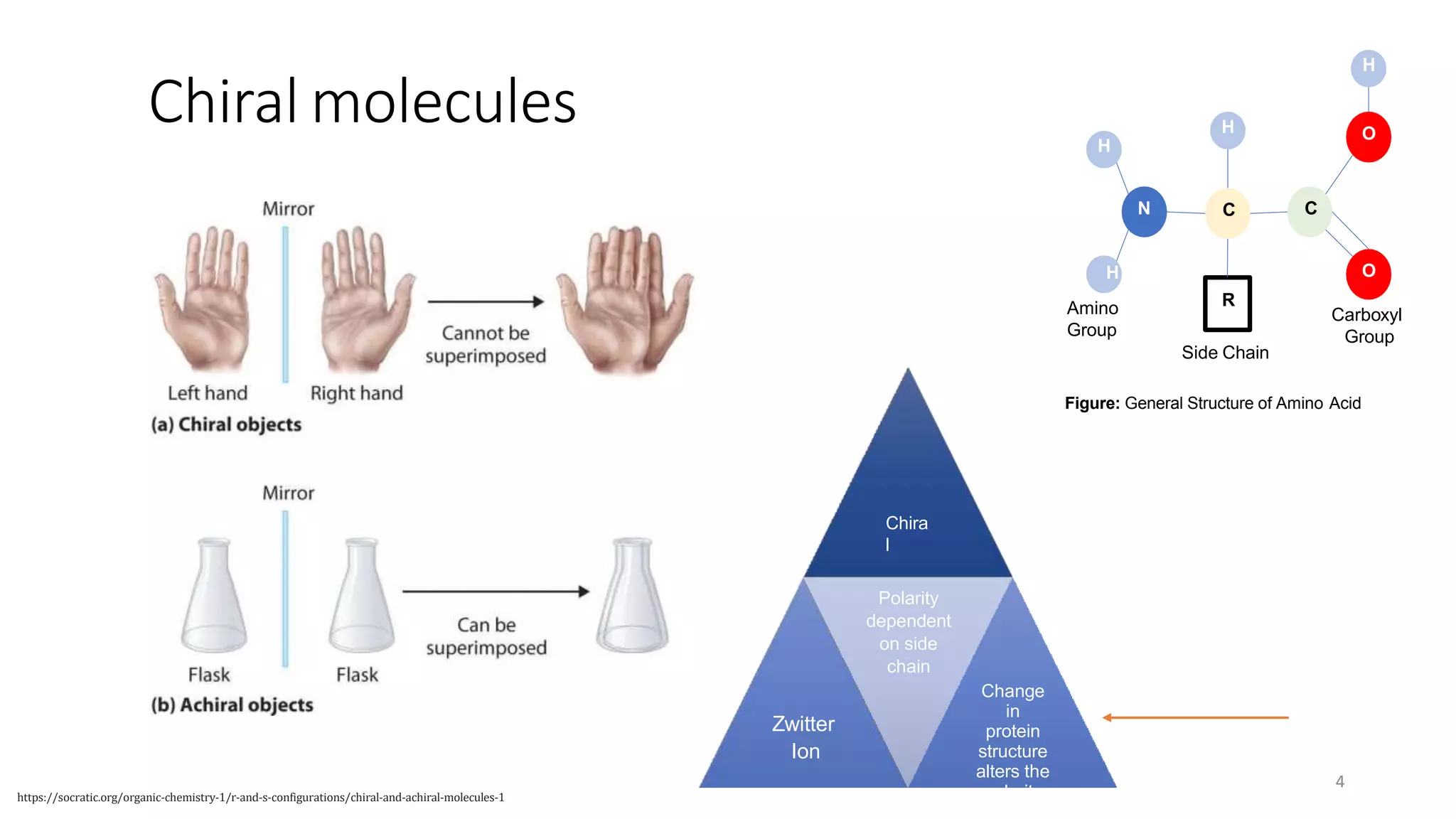
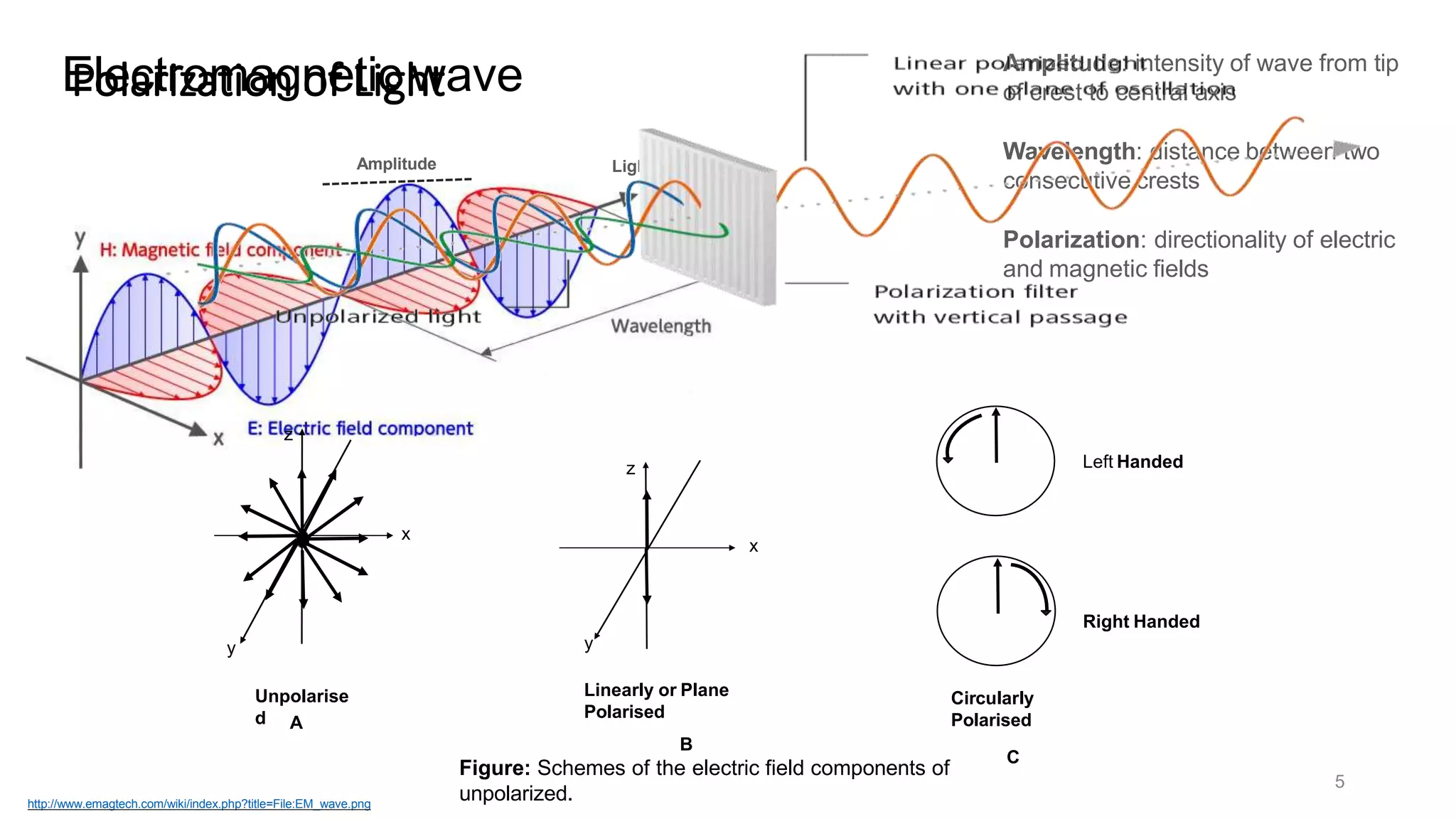
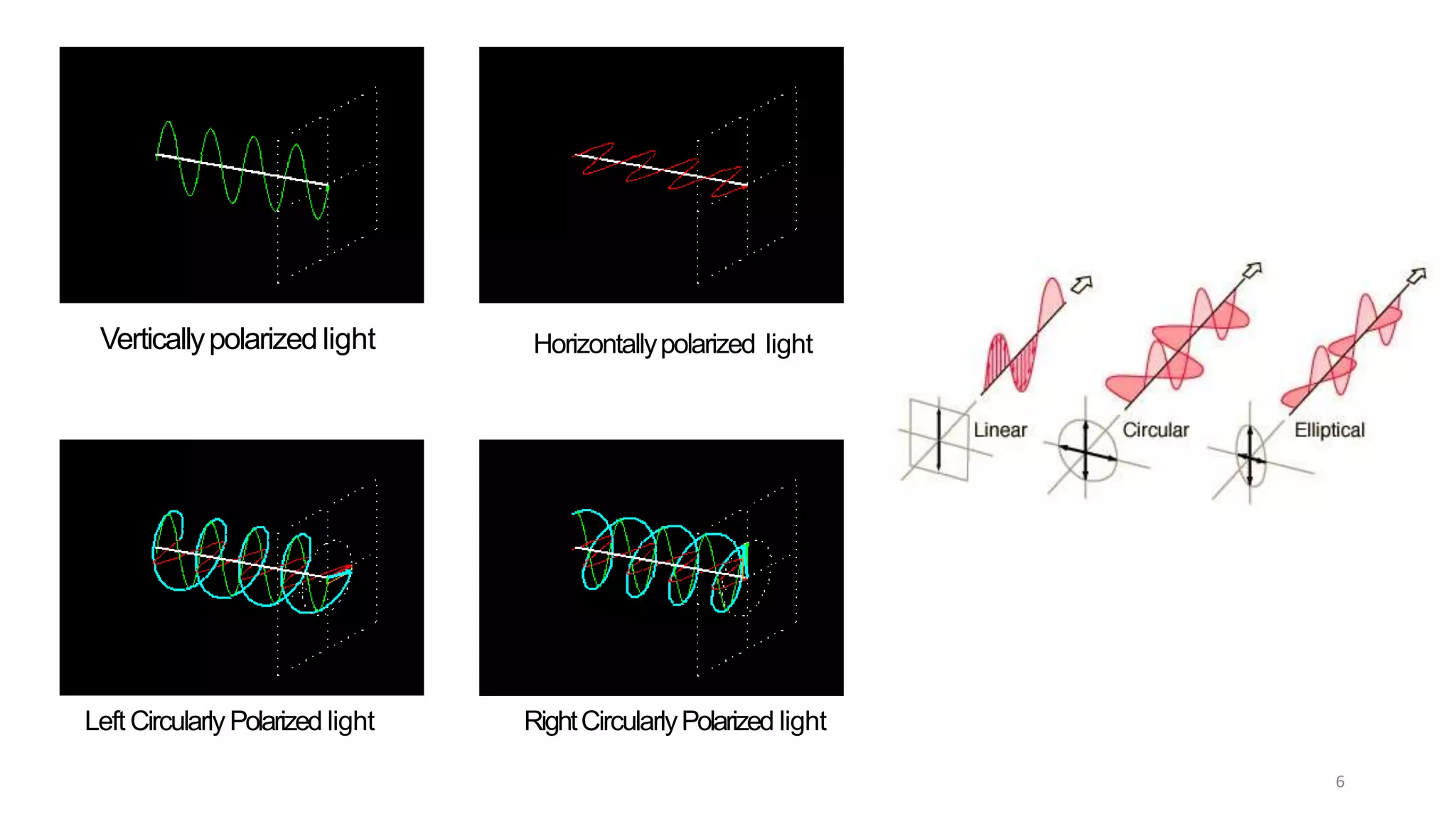
