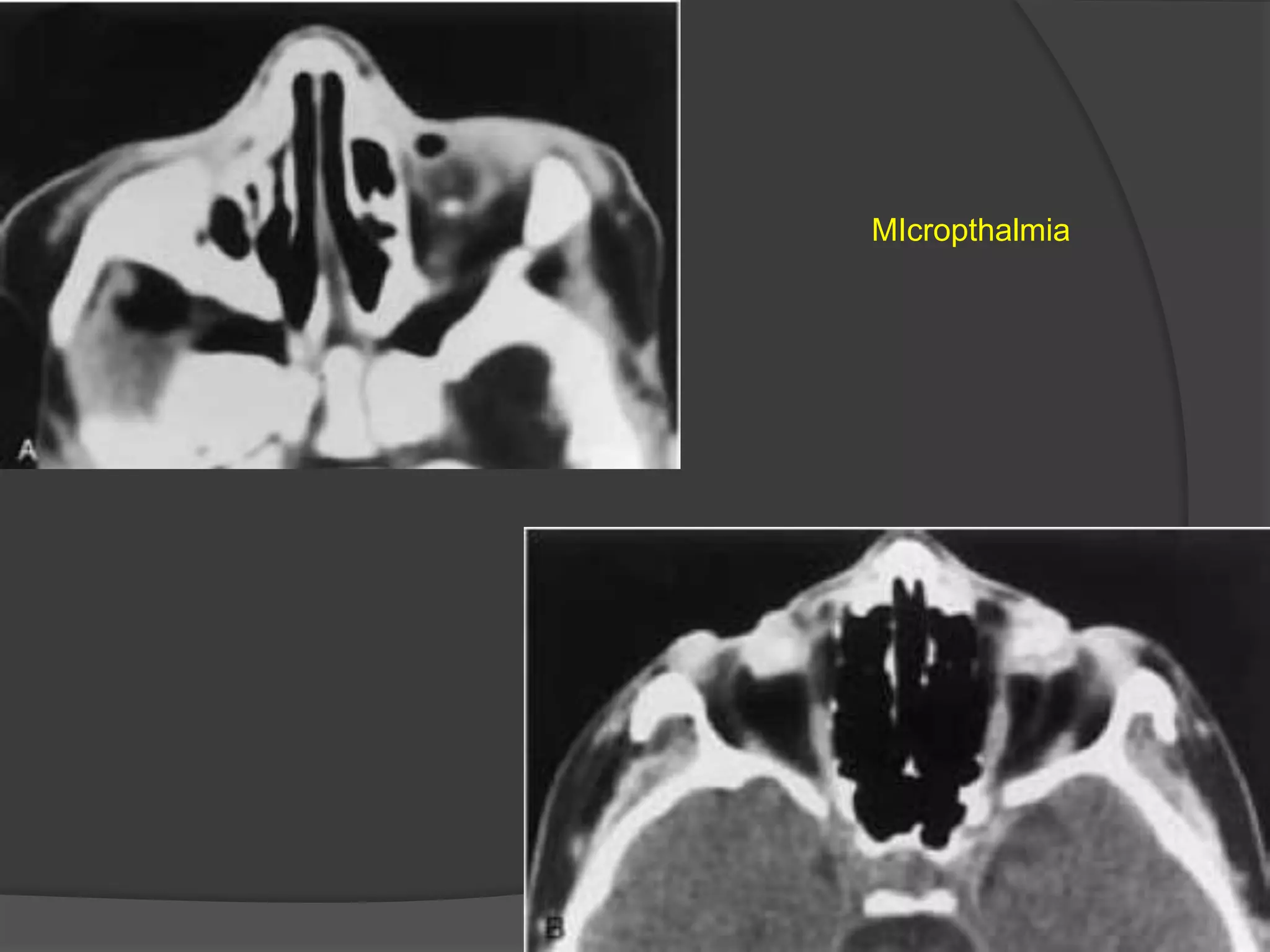
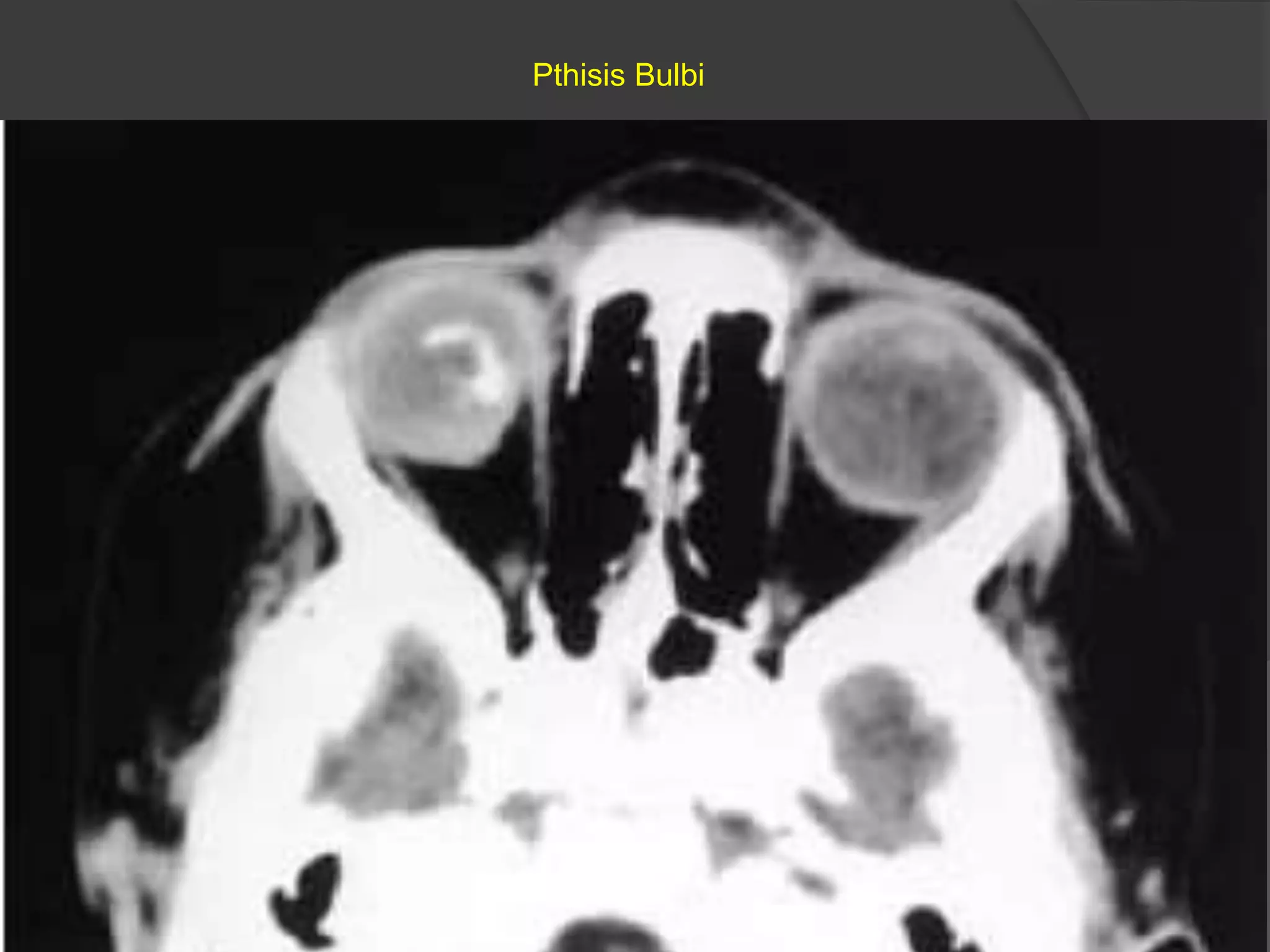
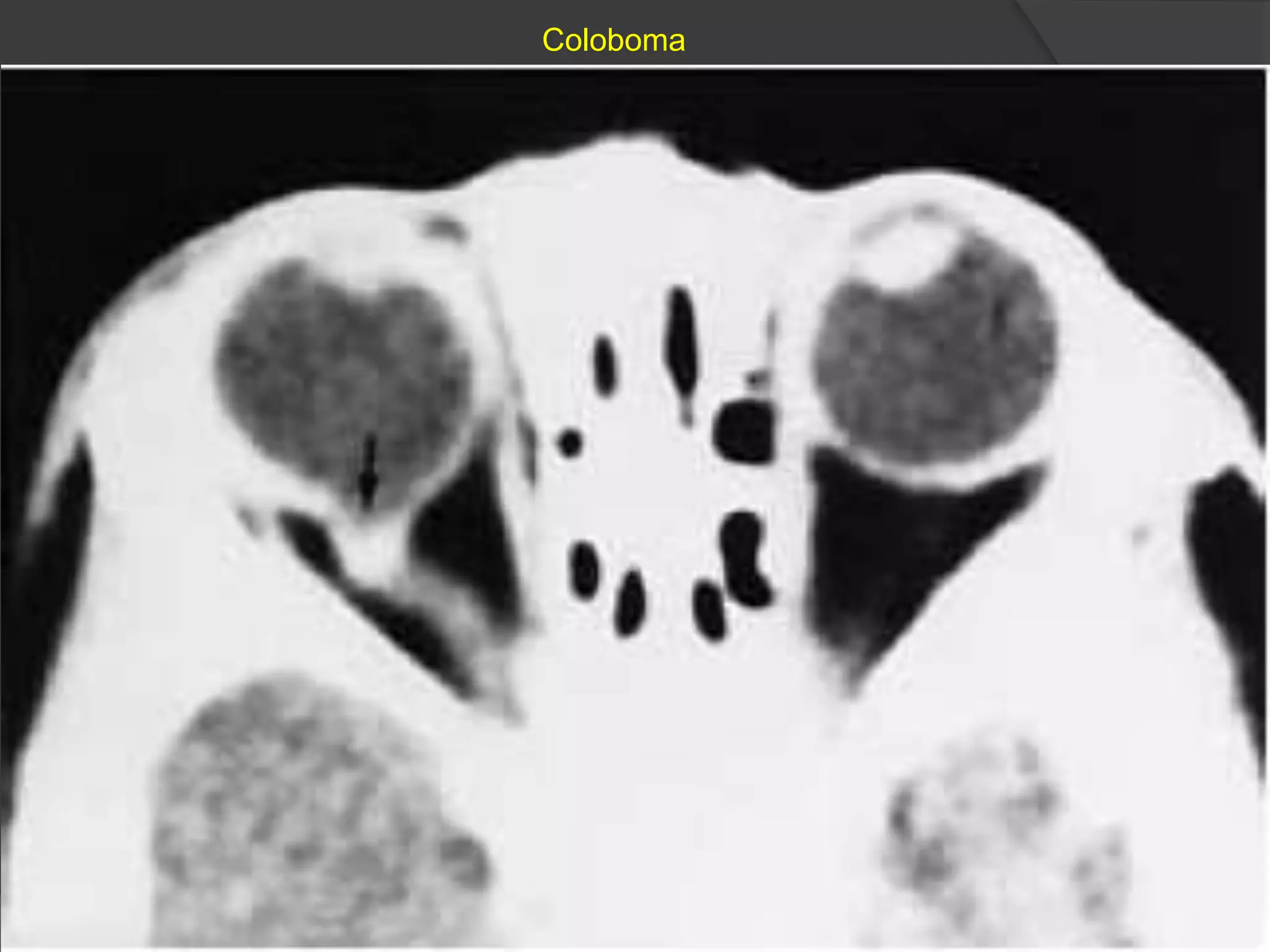
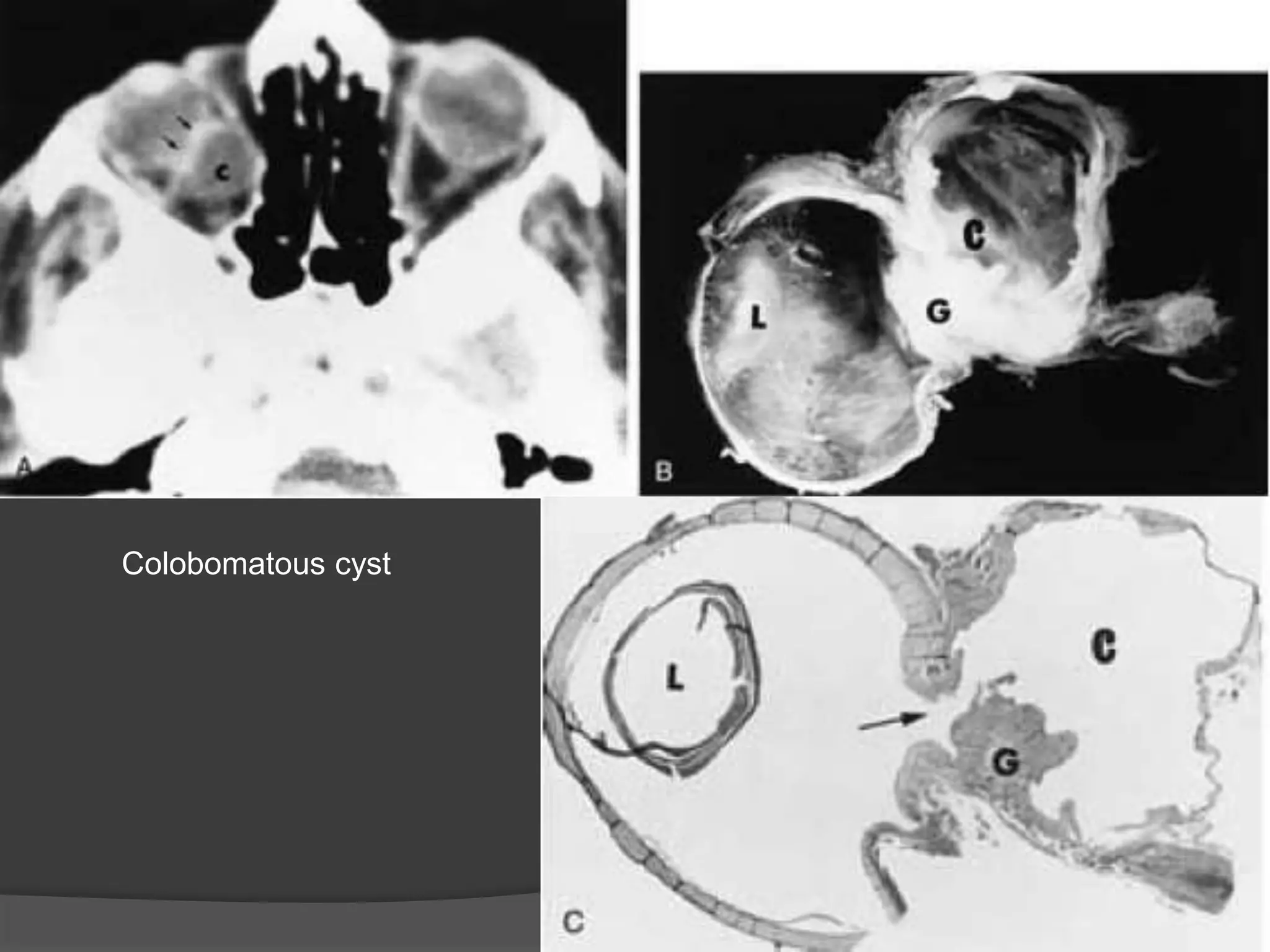
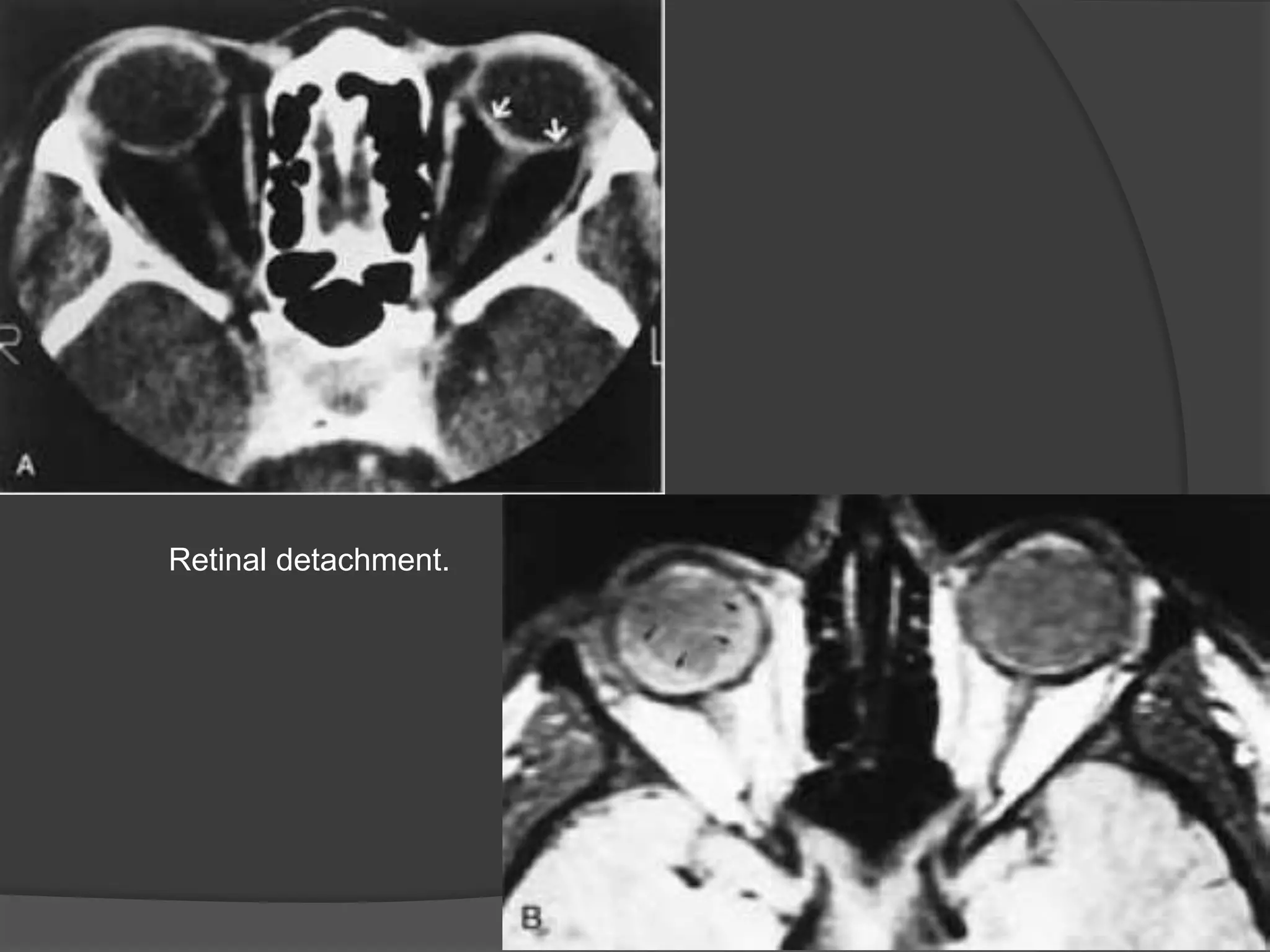
