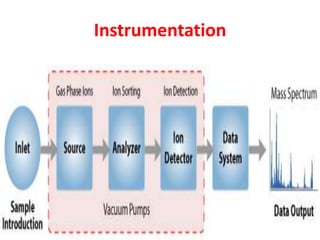
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that identifies chemicals in a sample by measuring the mass-to-charge ratio and abundance of gas-phase ions. It works by bombarding molecule samples with electrons to produce positively charged ions, which are then separated by mass and detected. Mass spectra plots show the relative abundance of ions and are used to determine molecular structure and composition.