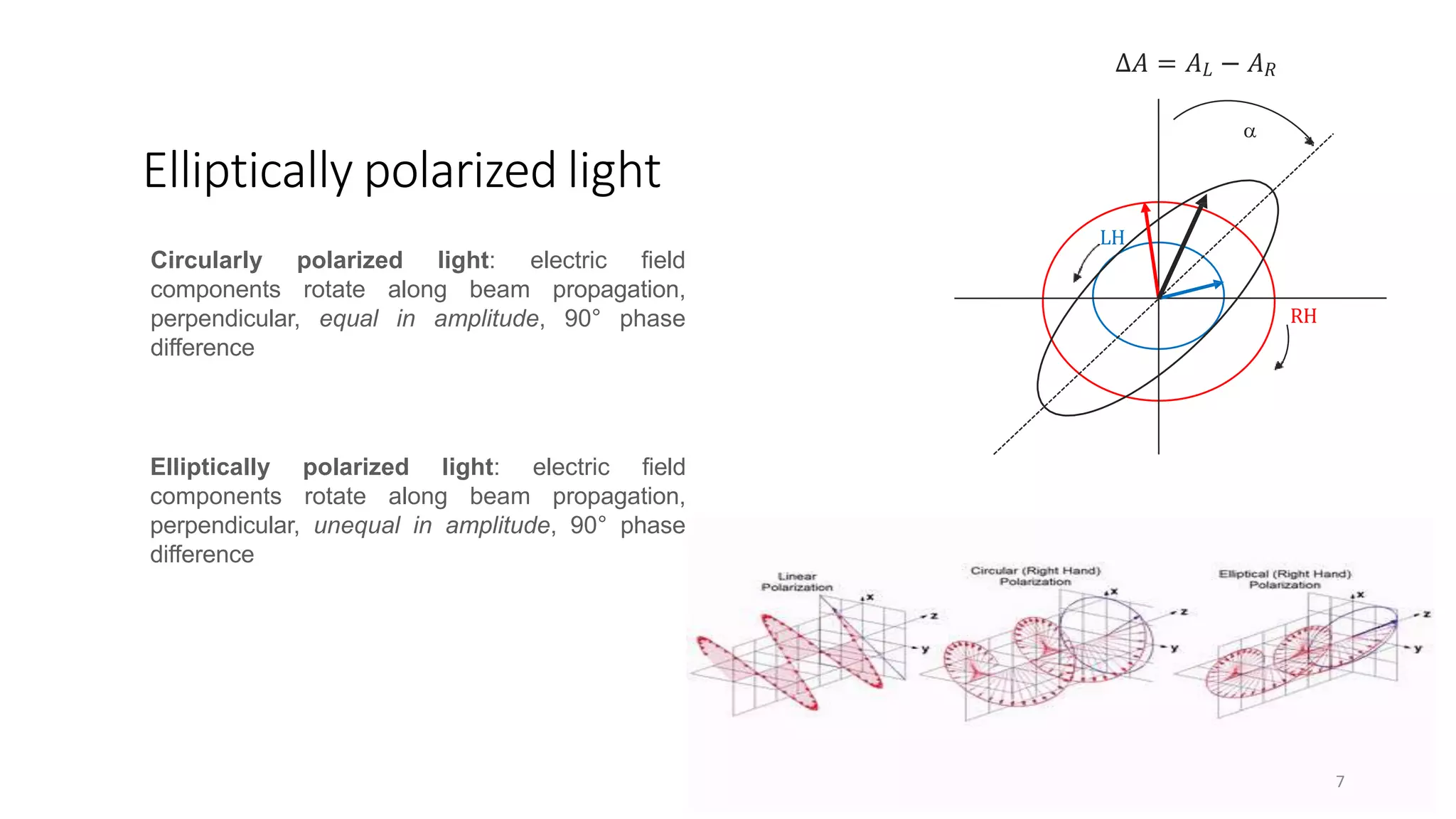
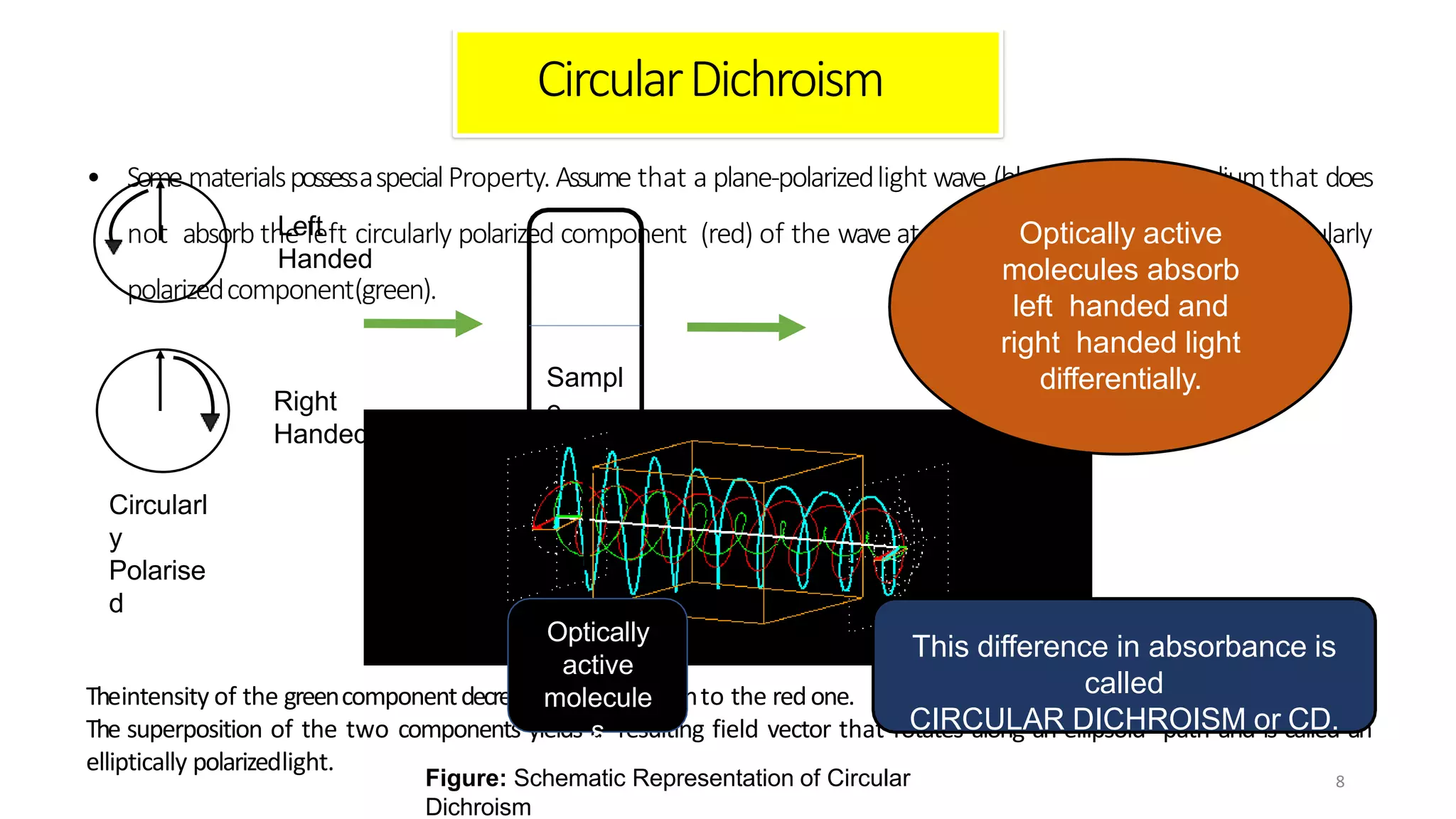
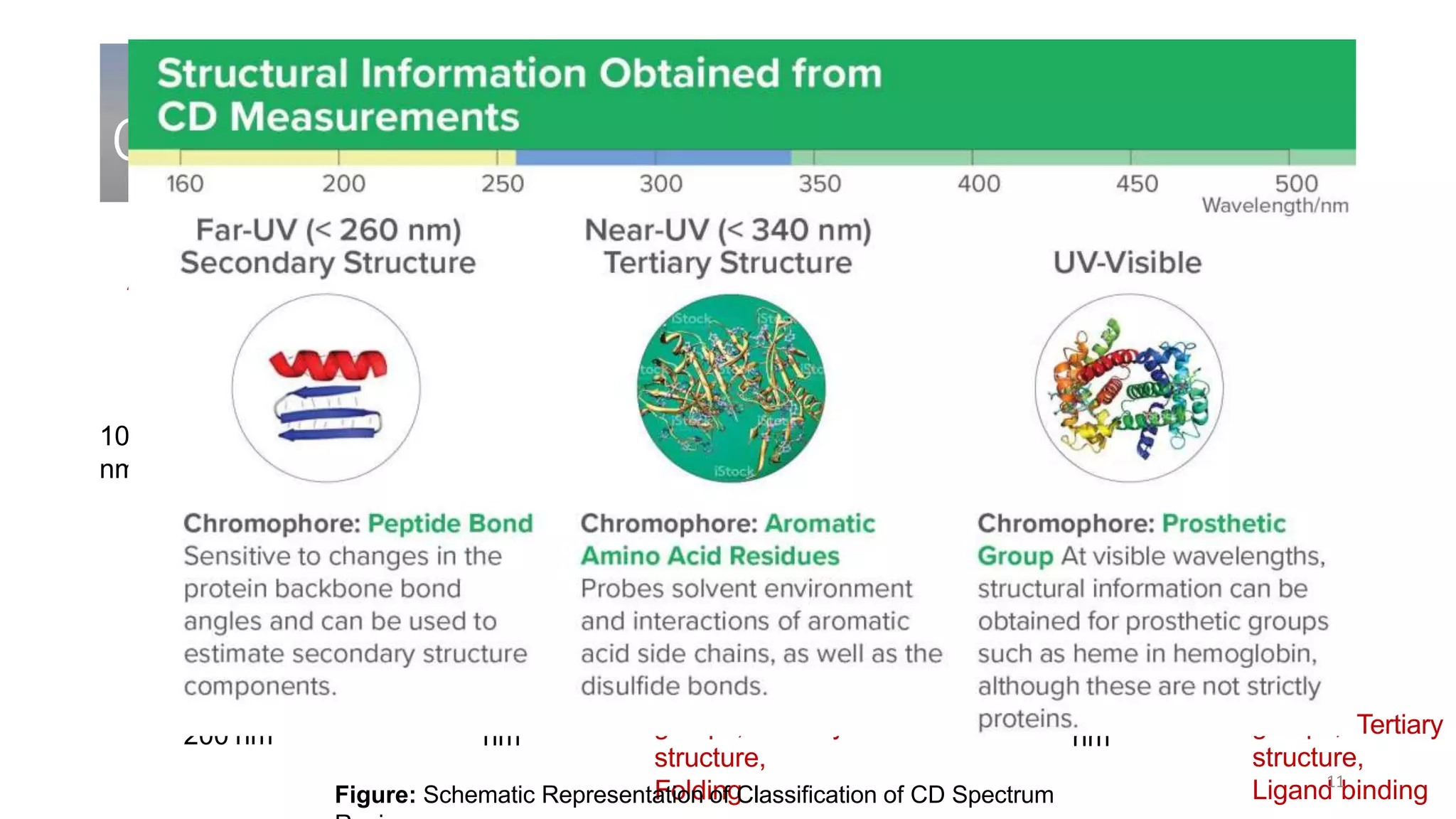