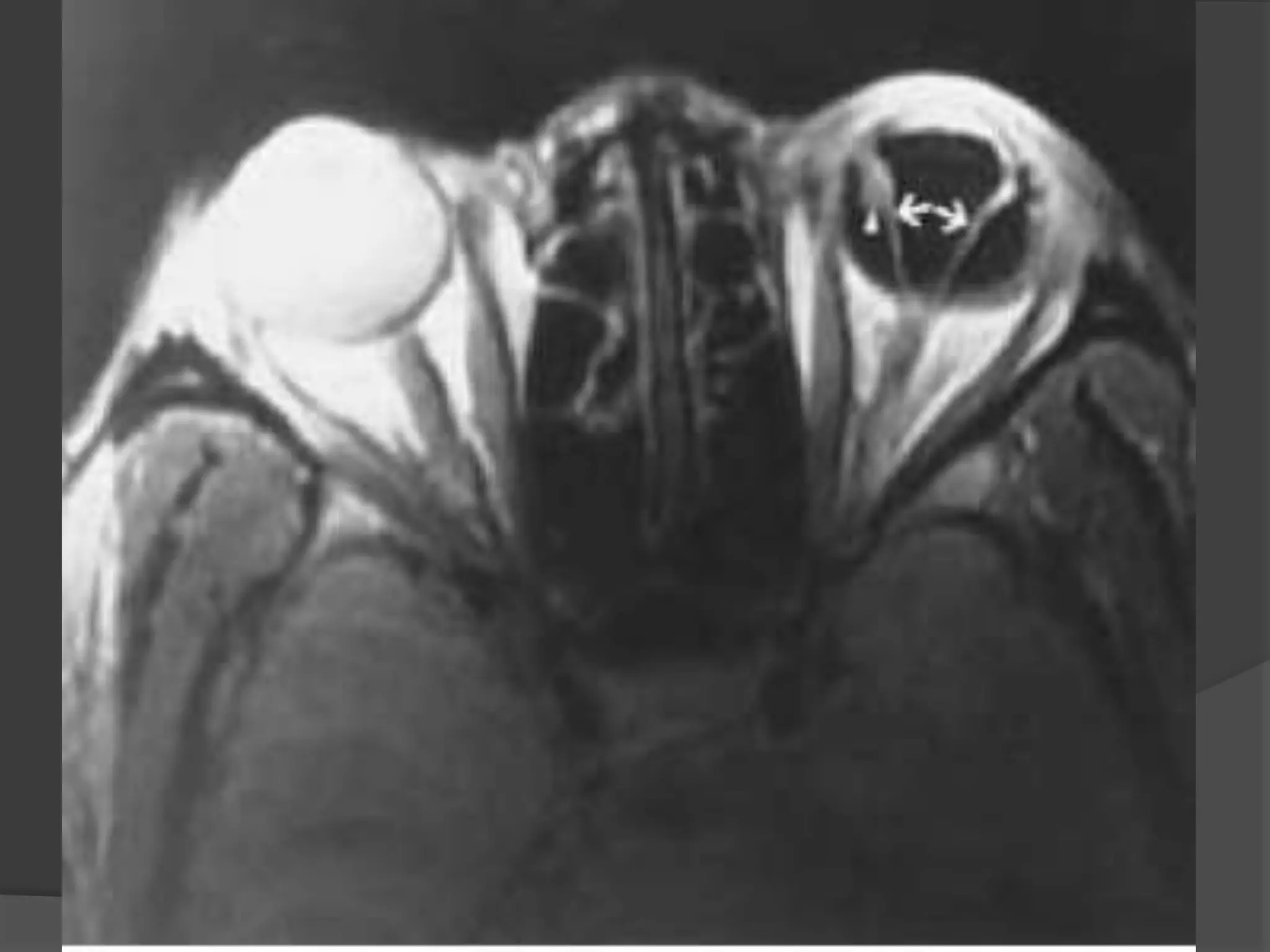
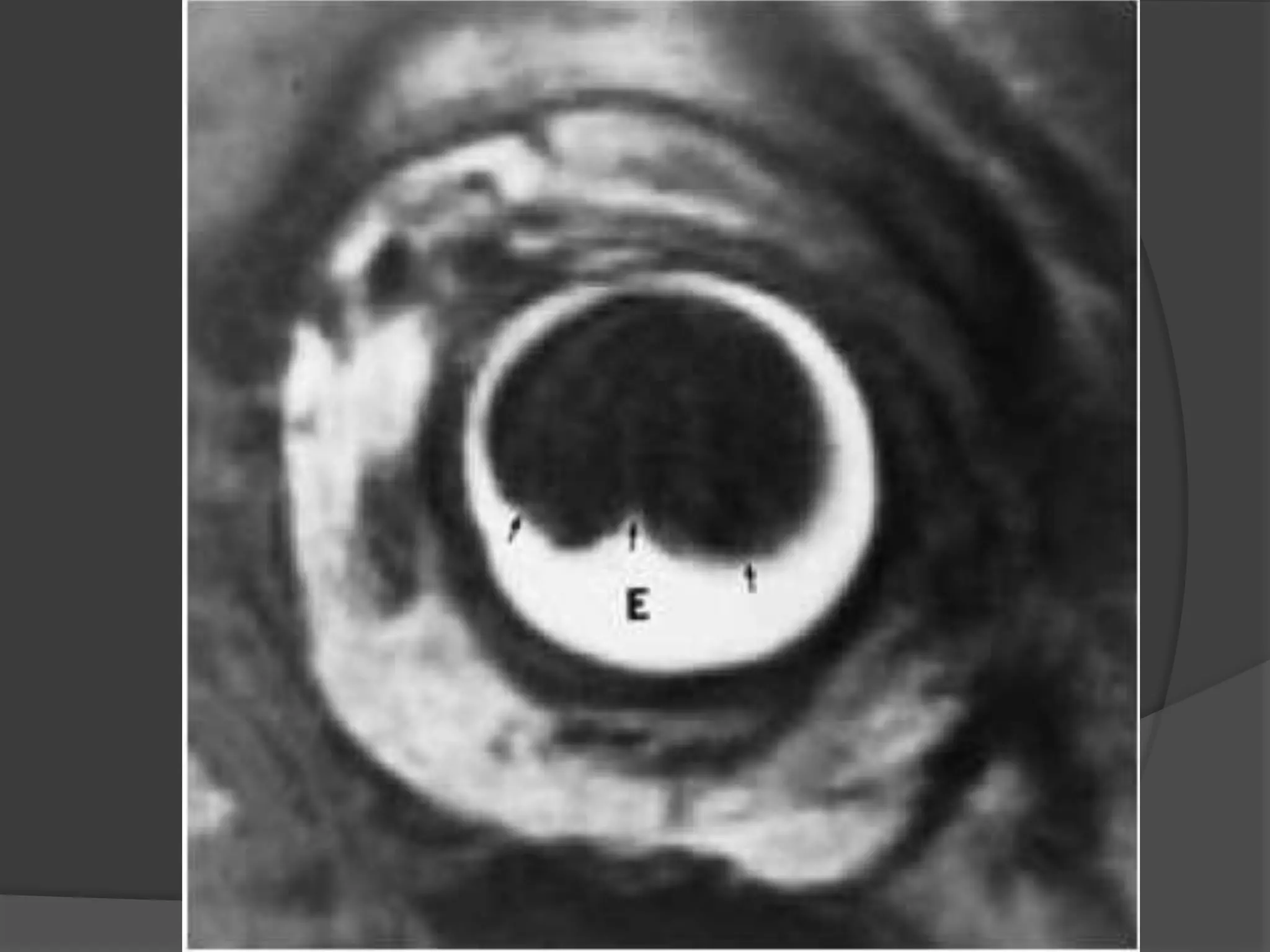
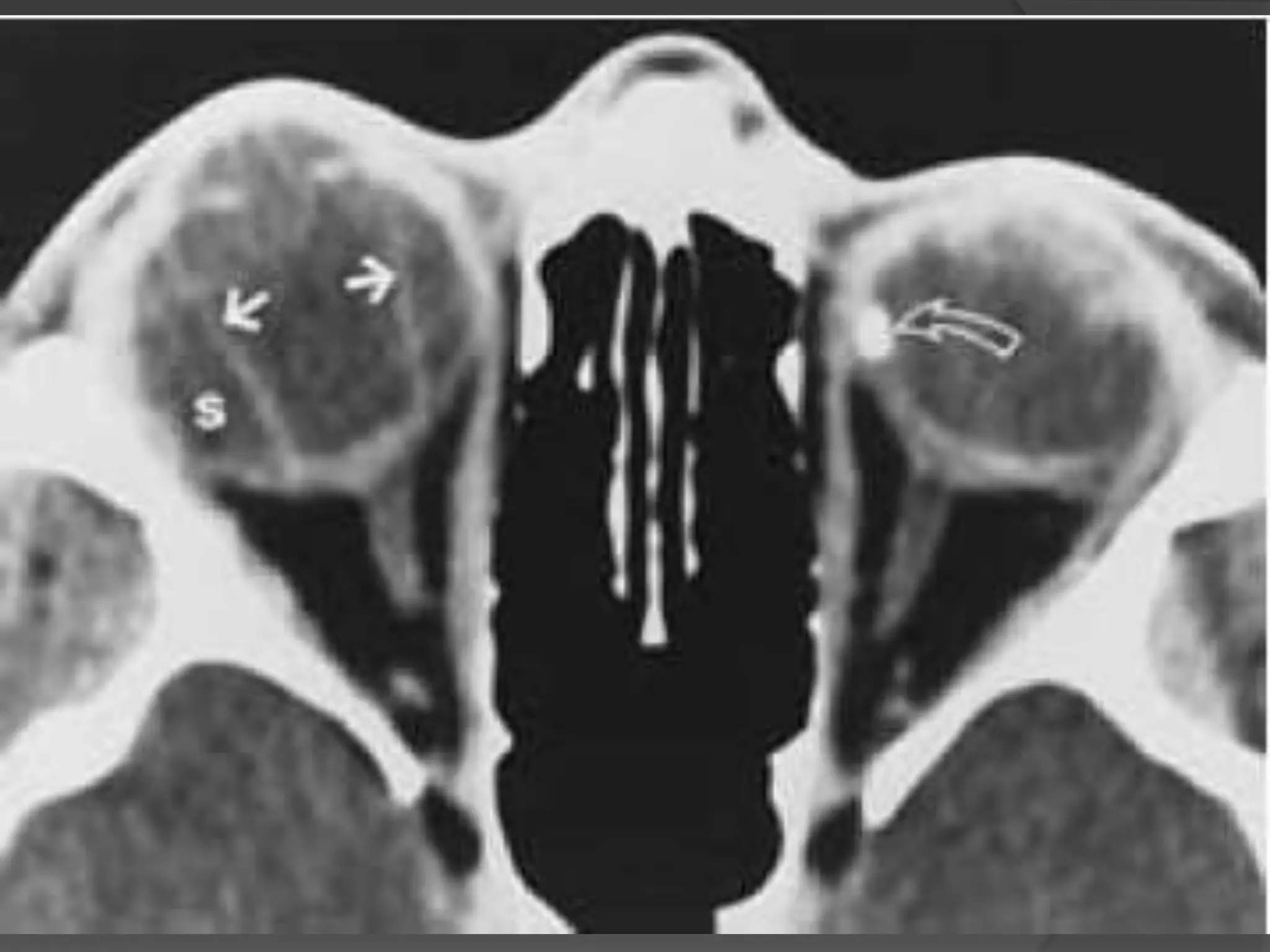
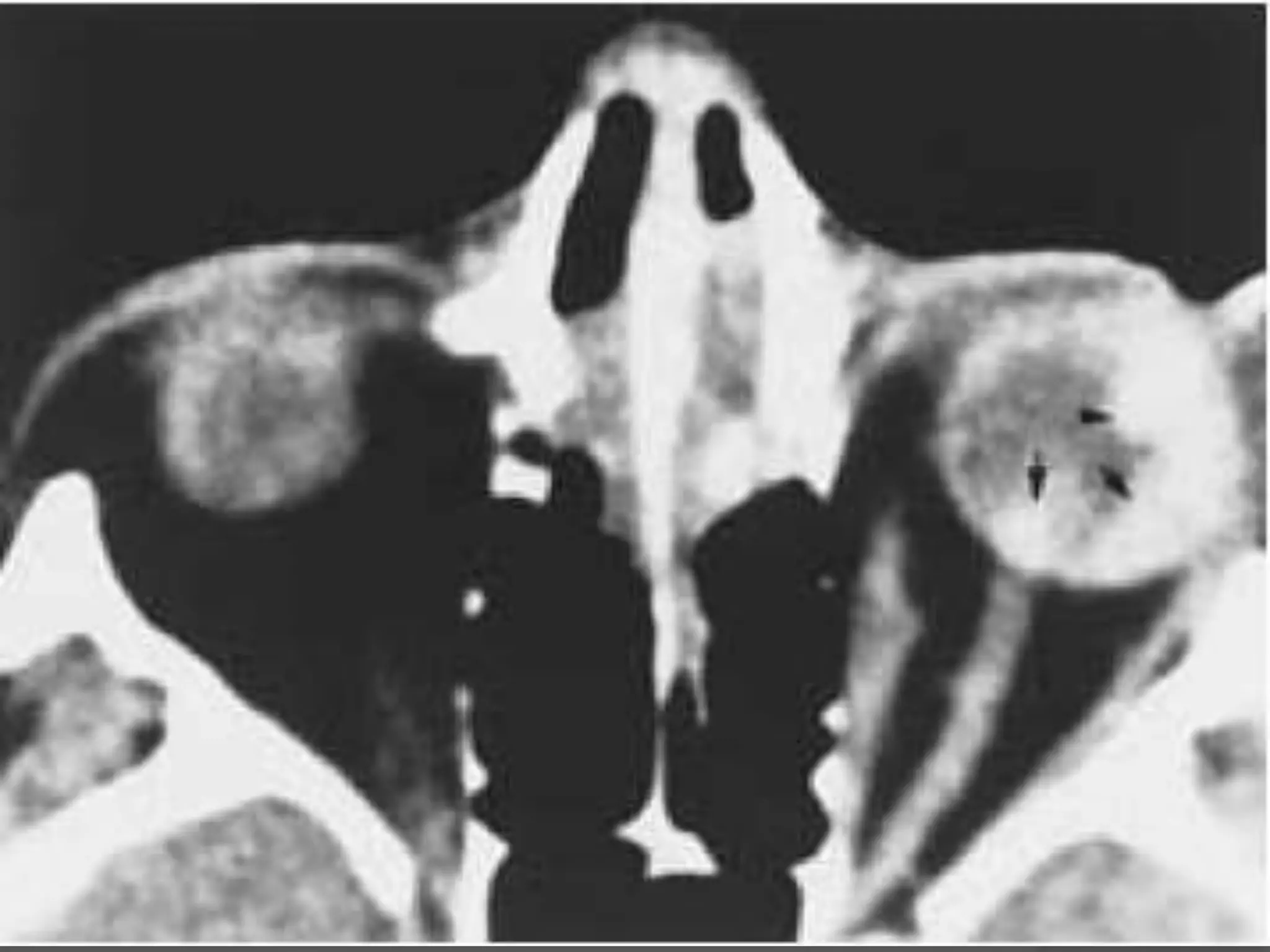
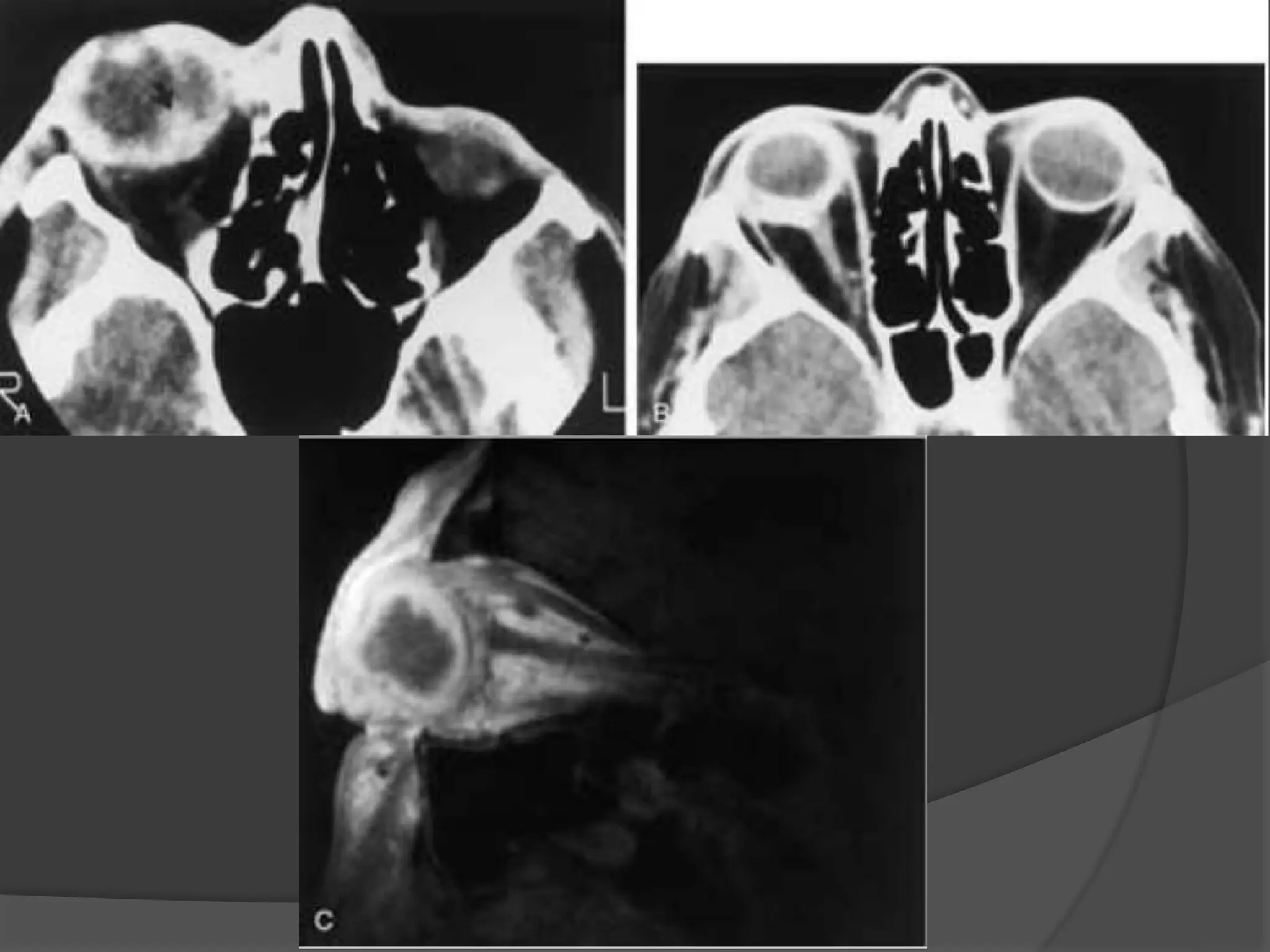
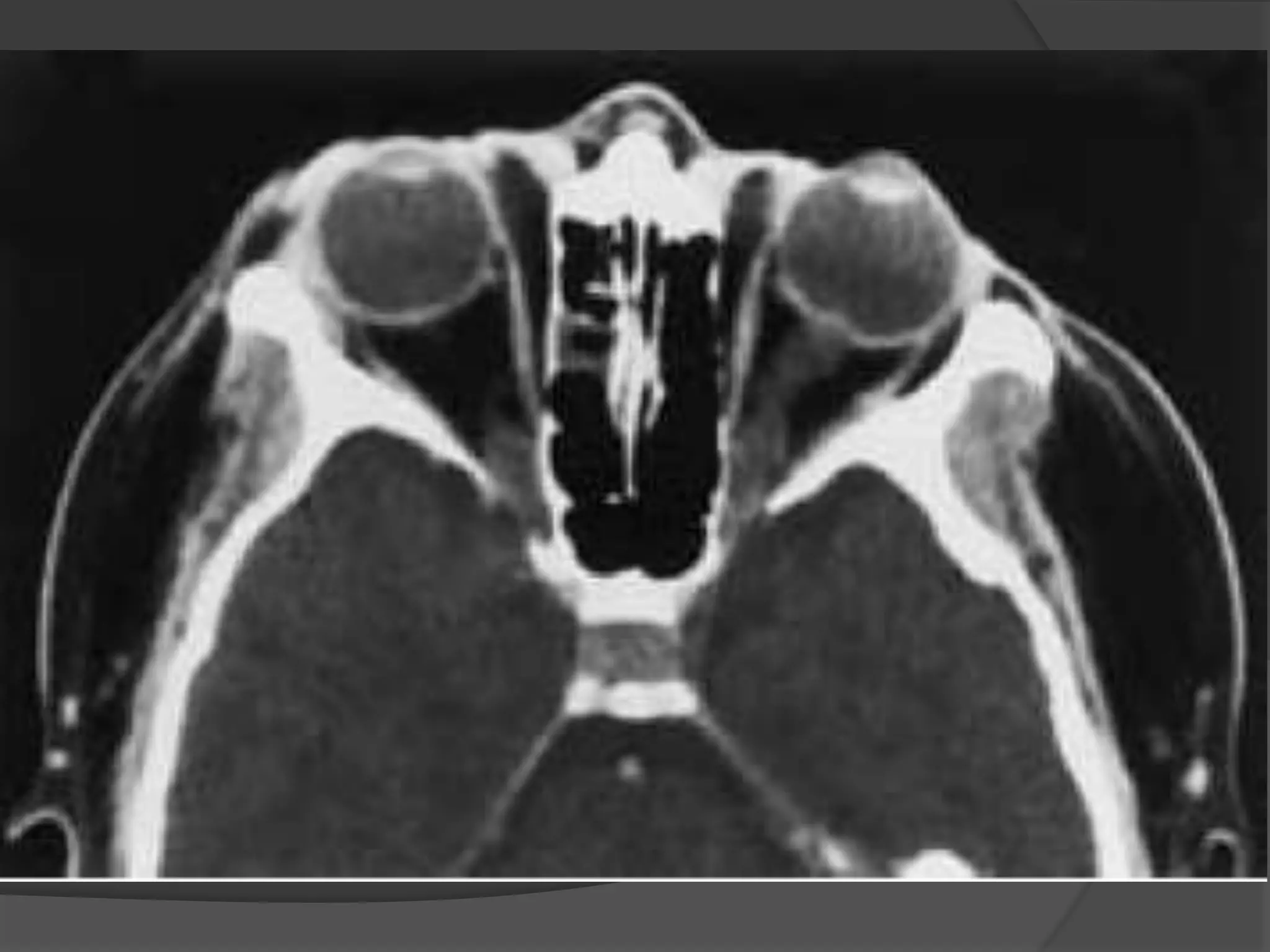
