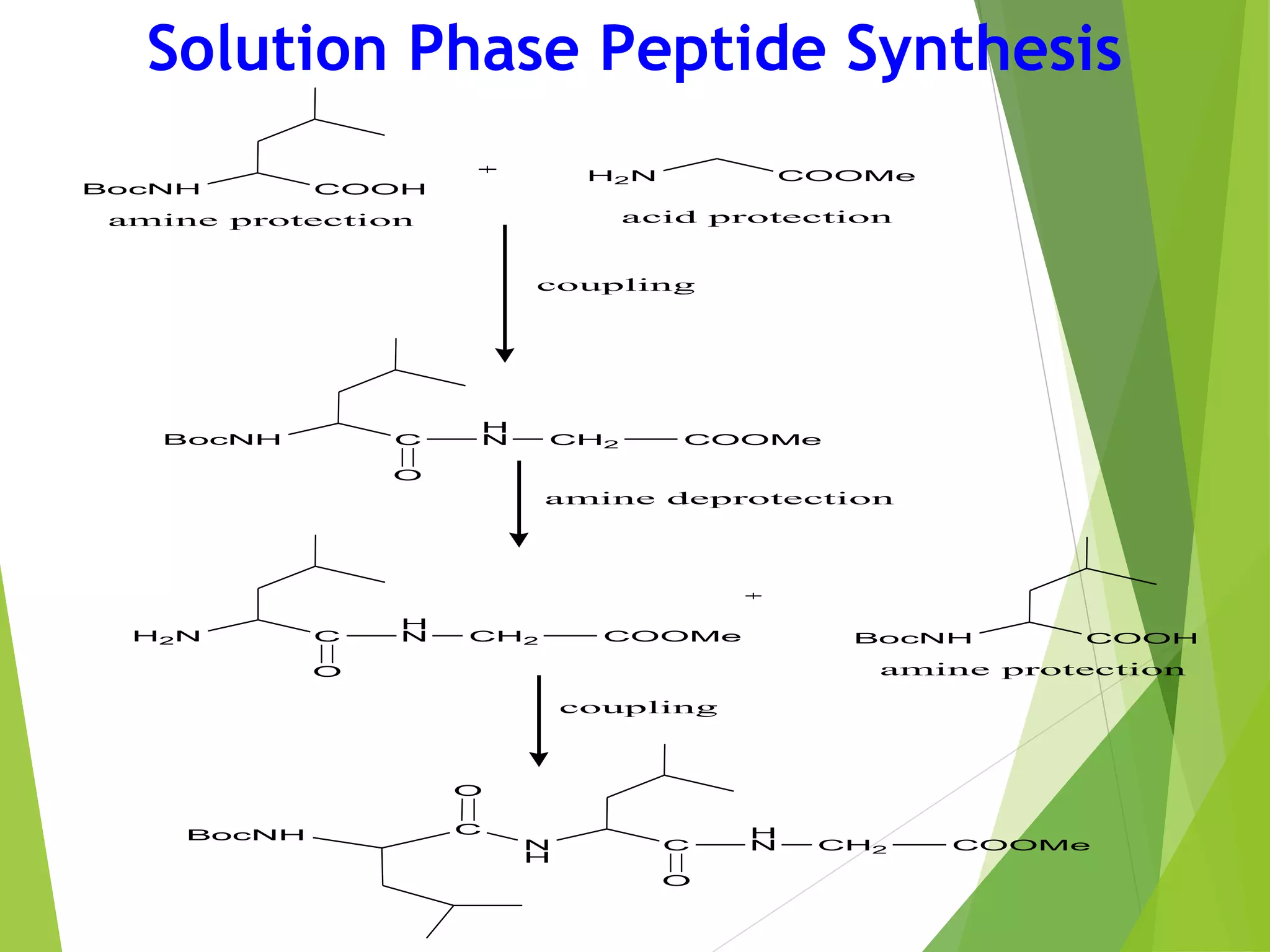
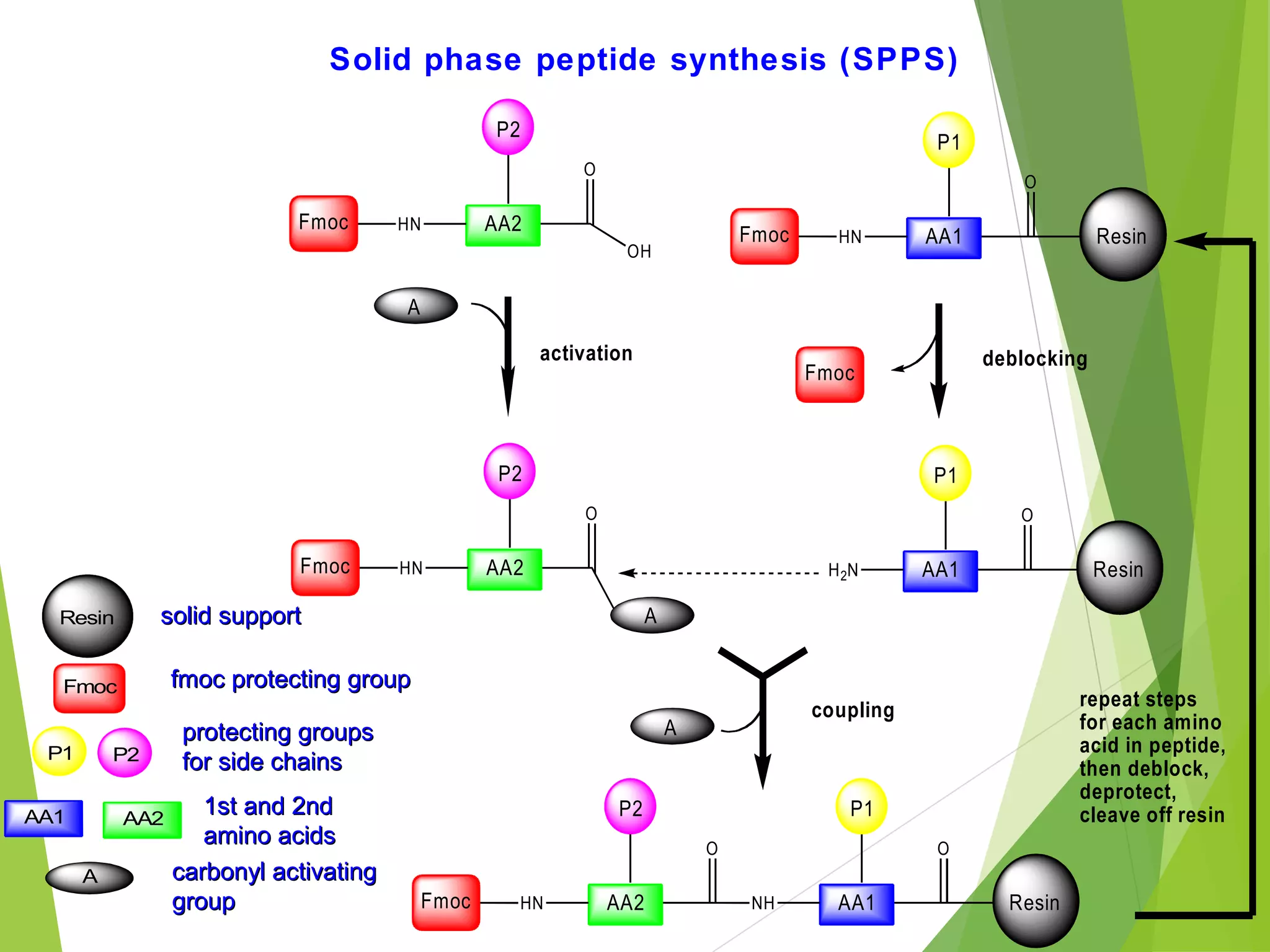
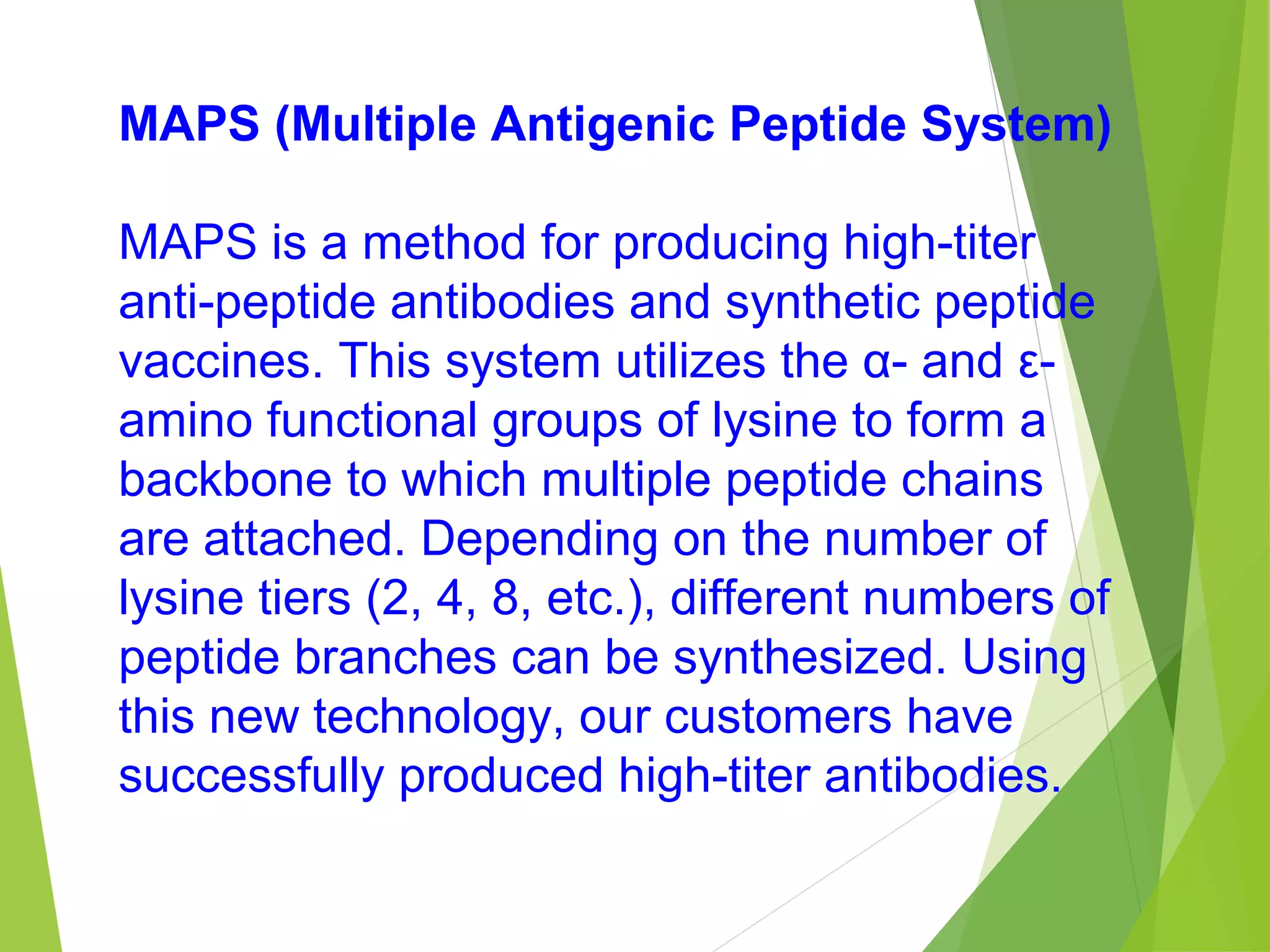
This document discusses peptide synthesis methods, including solution phase peptide synthesis and solid phase peptide synthesis (SPPS). SPPS involves attaching the starting peptide to an inert resin bead and performing sequential amino acid couplings and deprotections while the growing peptide remains attached to the resin. This allows for easy purification after each step. Once the full peptide is synthesized, it is cleaved off the resin bead. SPPS allows for faster synthesis of longer peptides up to 70-100 amino acids in length compared to solution phase synthesis. Applications of synthetic peptides include vaccines, hormones, antibiotics, toxins, and enzyme inhibitors.