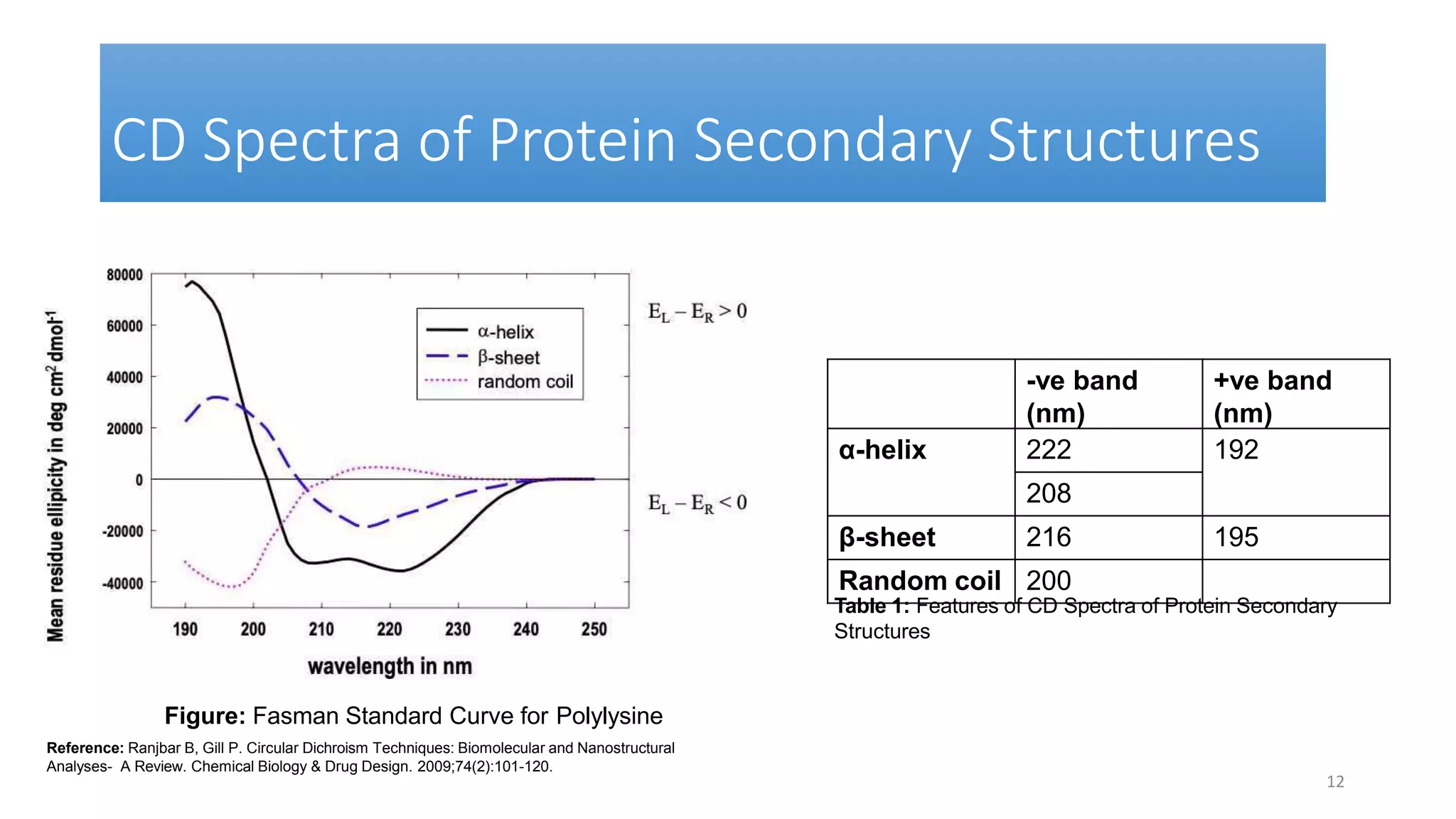
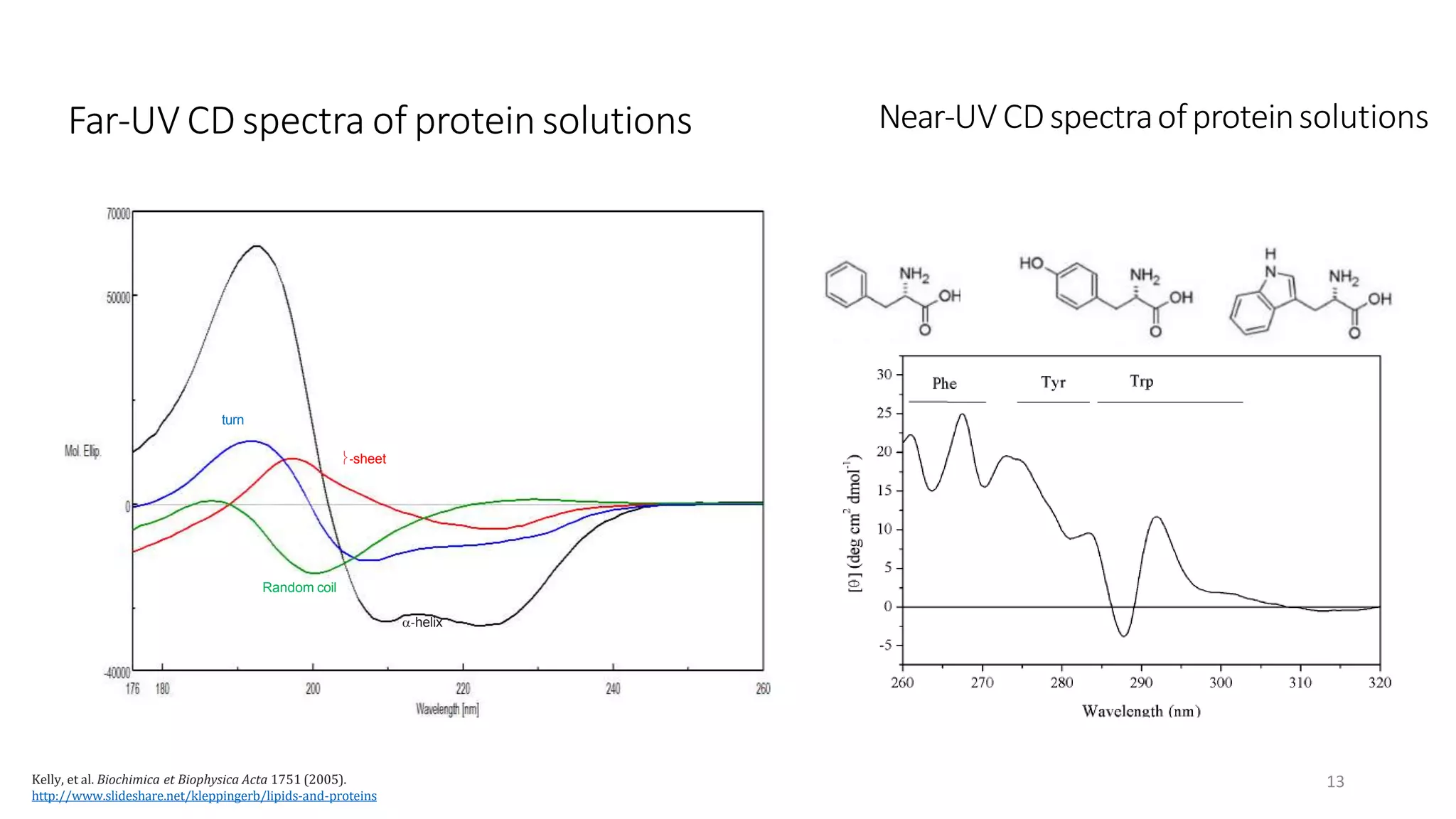
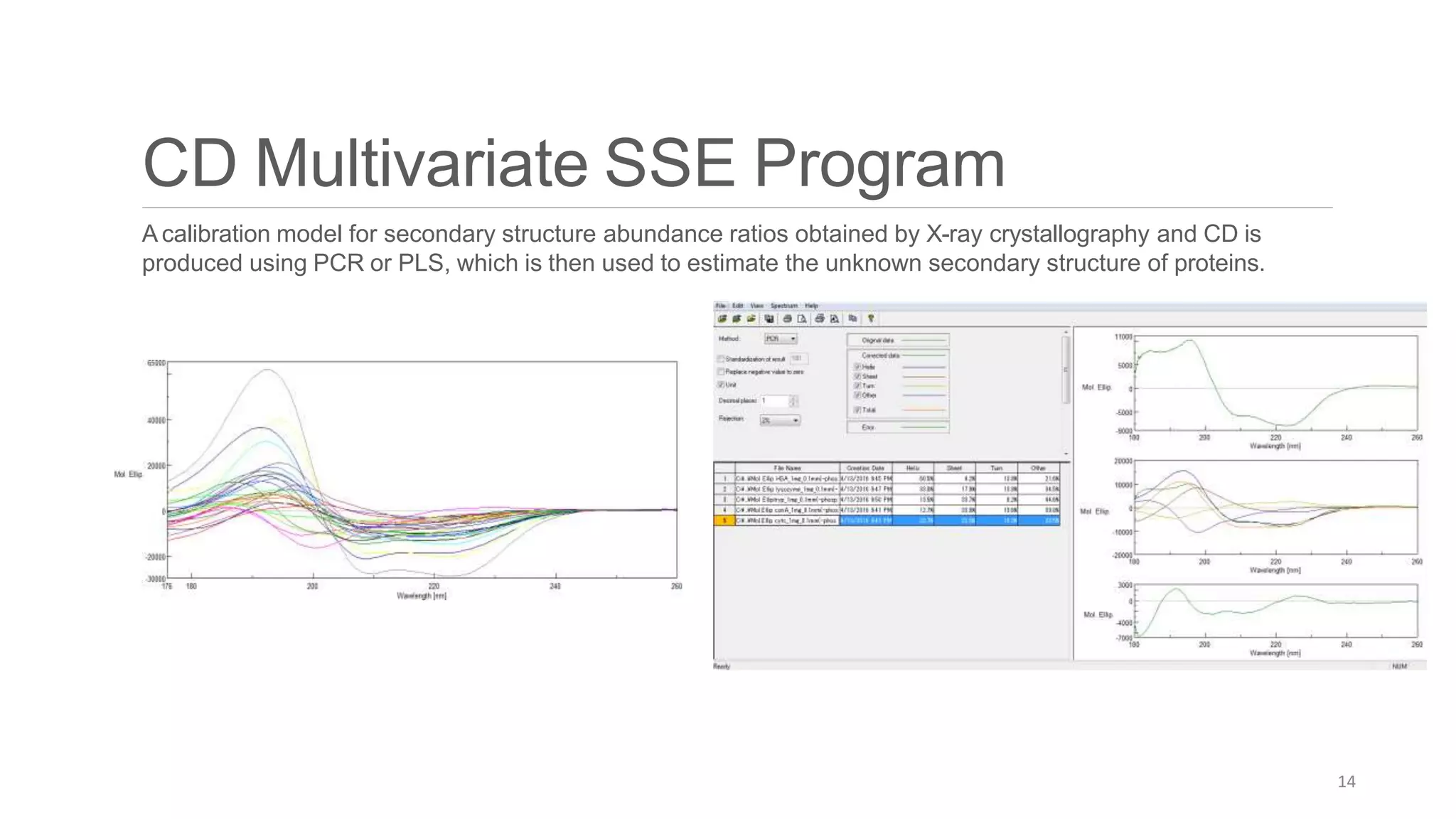
Circular dichroism (CD) is a technique that measures the difference in absorption of left and right circularly polarized light. CD provides information about molecular structure like secondary structure of proteins. It has advantages like being a quick, non-destructive technique that works with small sample sizes in solution. CD spectra can give information about secondary structure features like alpha helices and beta sheets. The document discusses the principles and instrumentation of CD measurement and how CD spectra at different wavelength ranges provide structural information.