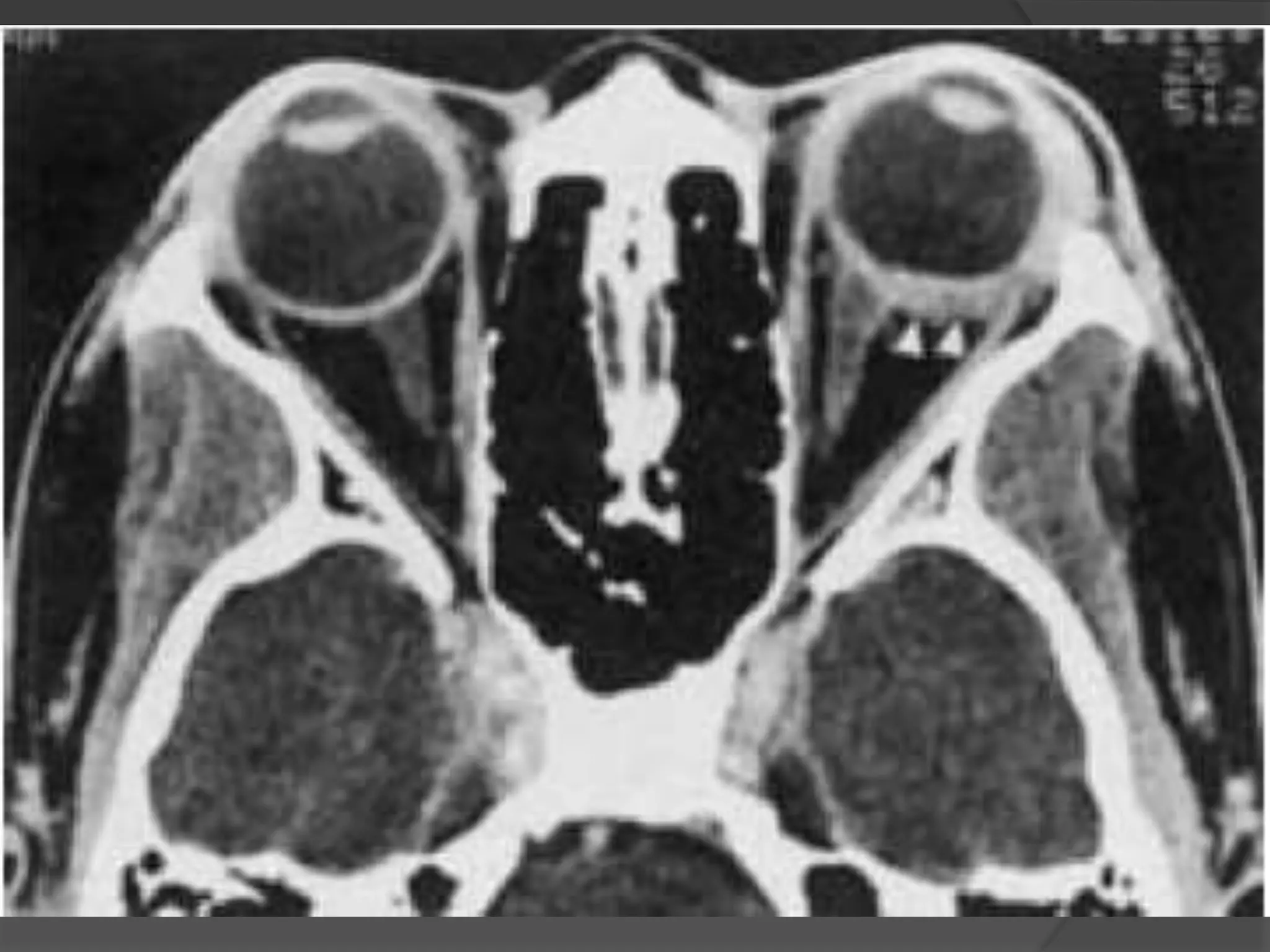
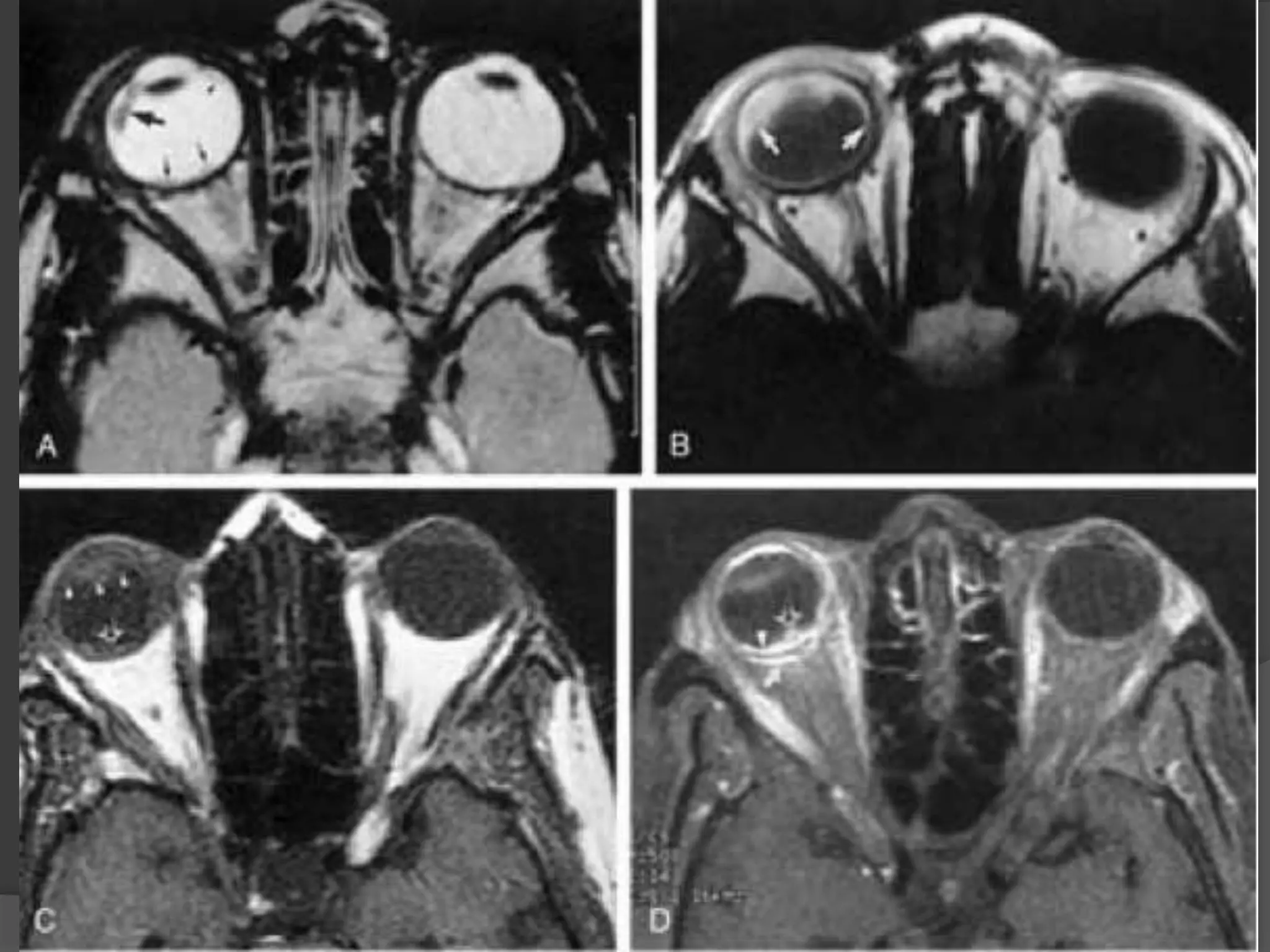
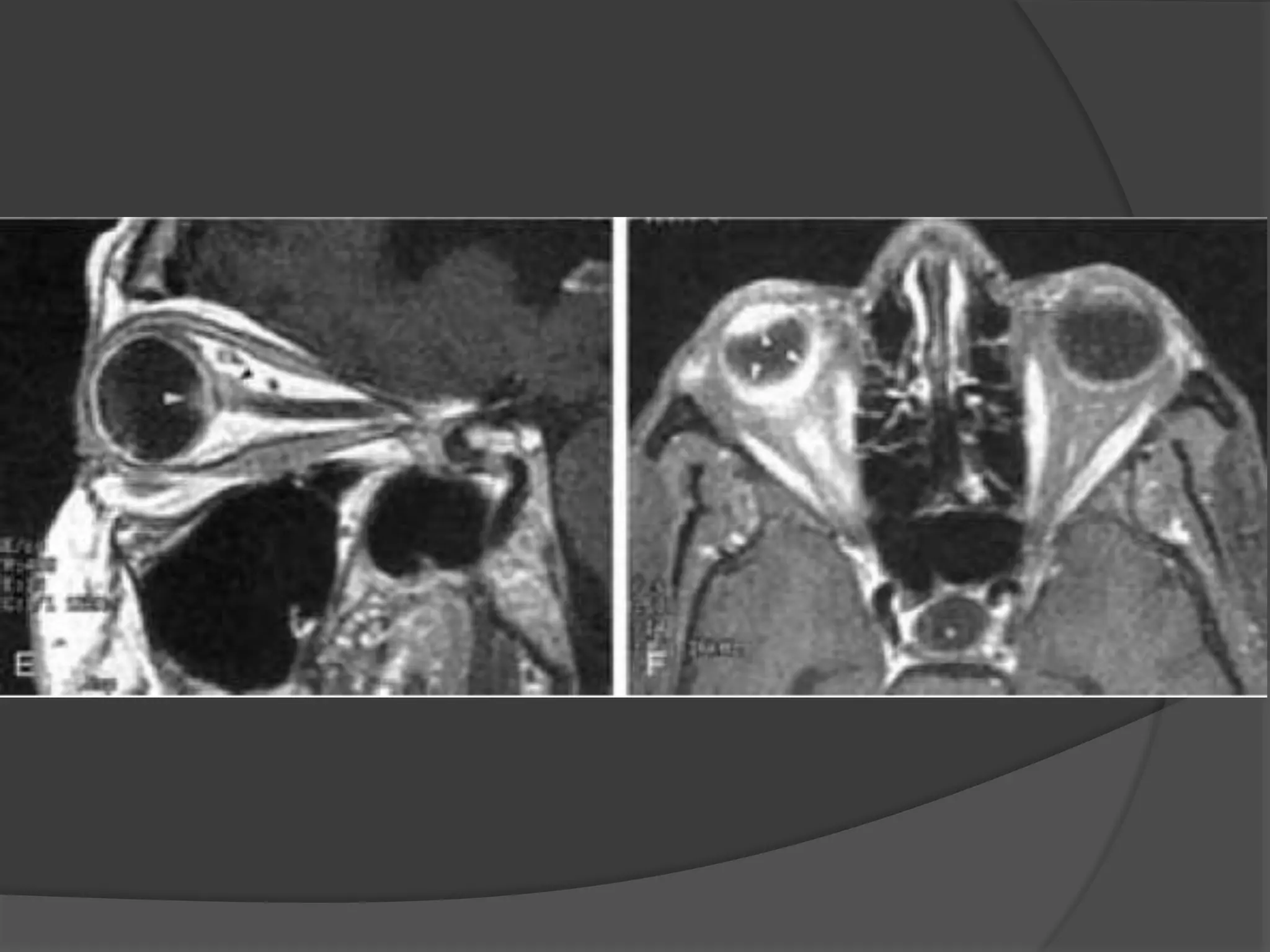
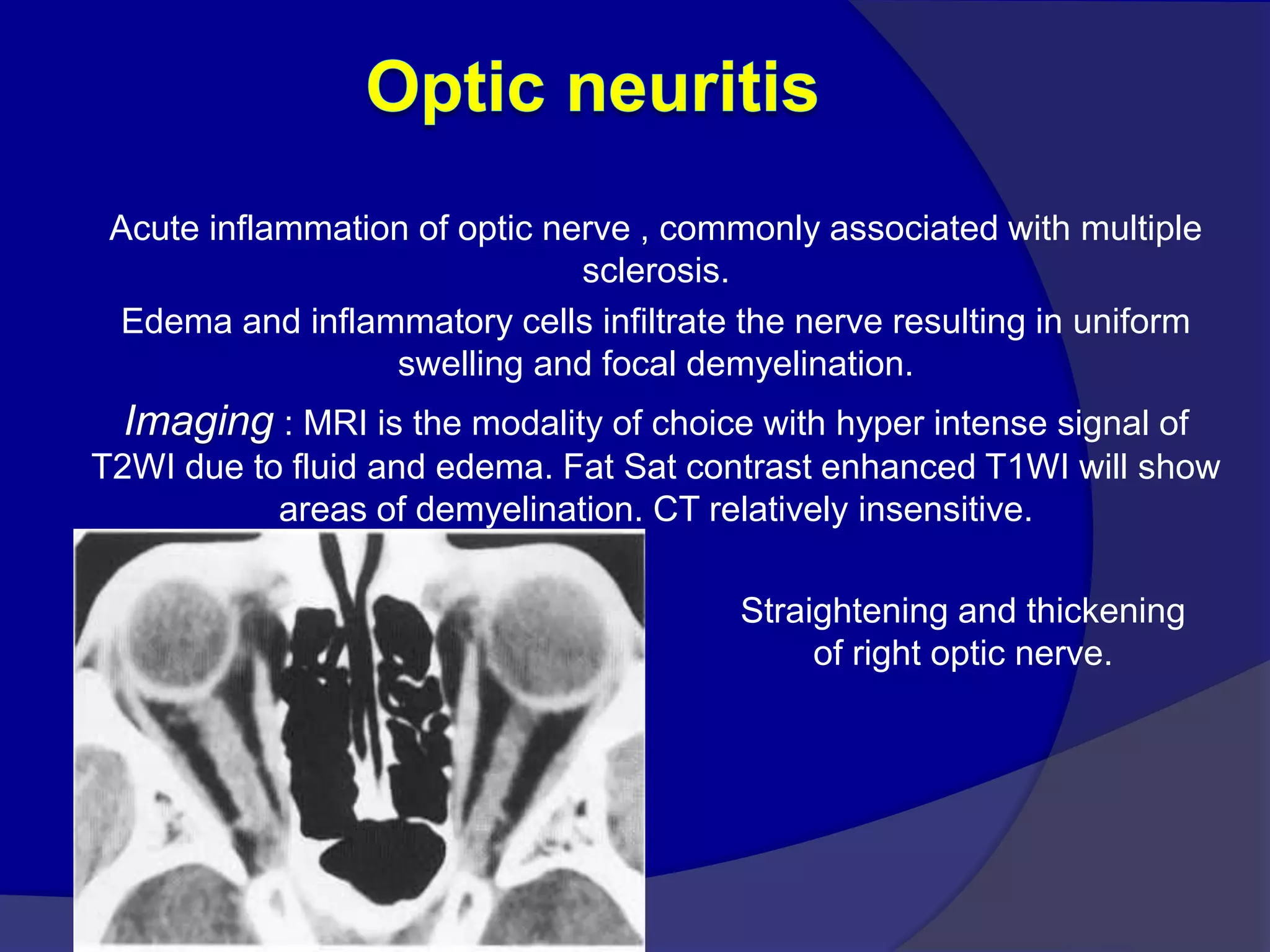
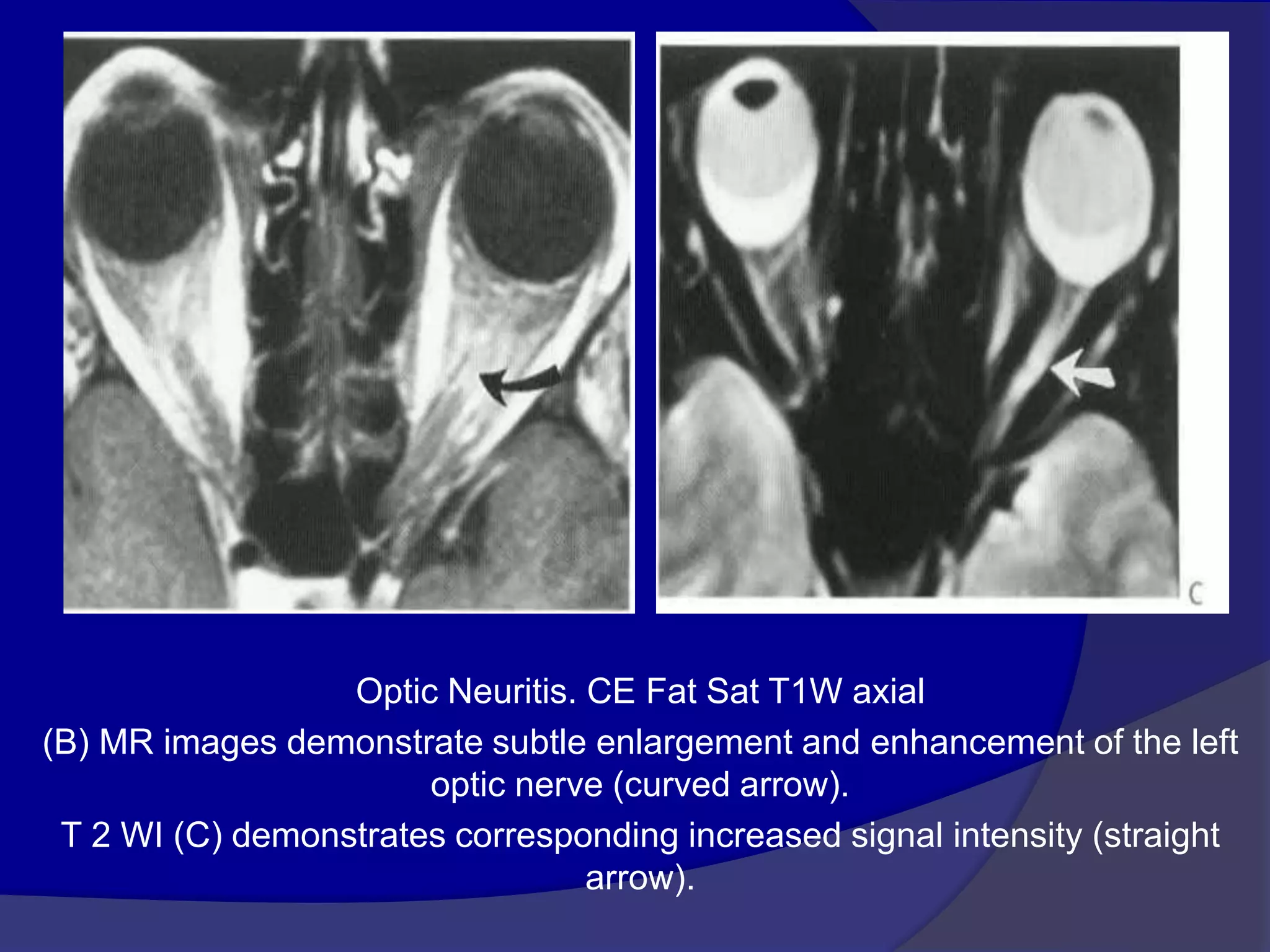
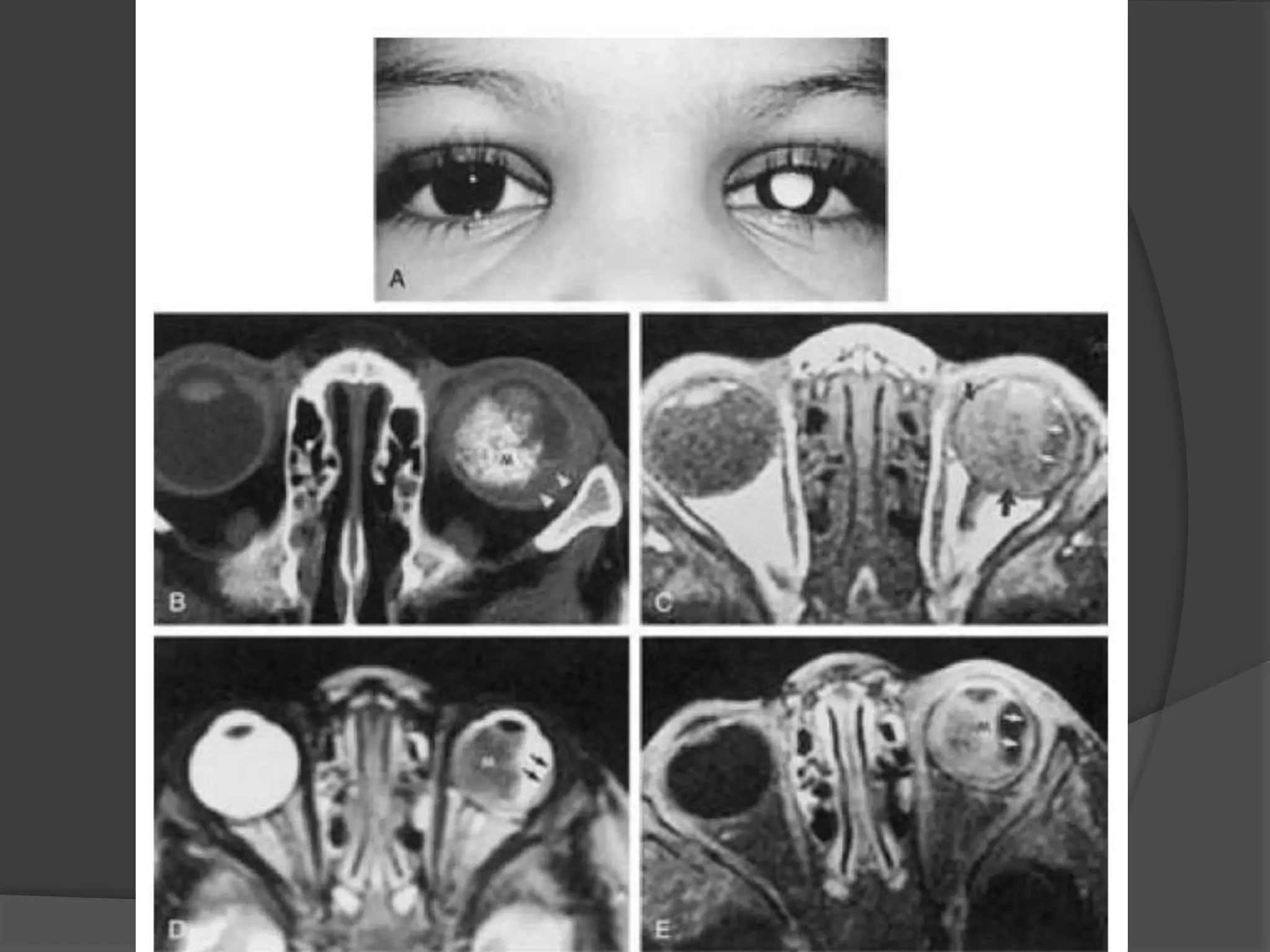
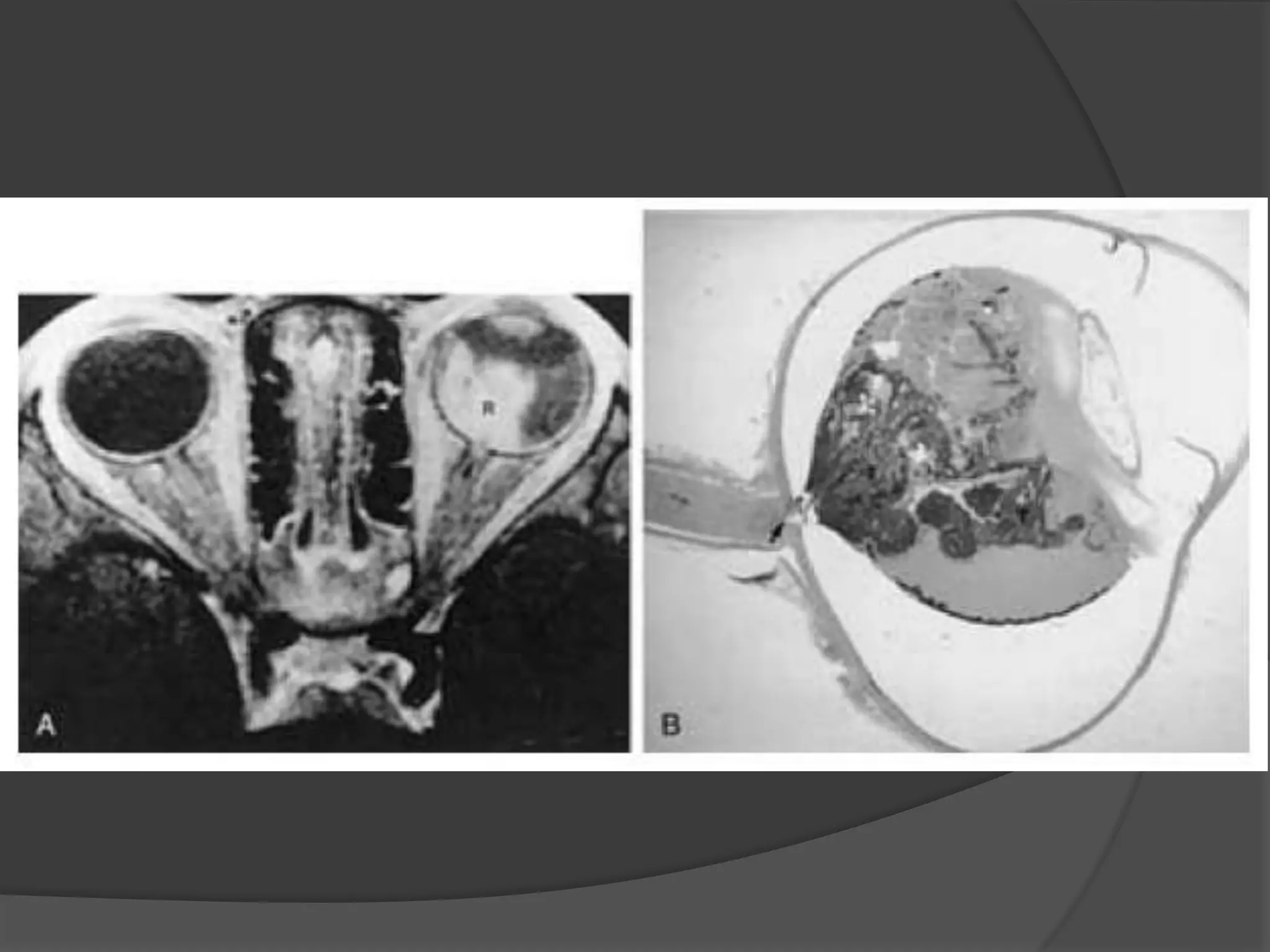
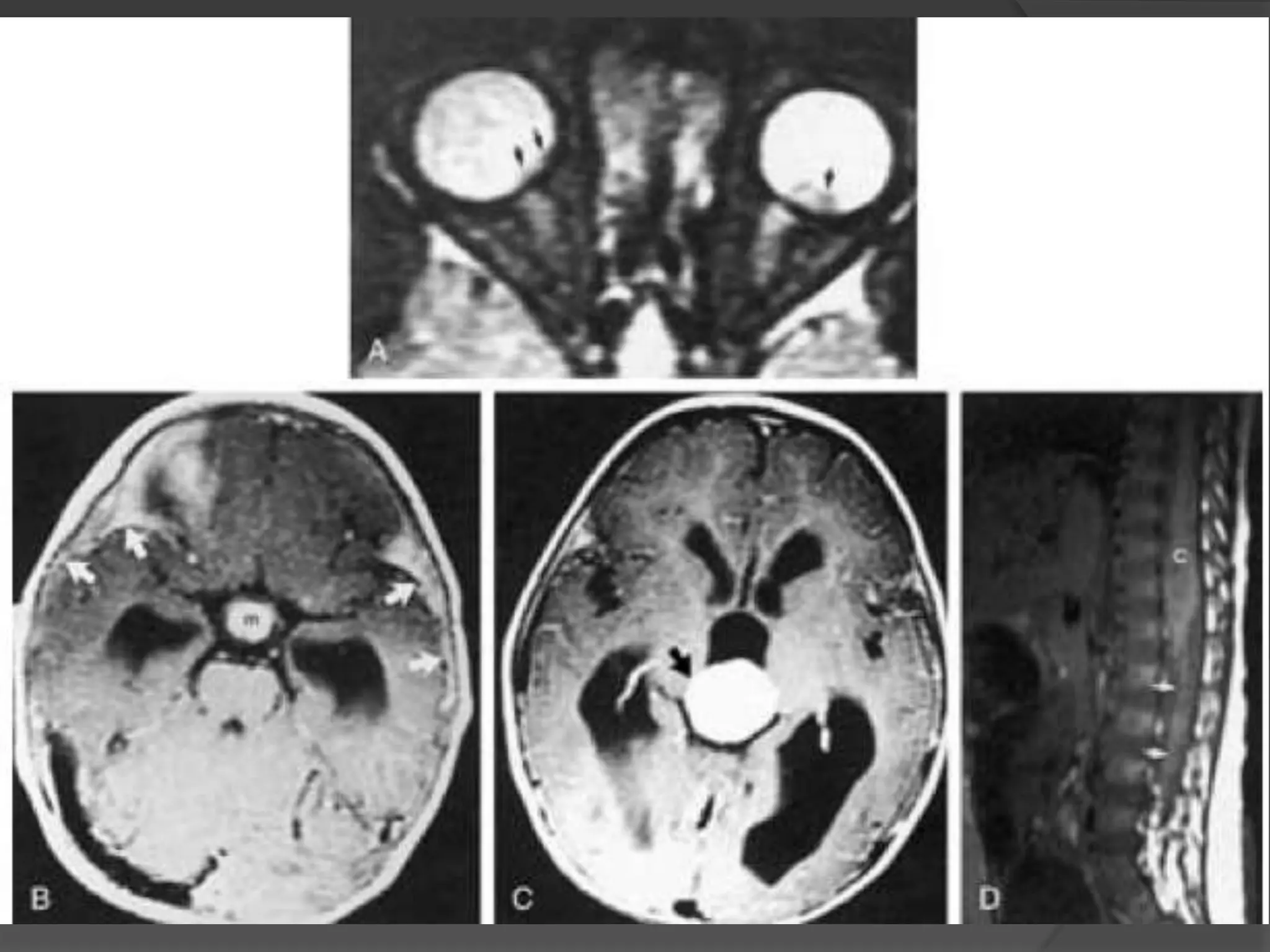
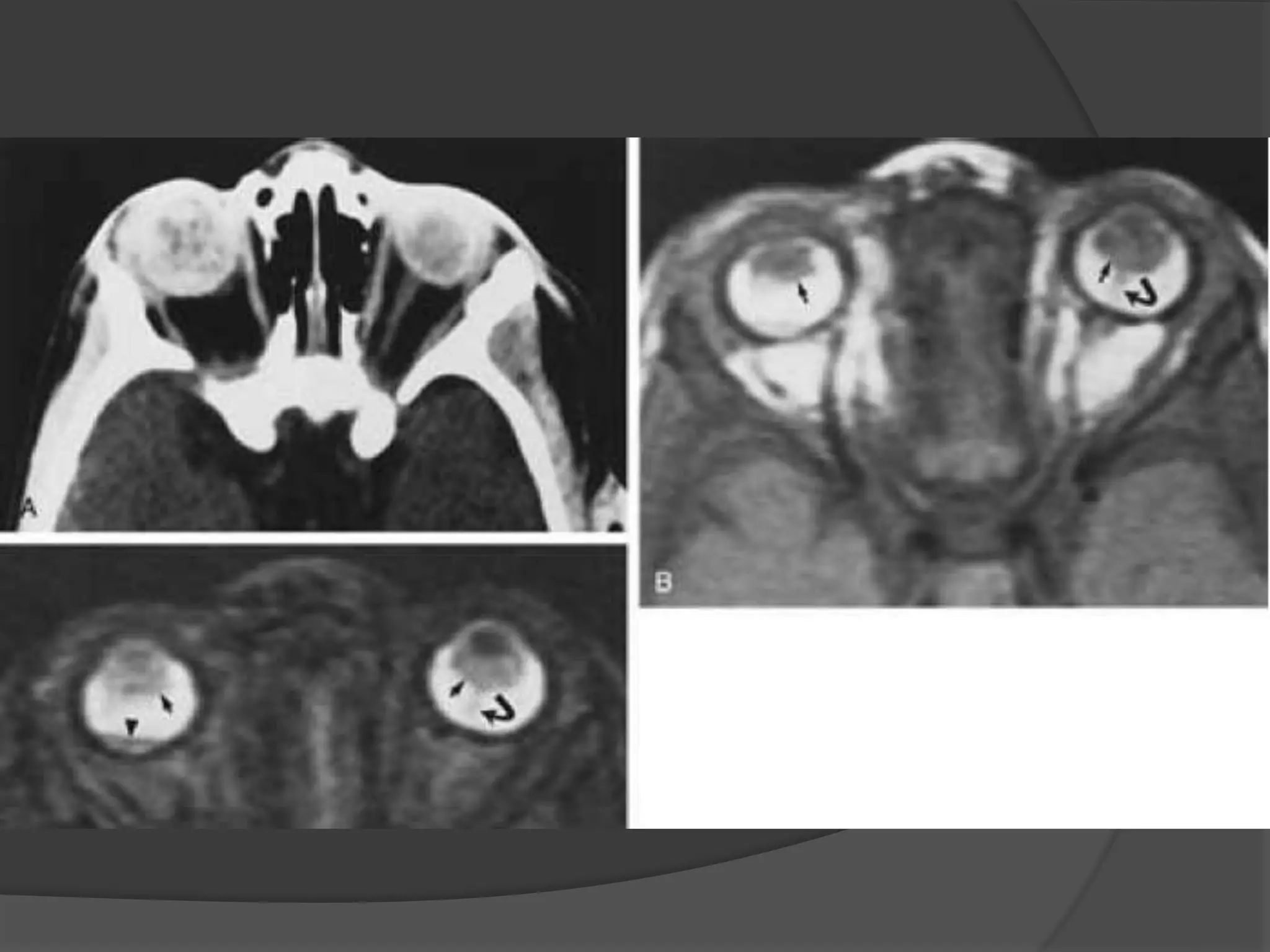
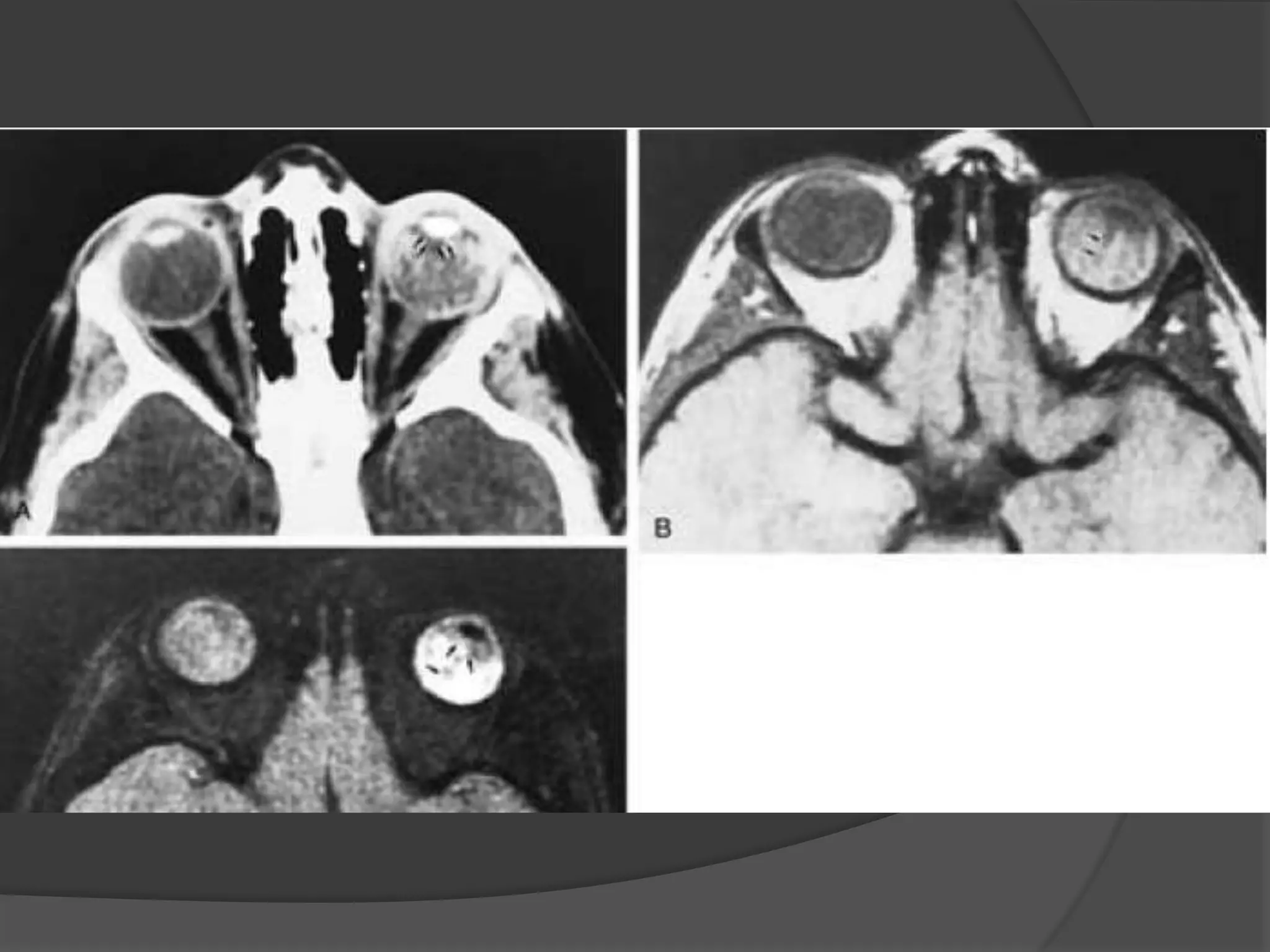
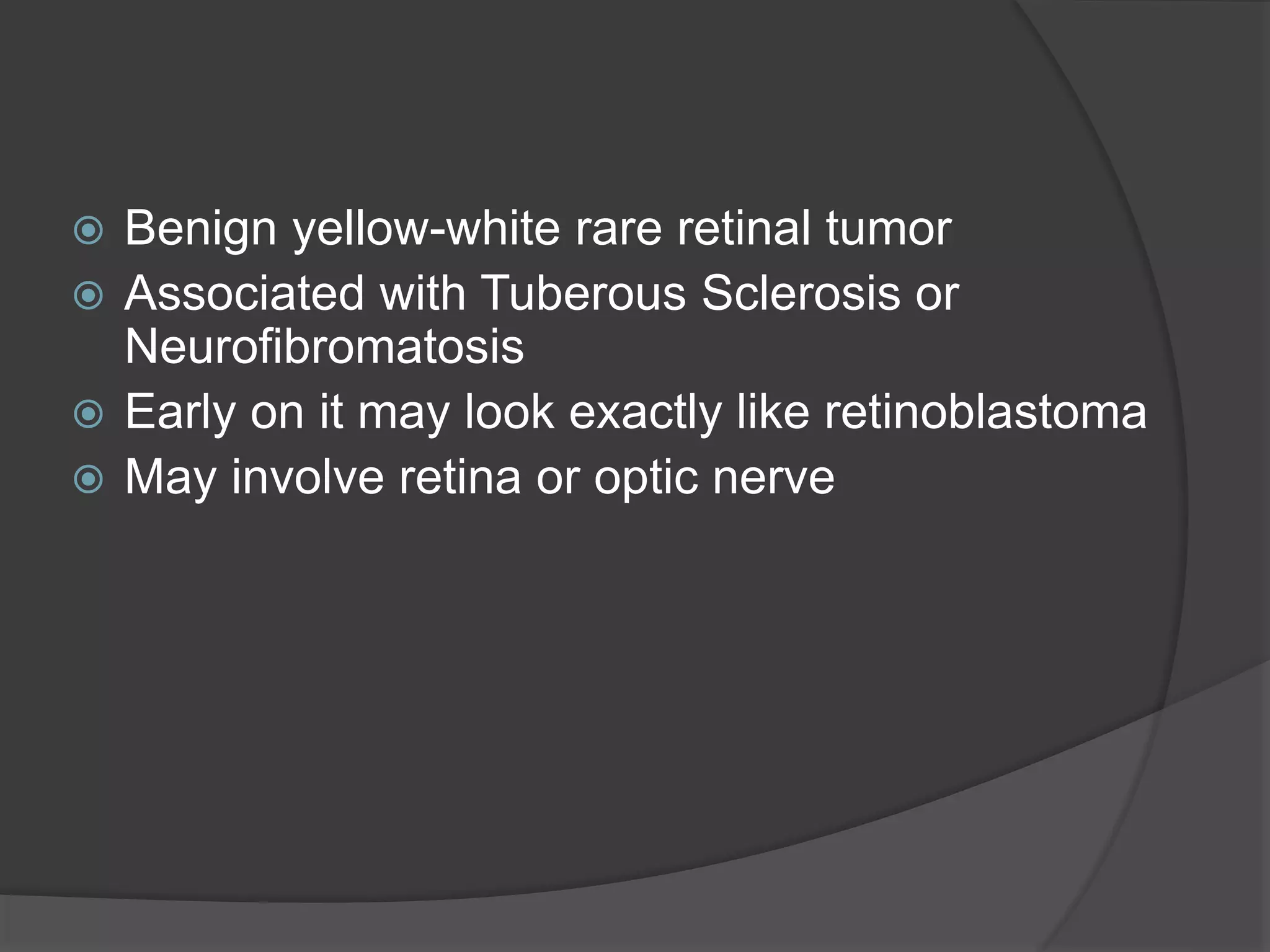
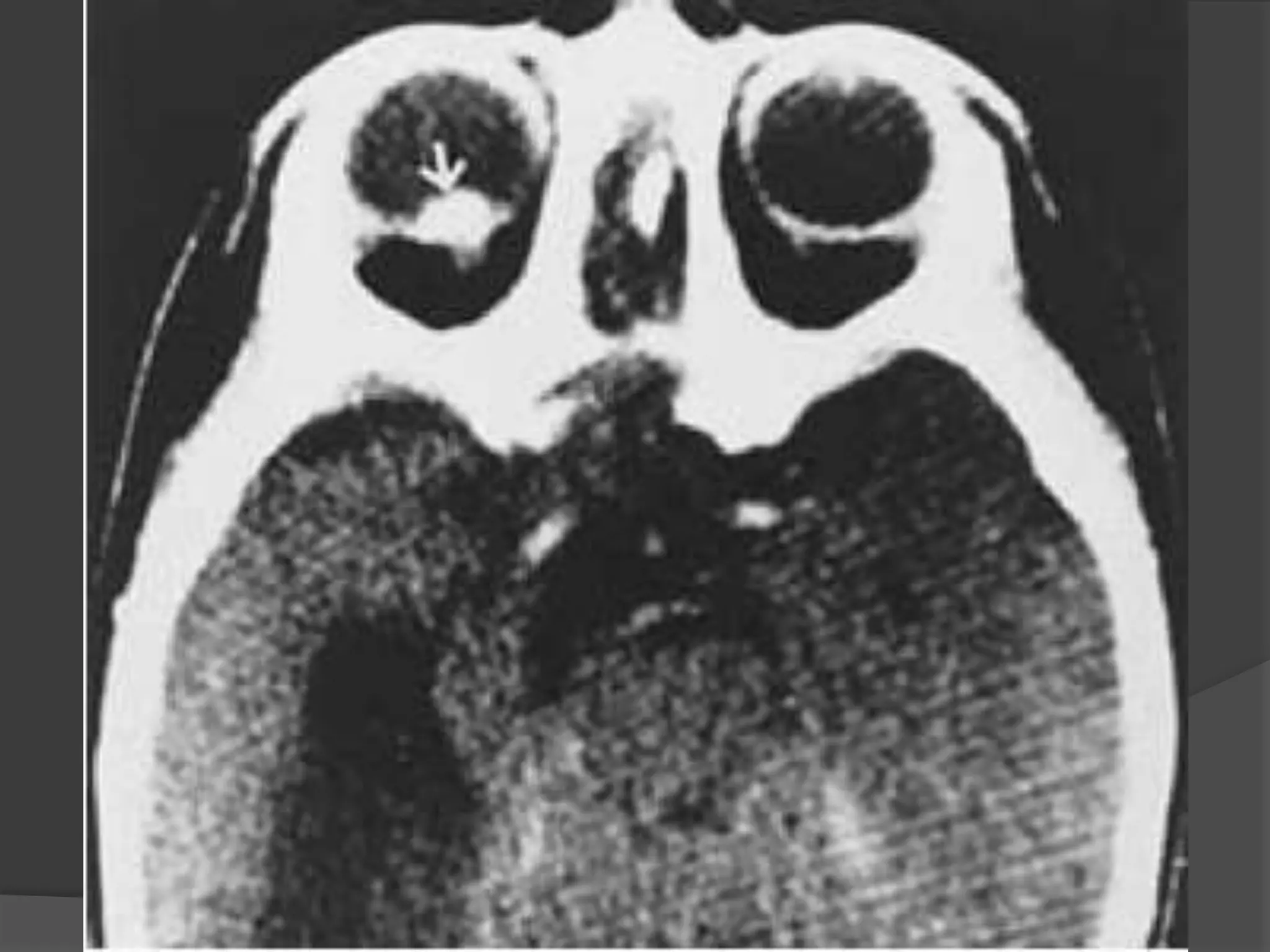
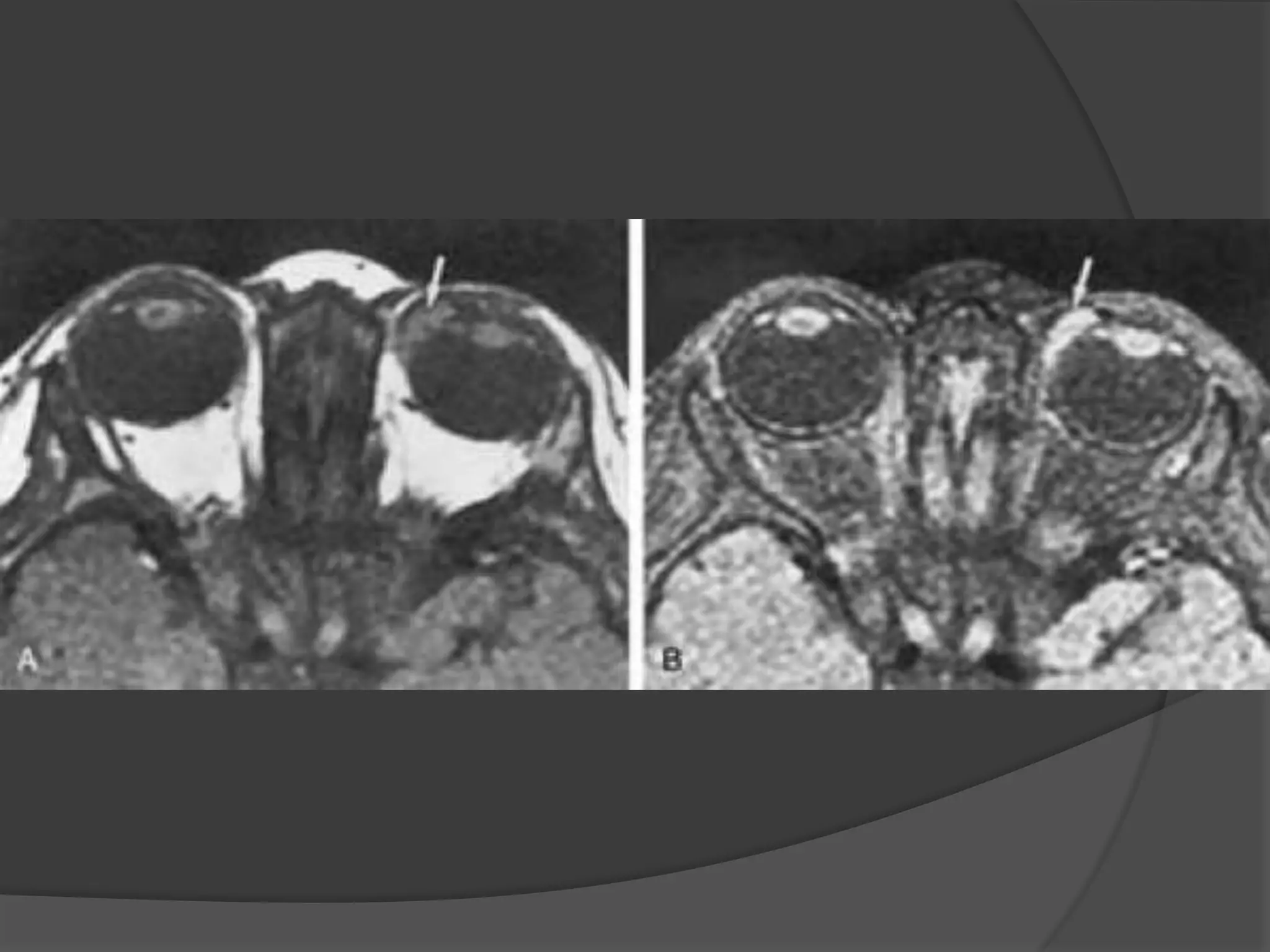
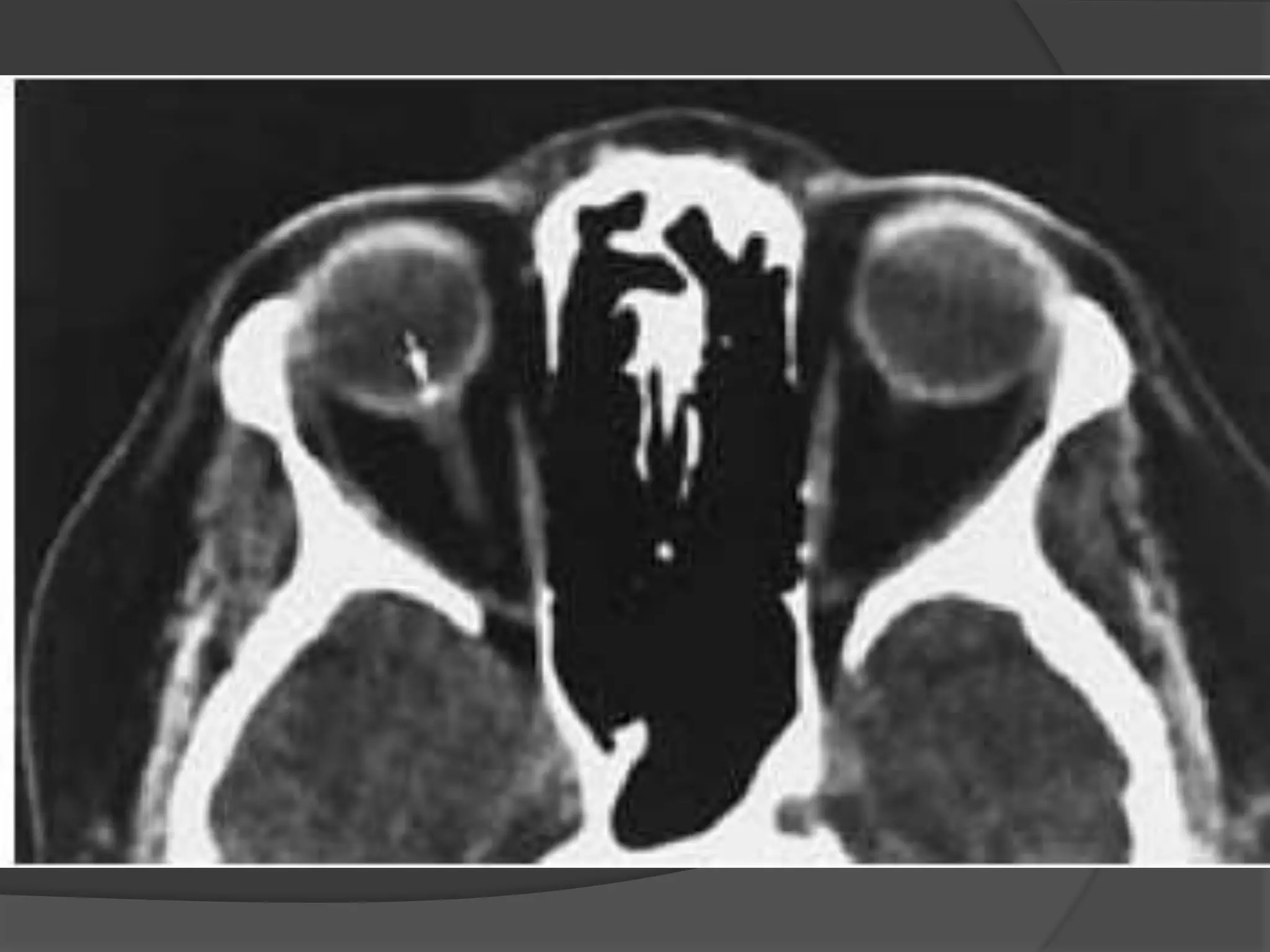
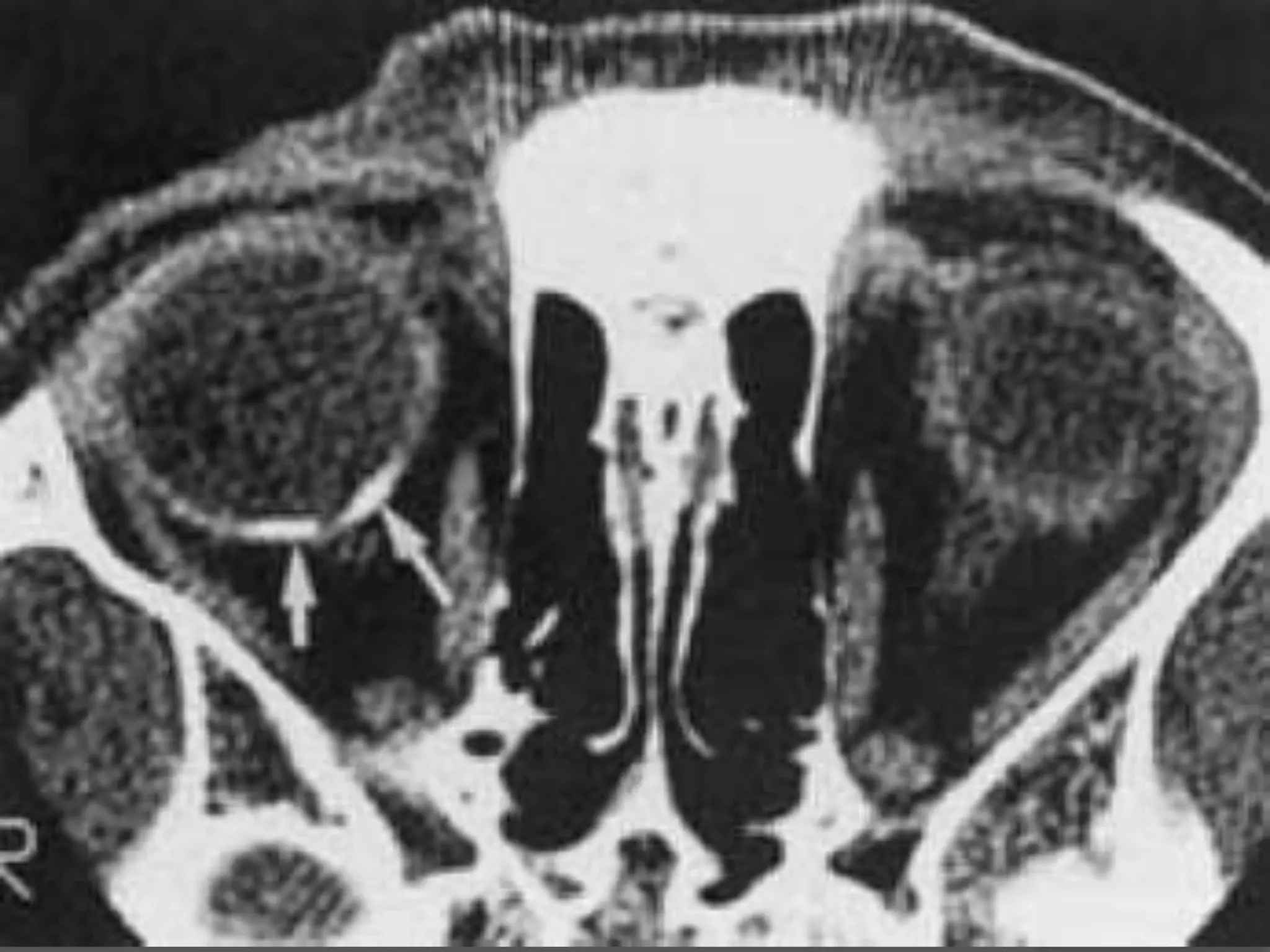
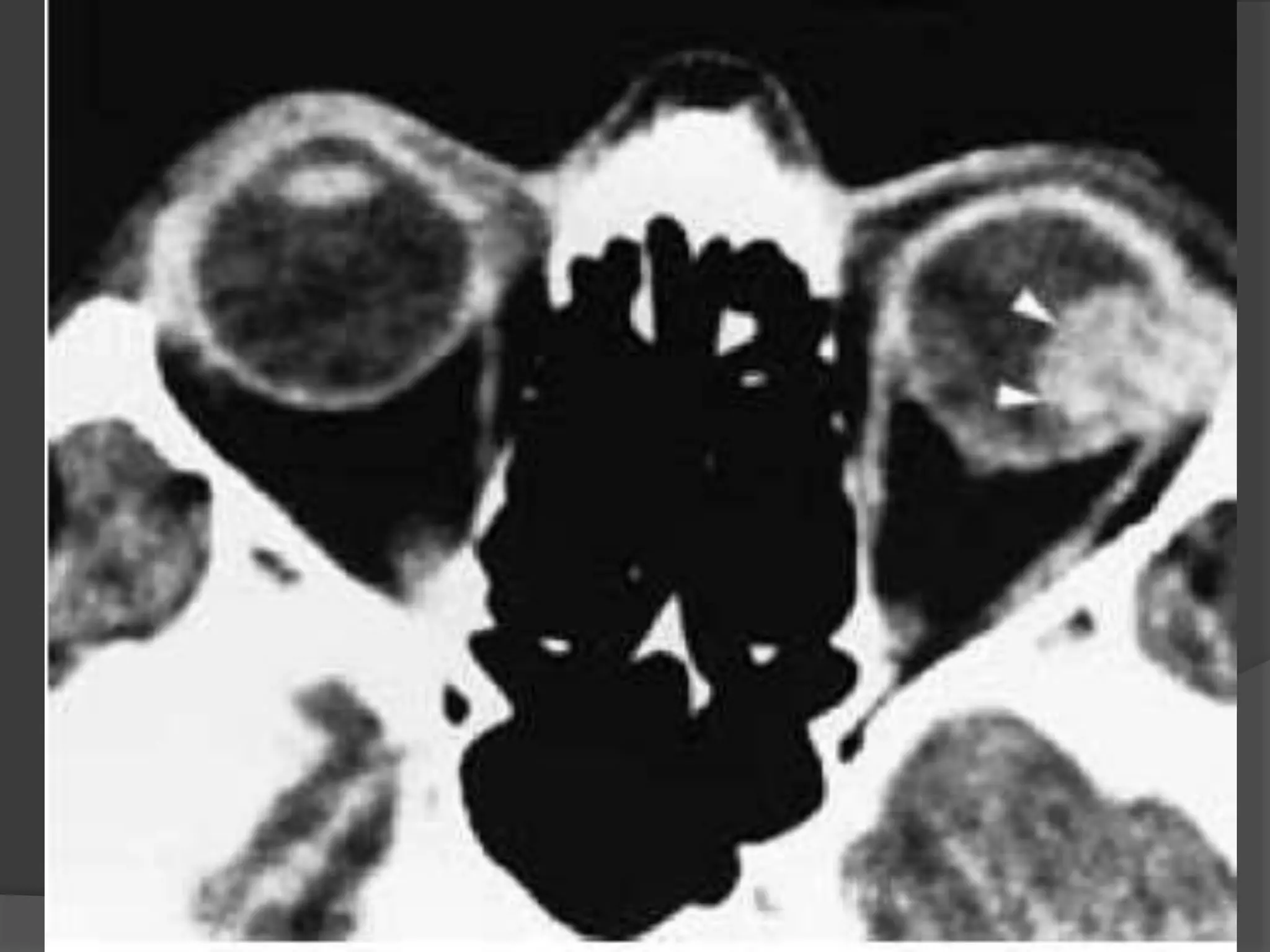
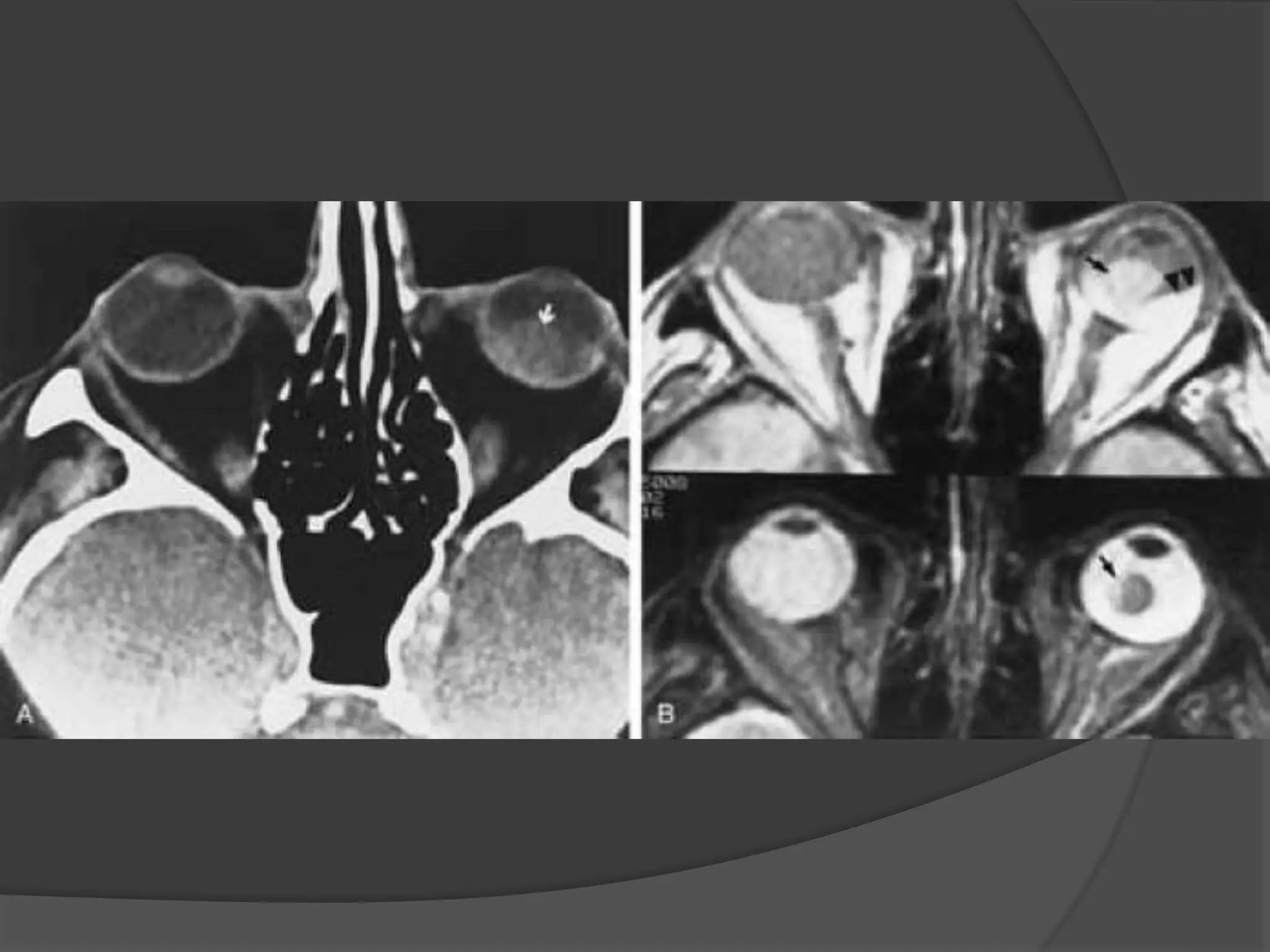
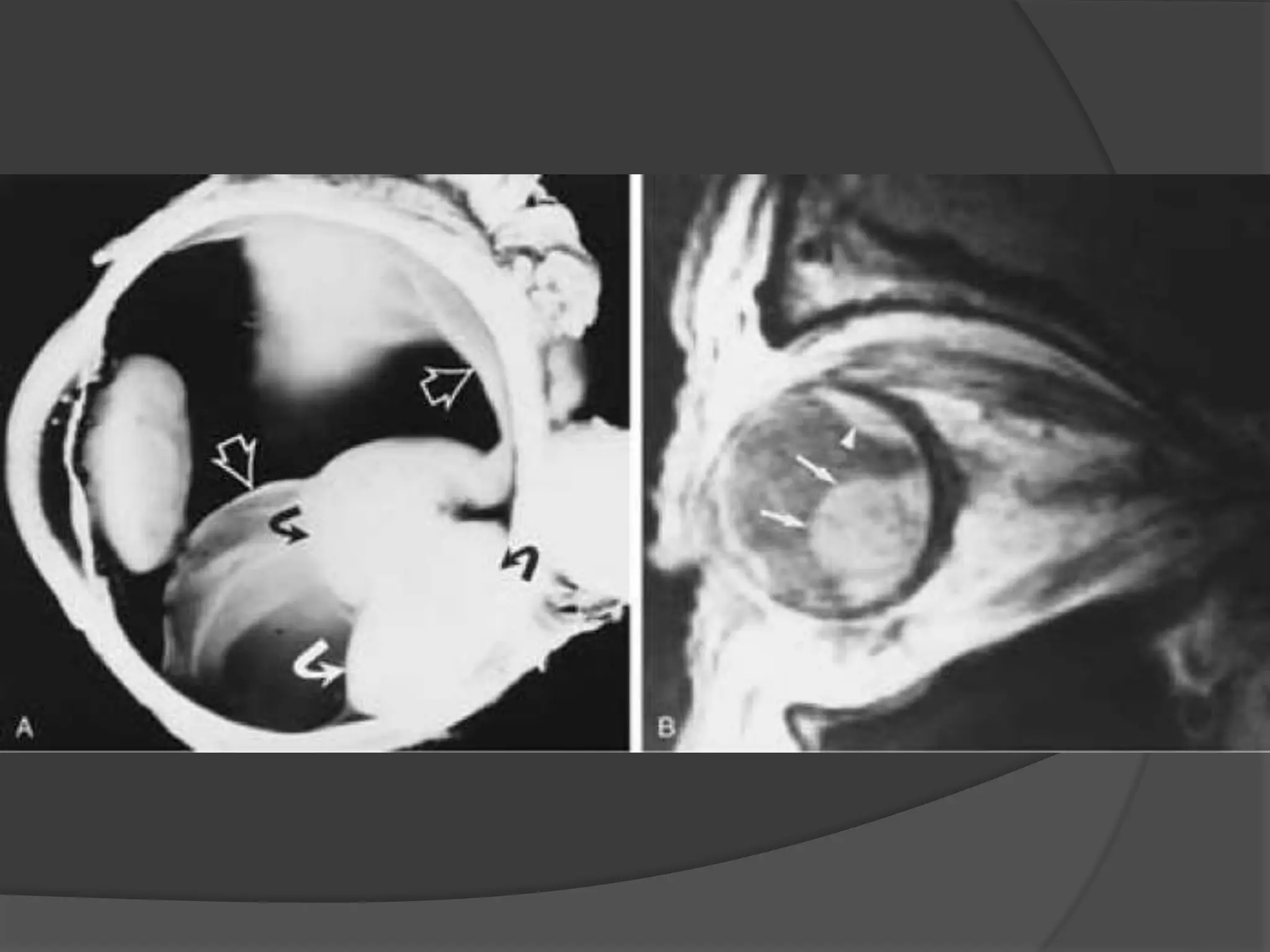
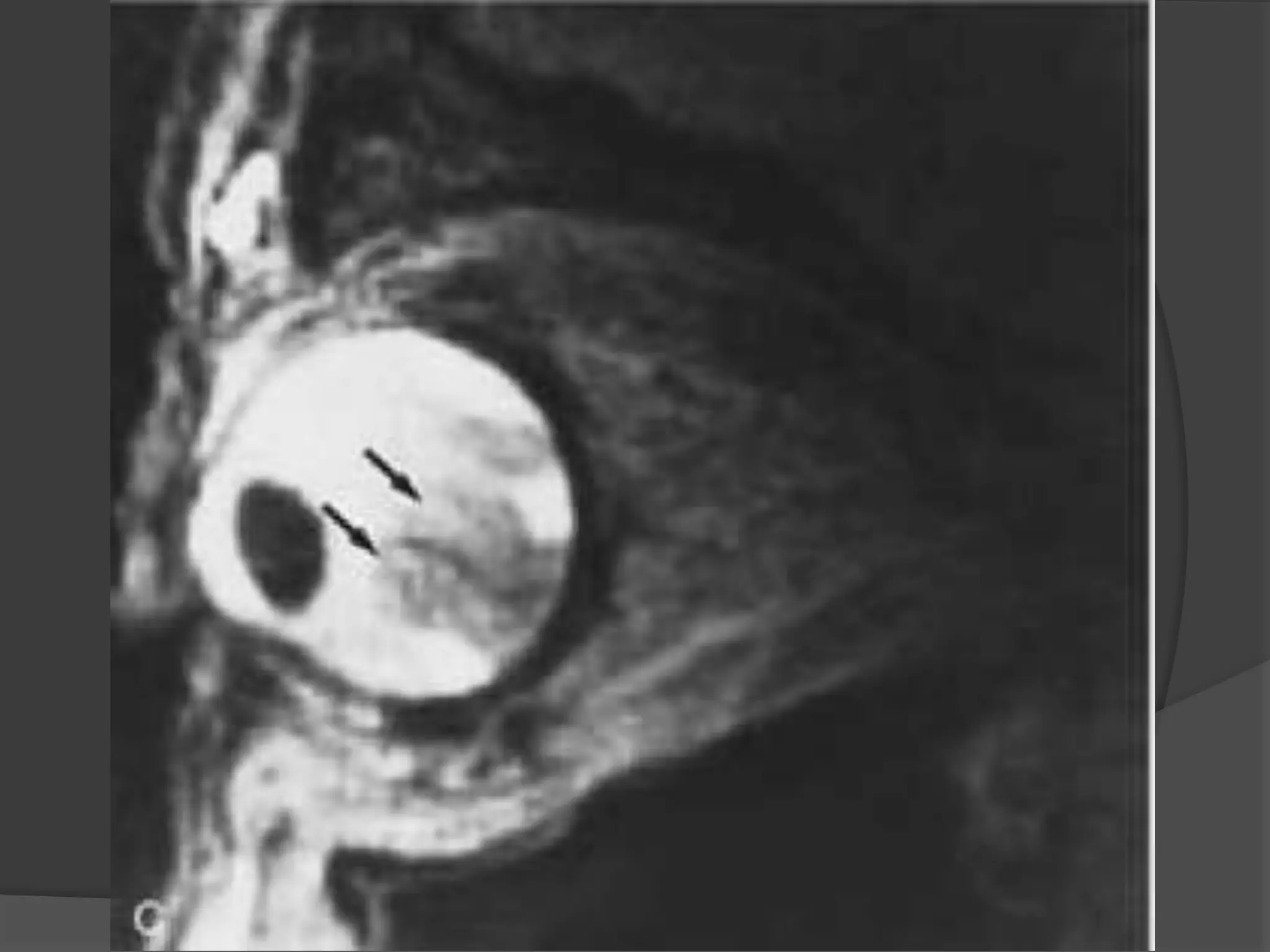
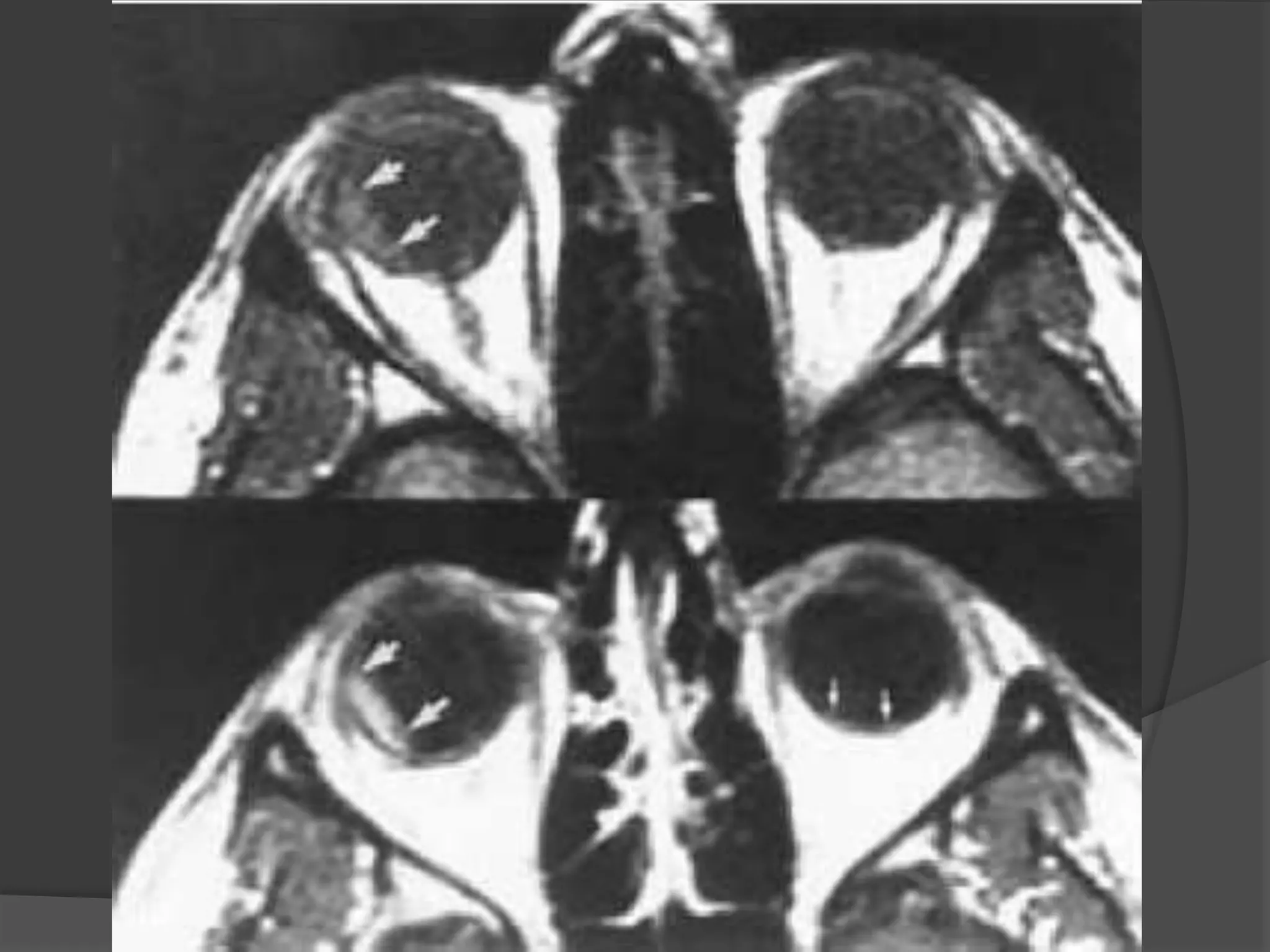
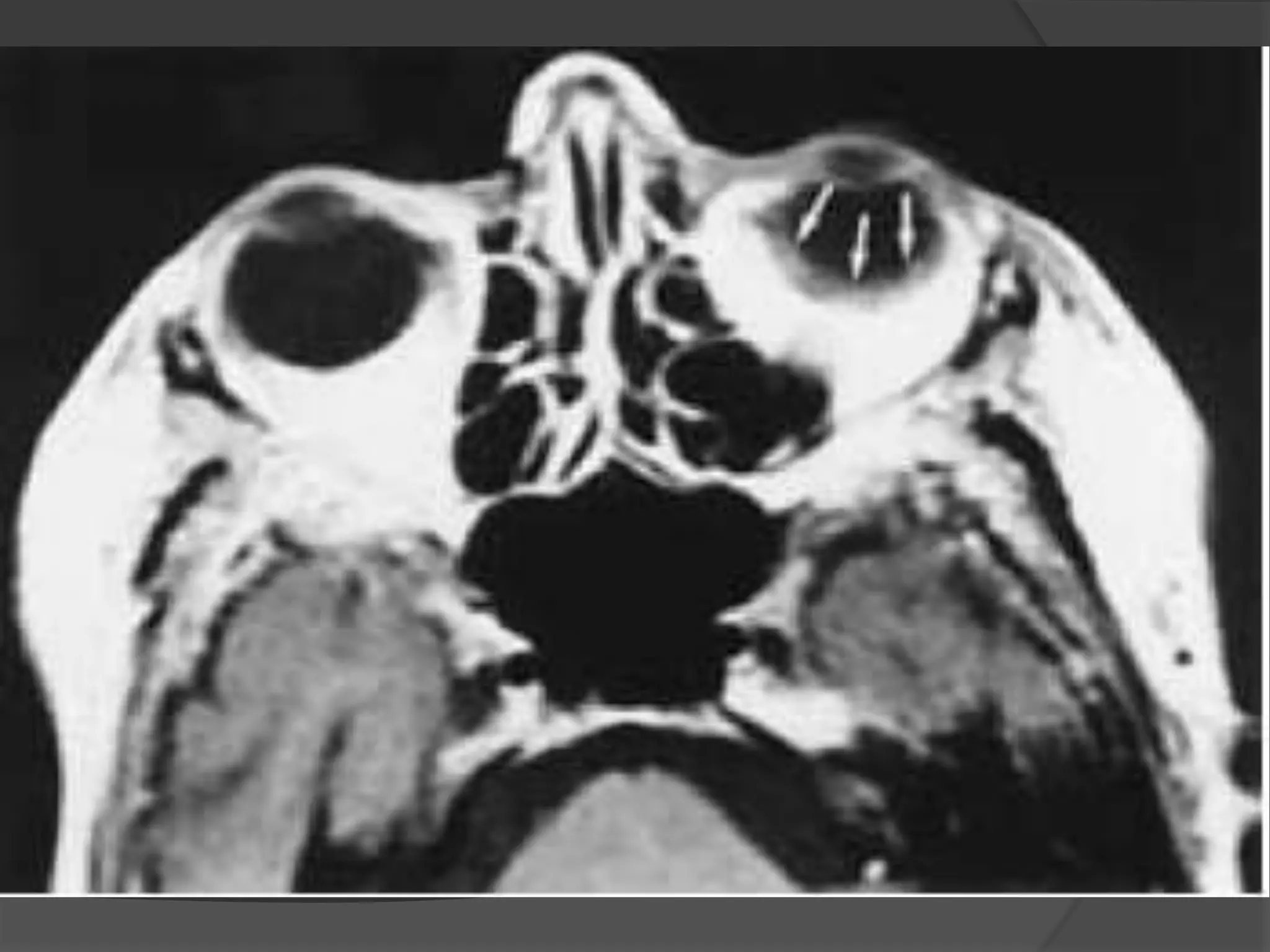
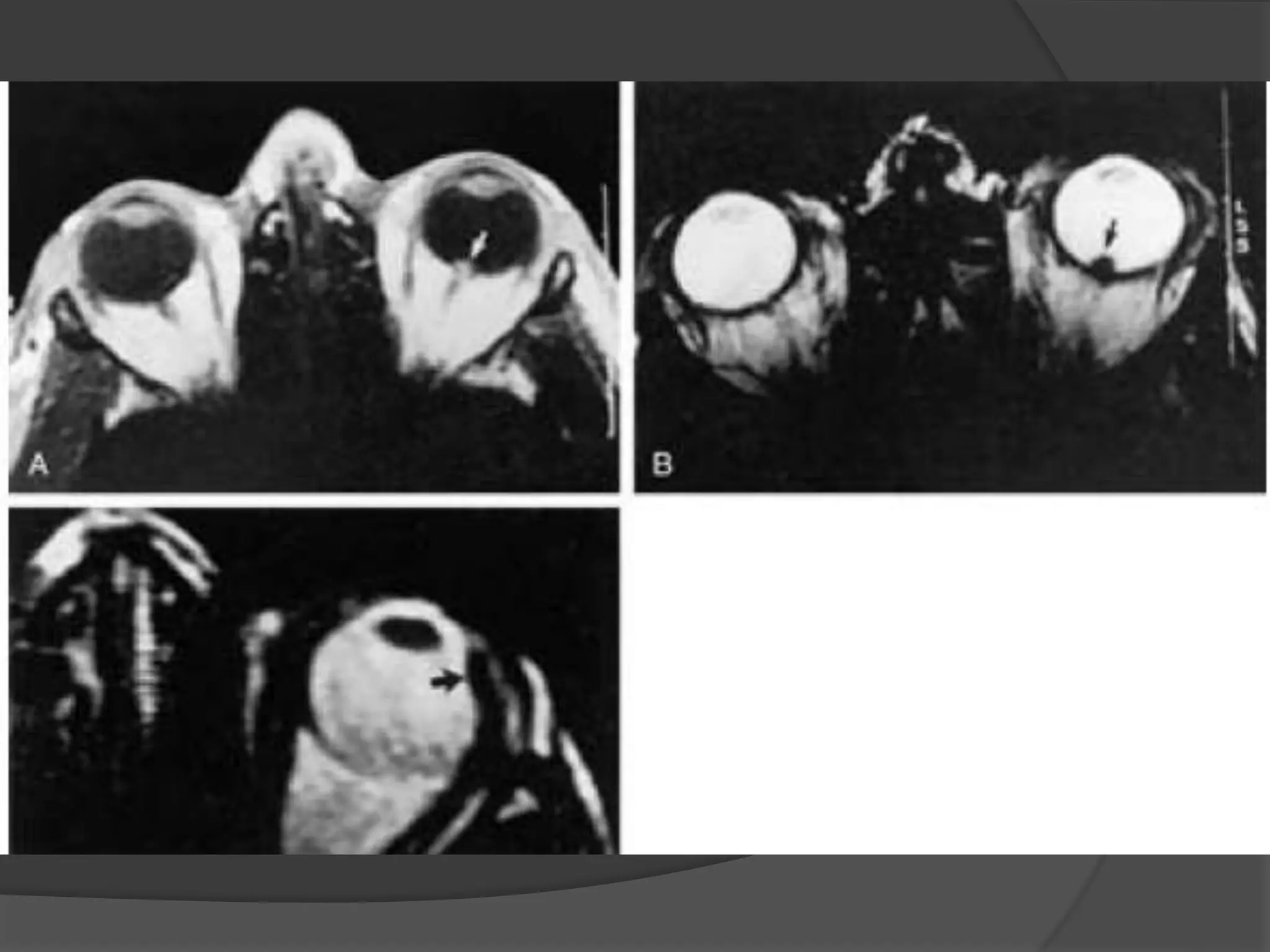
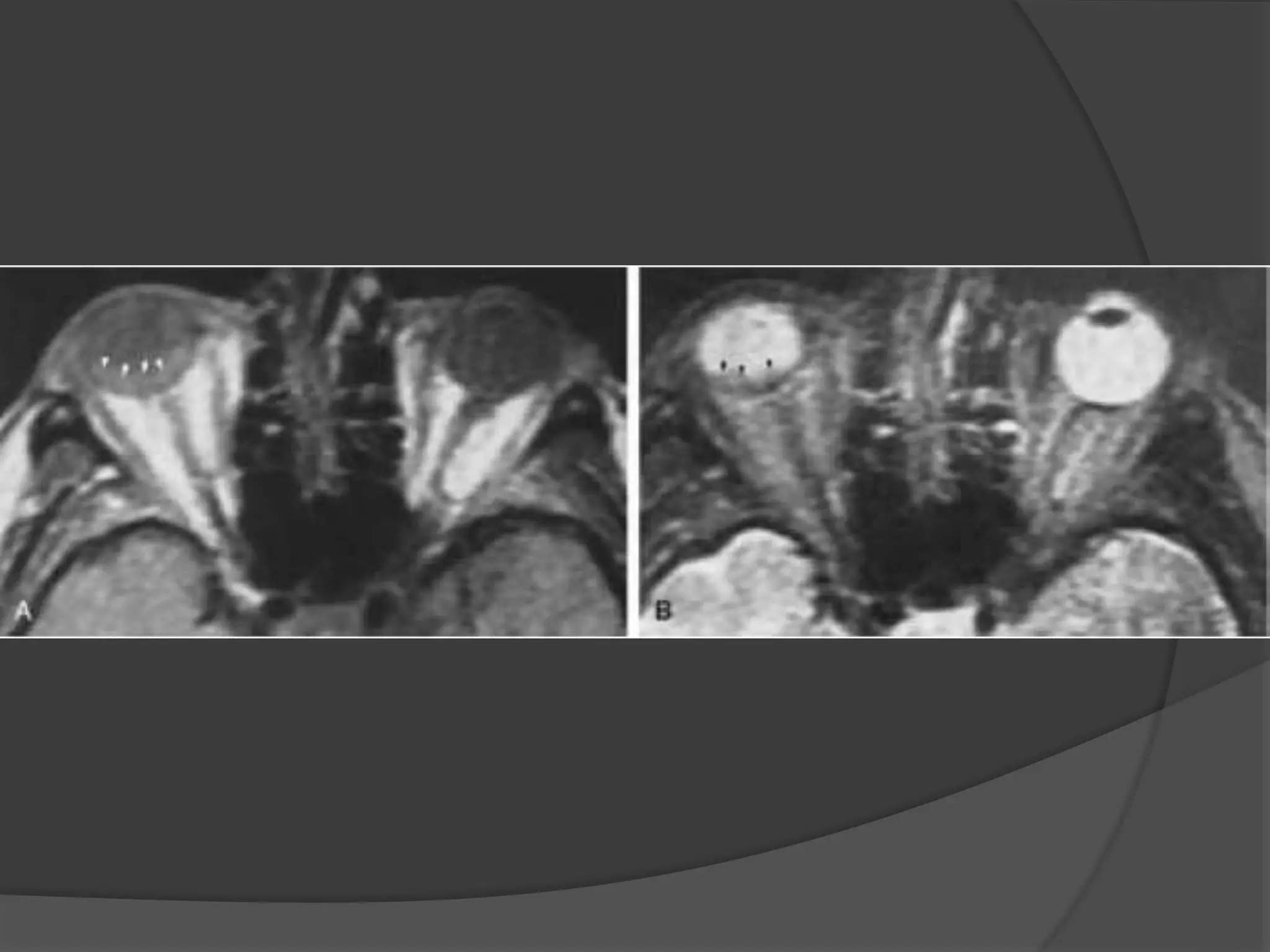
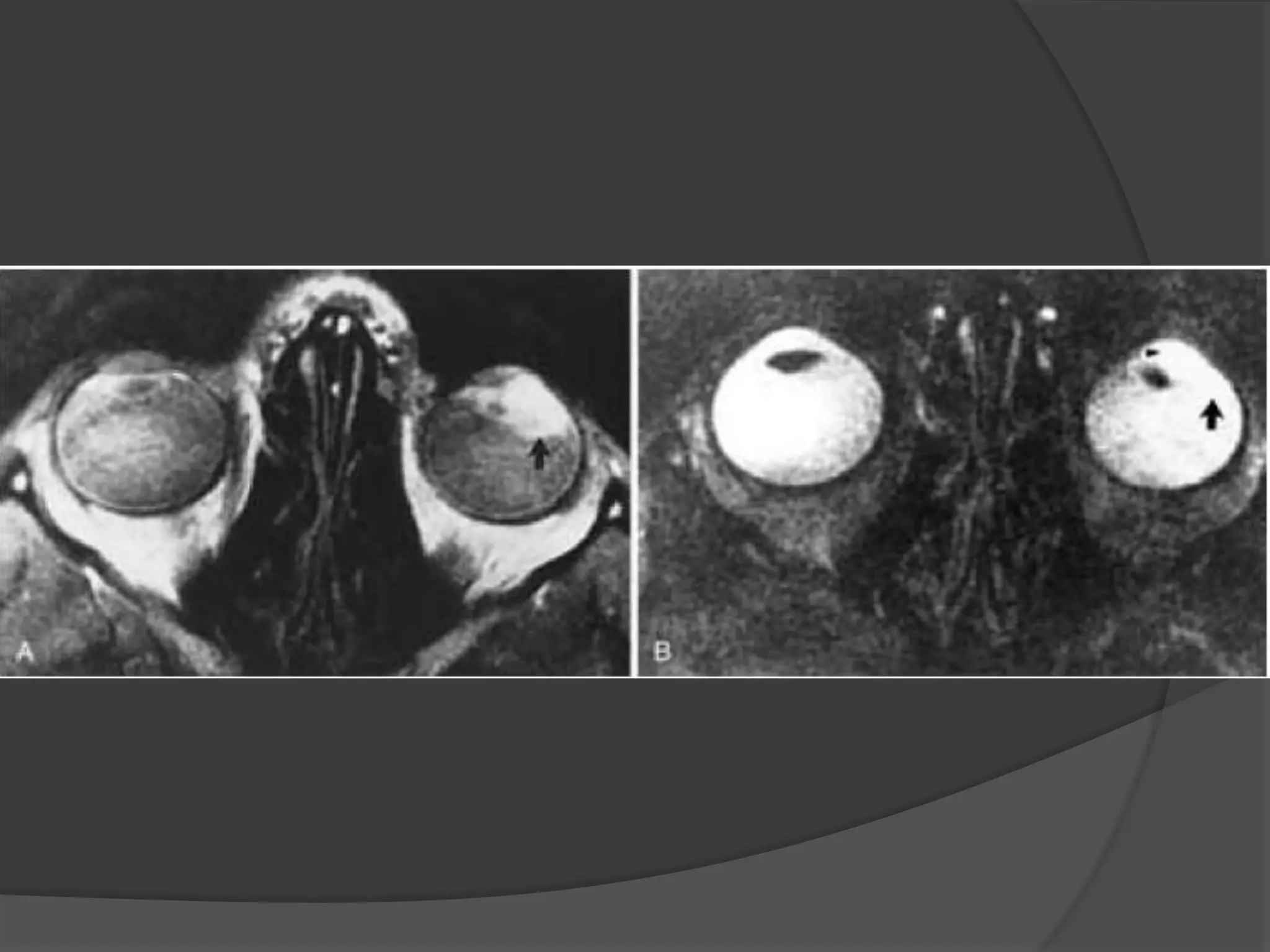
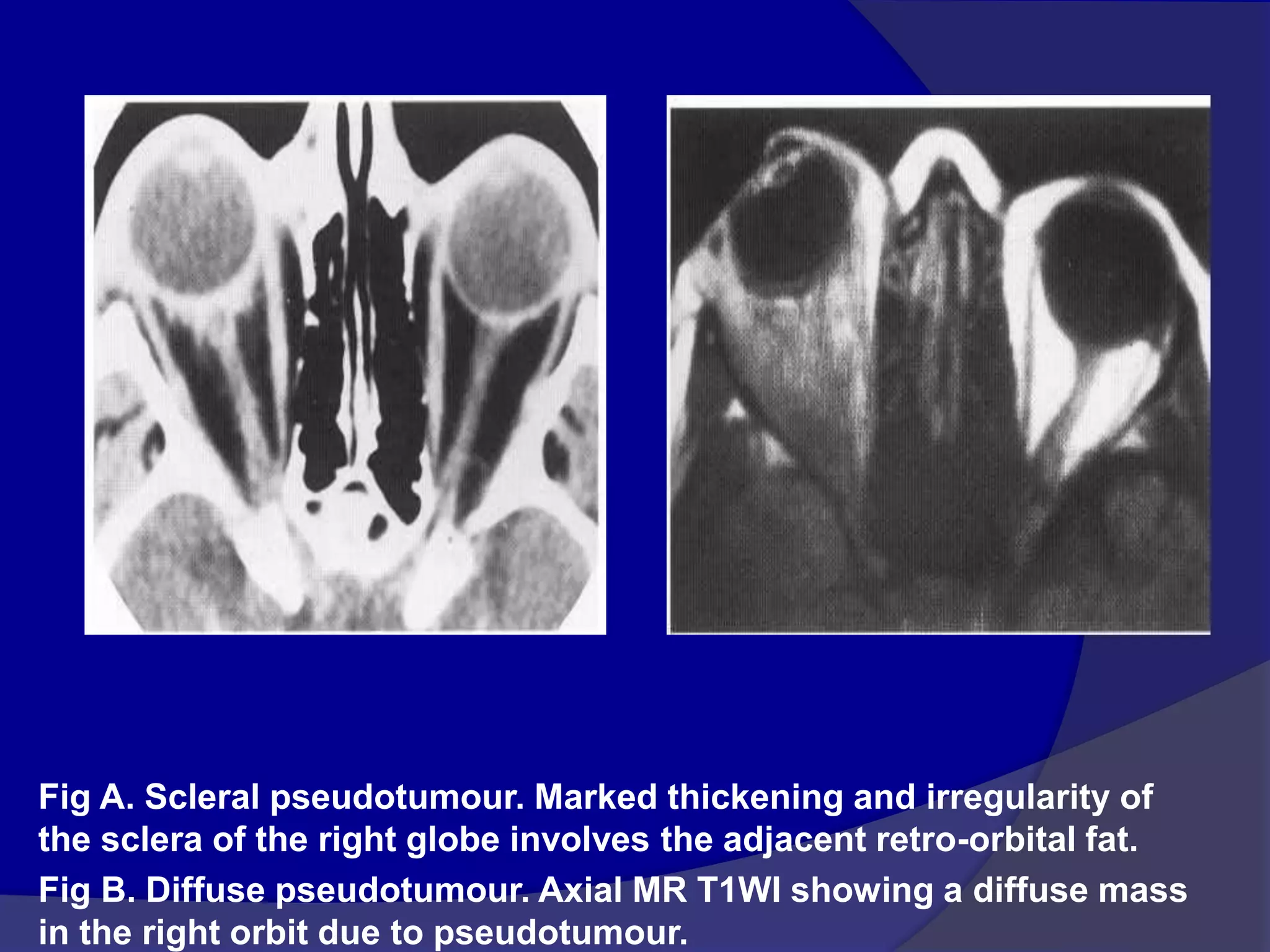
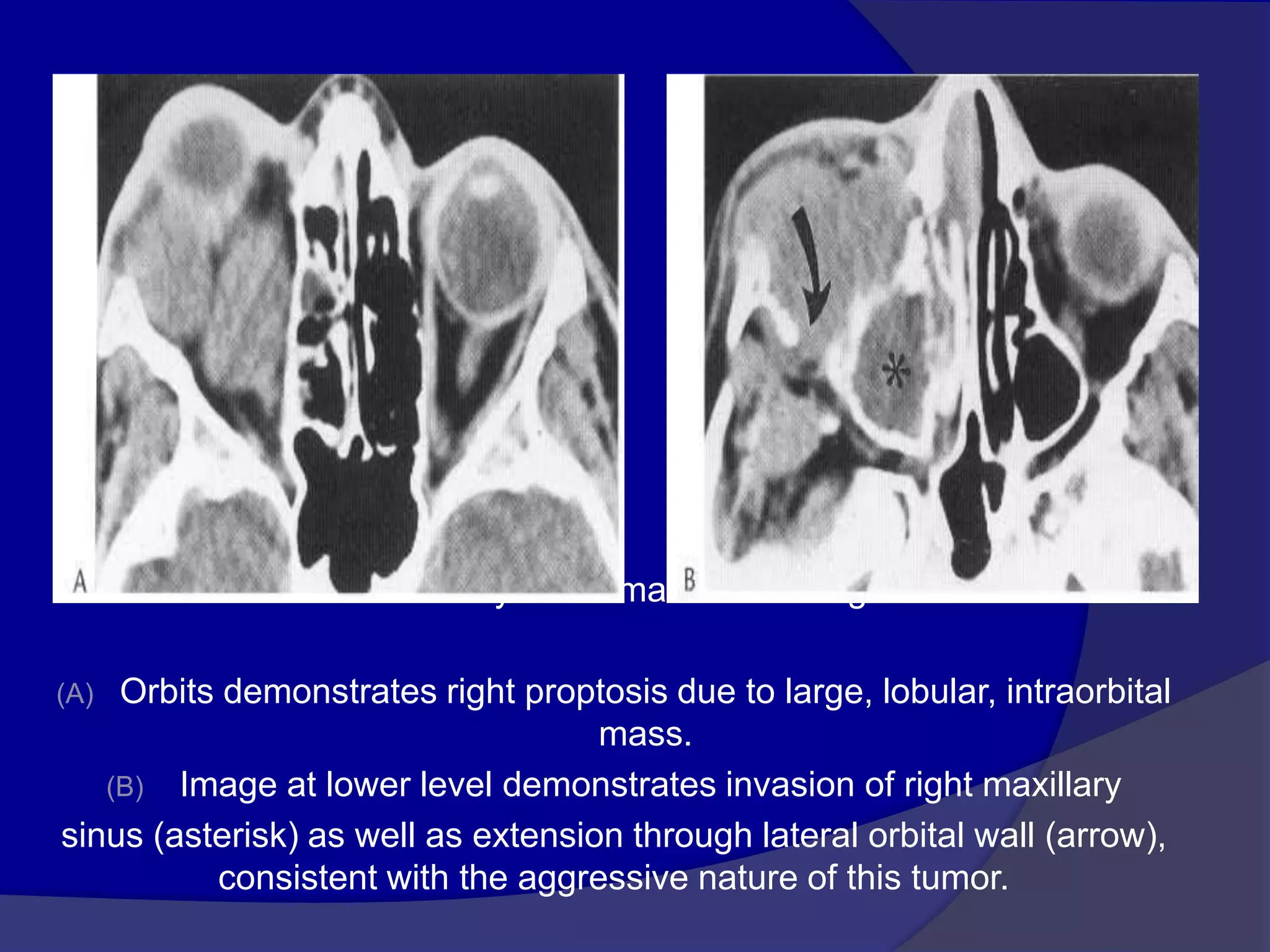
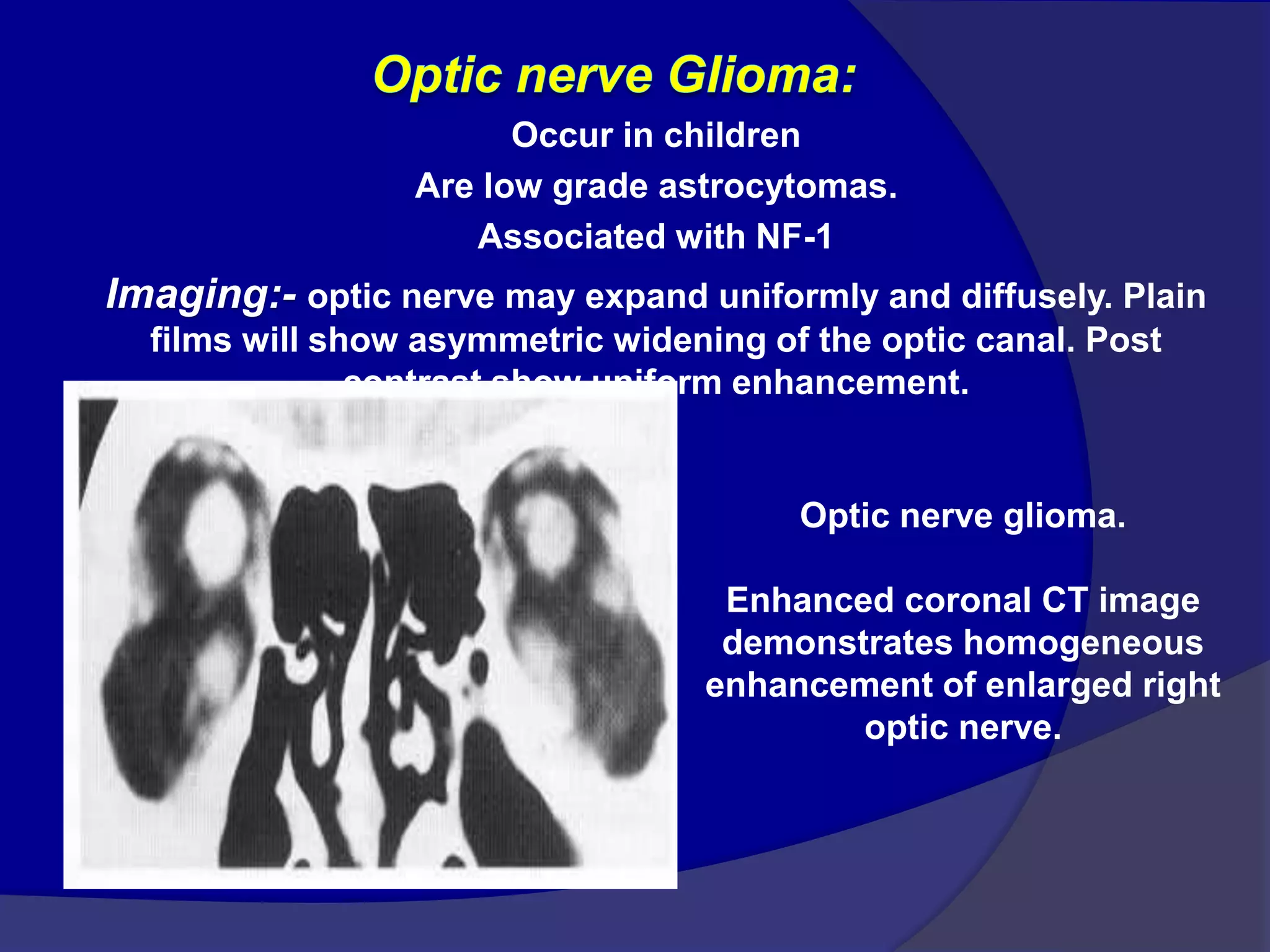
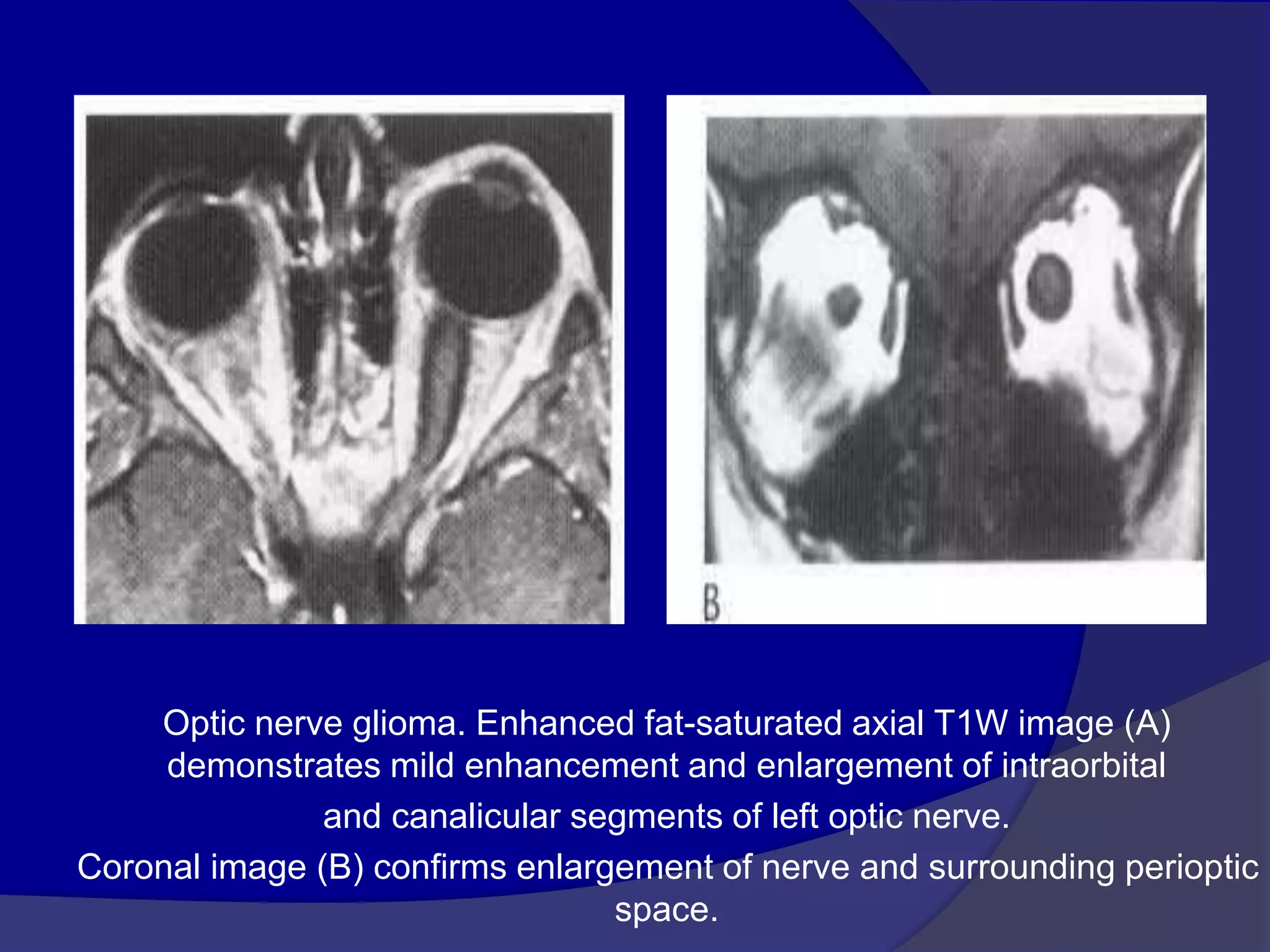
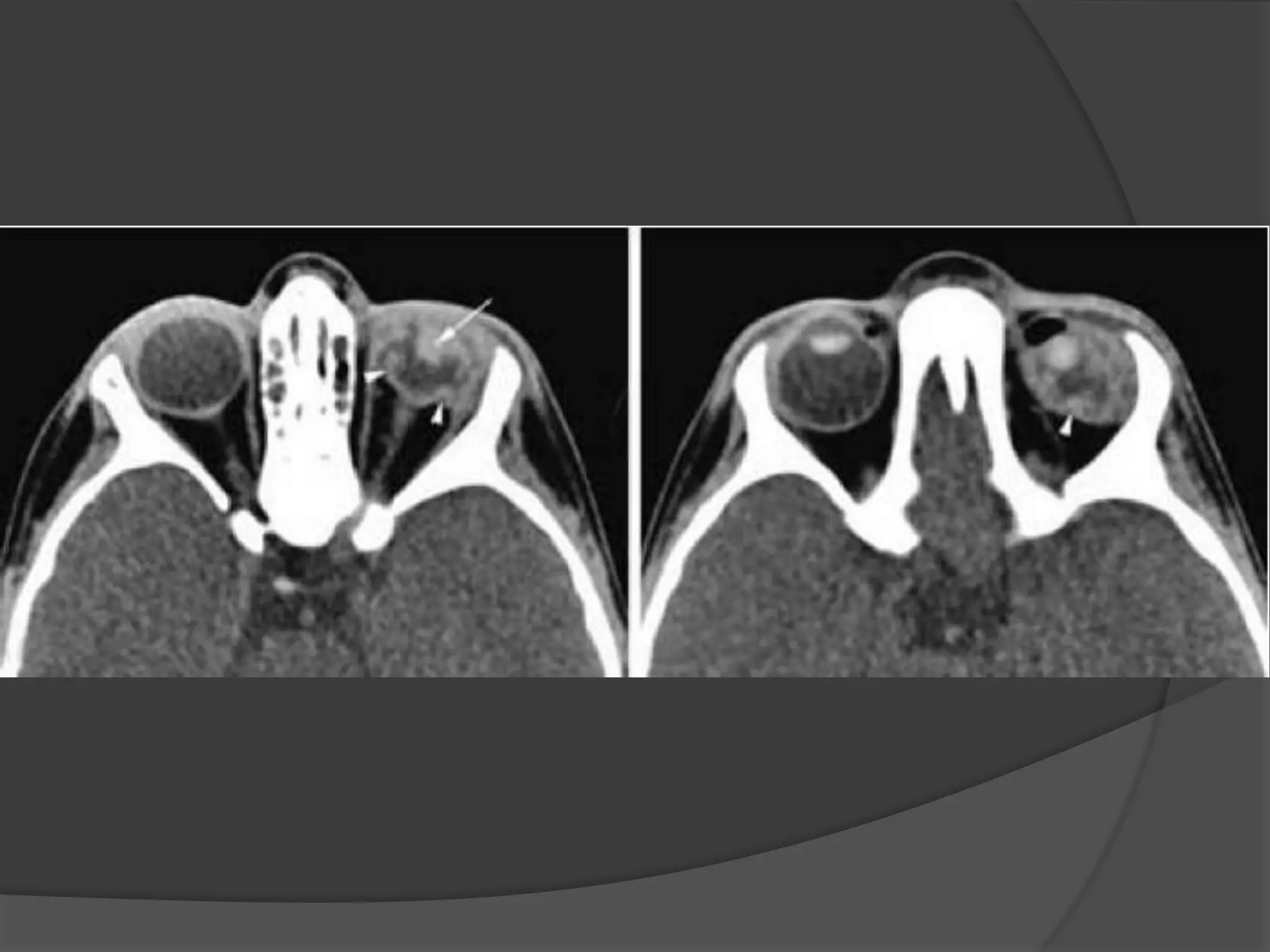
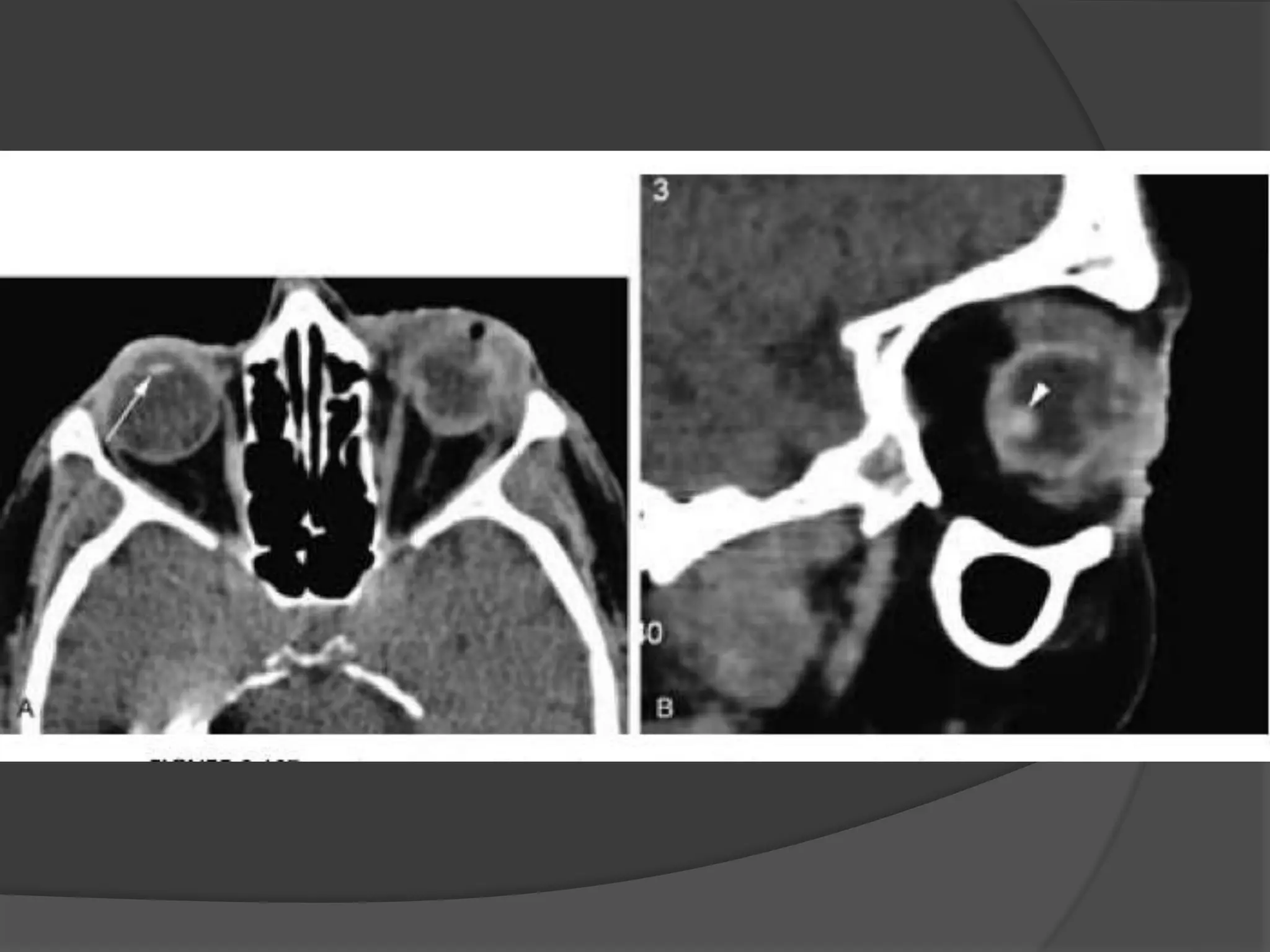
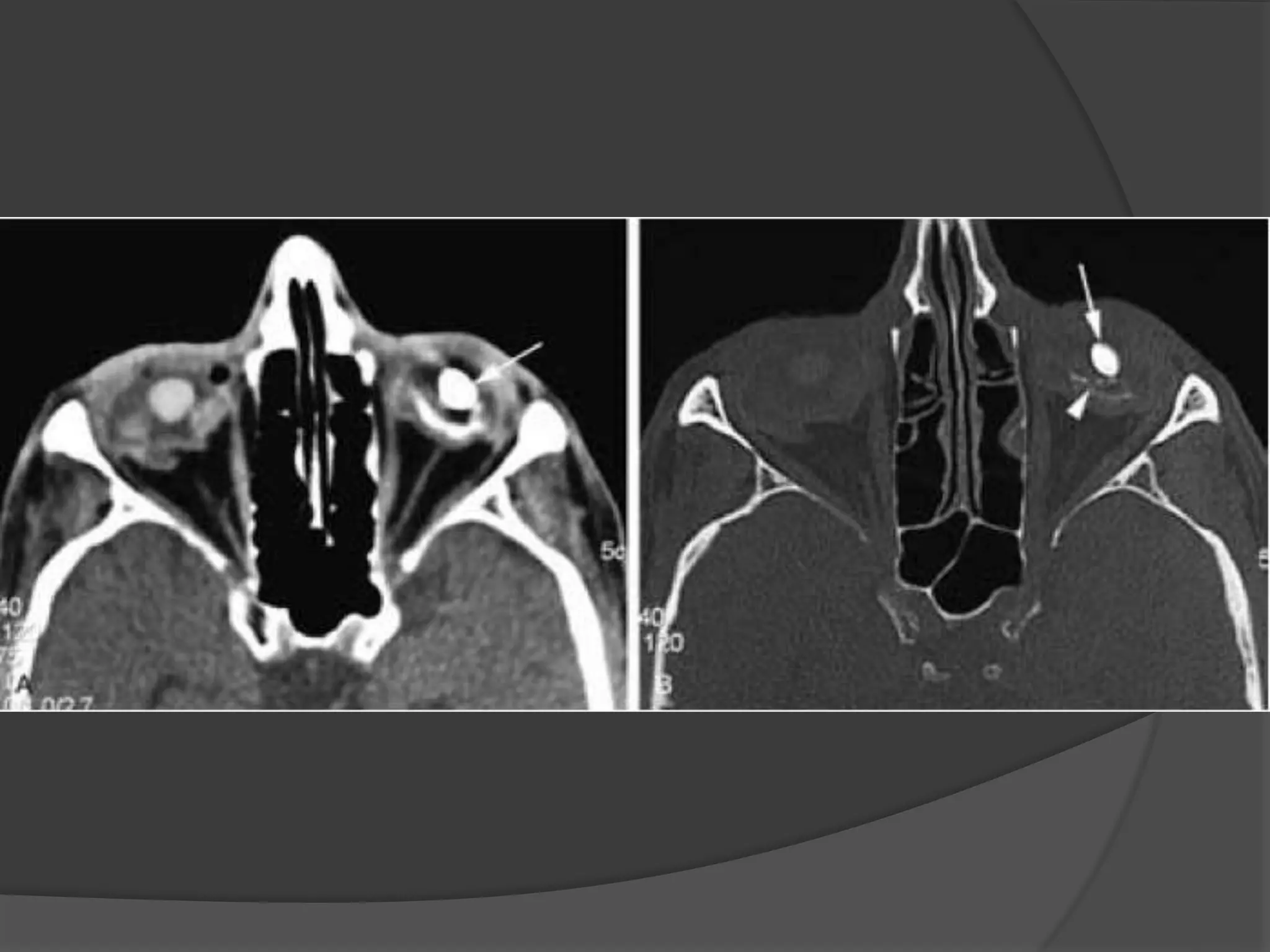
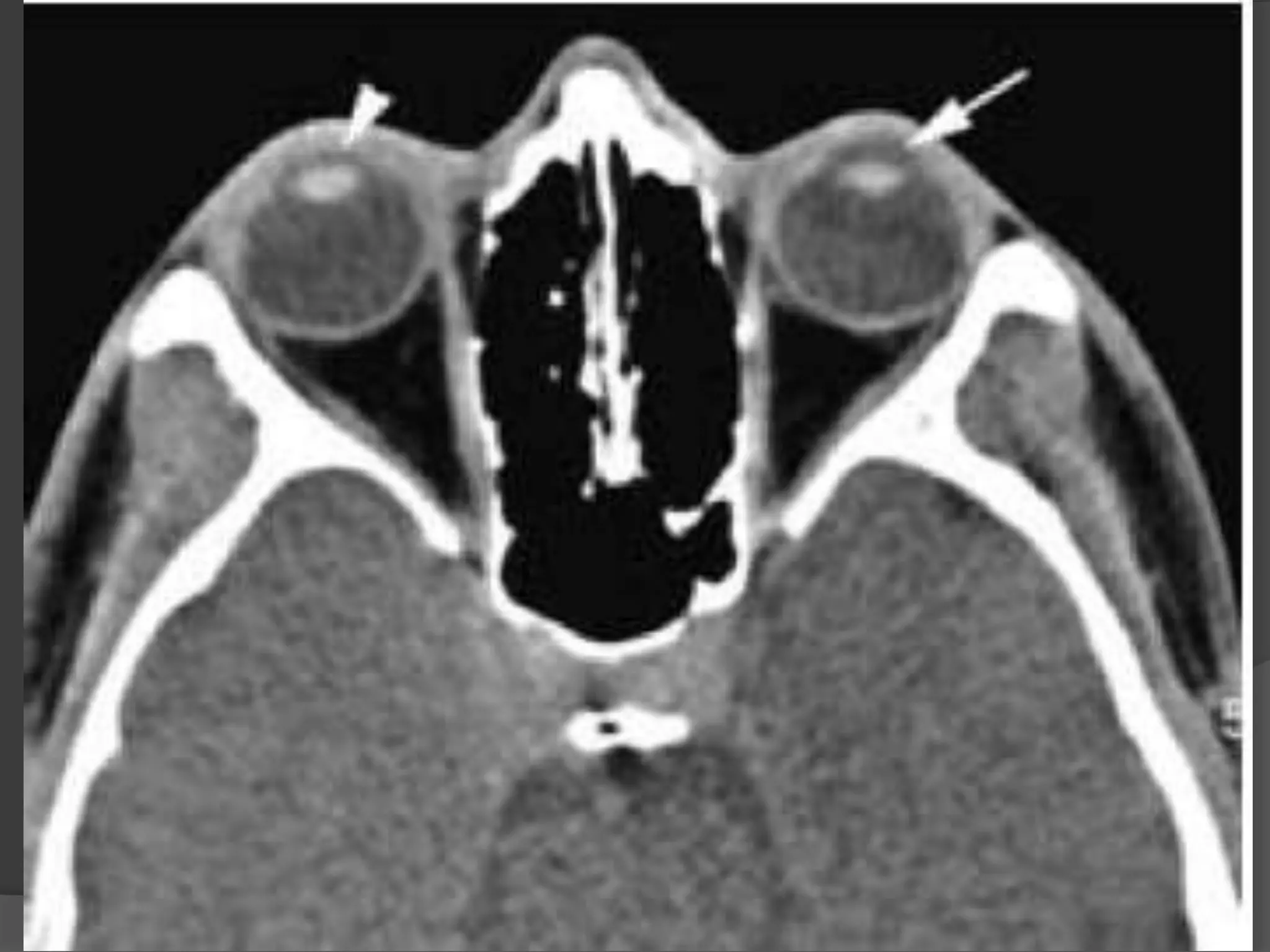
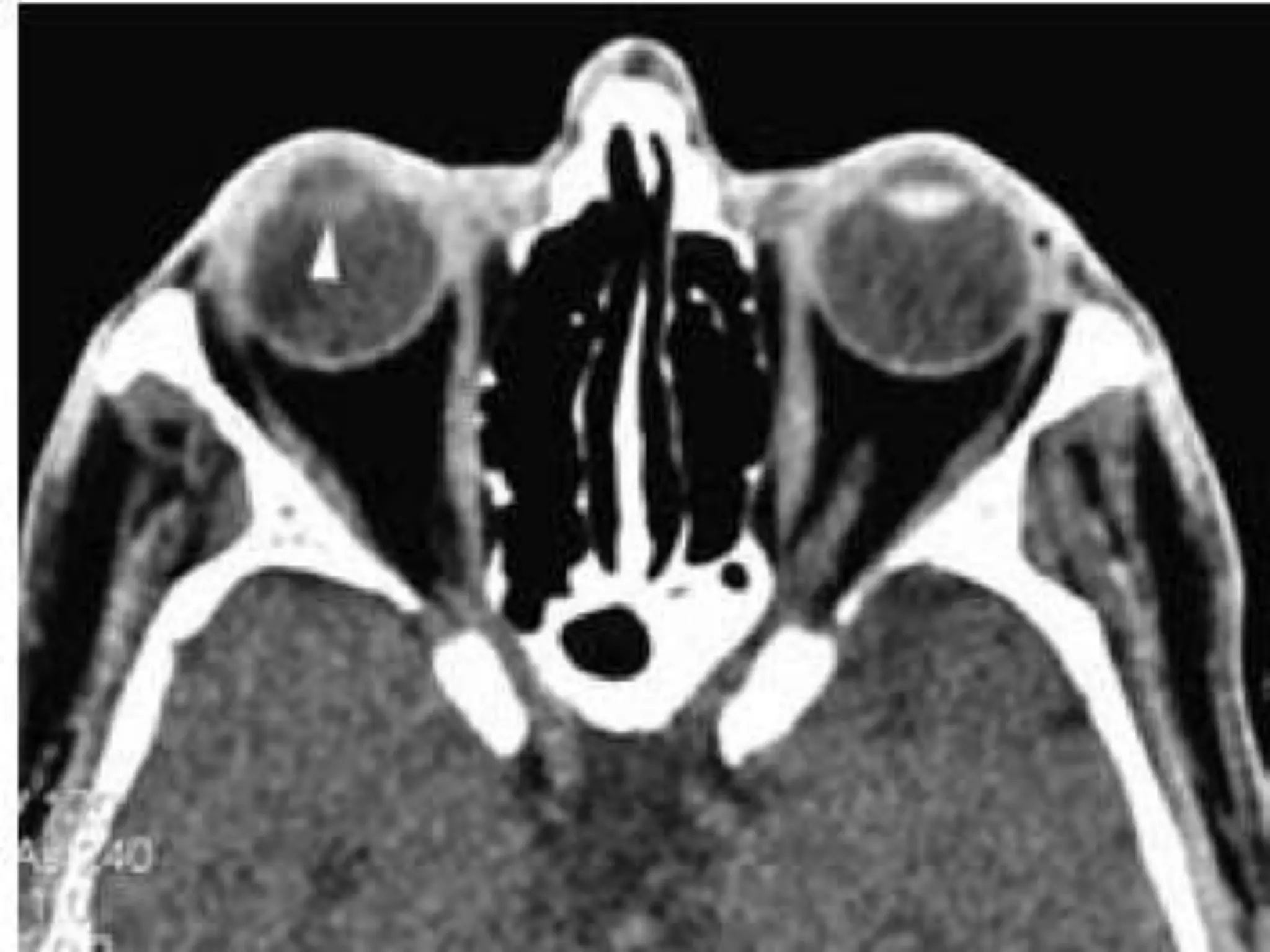
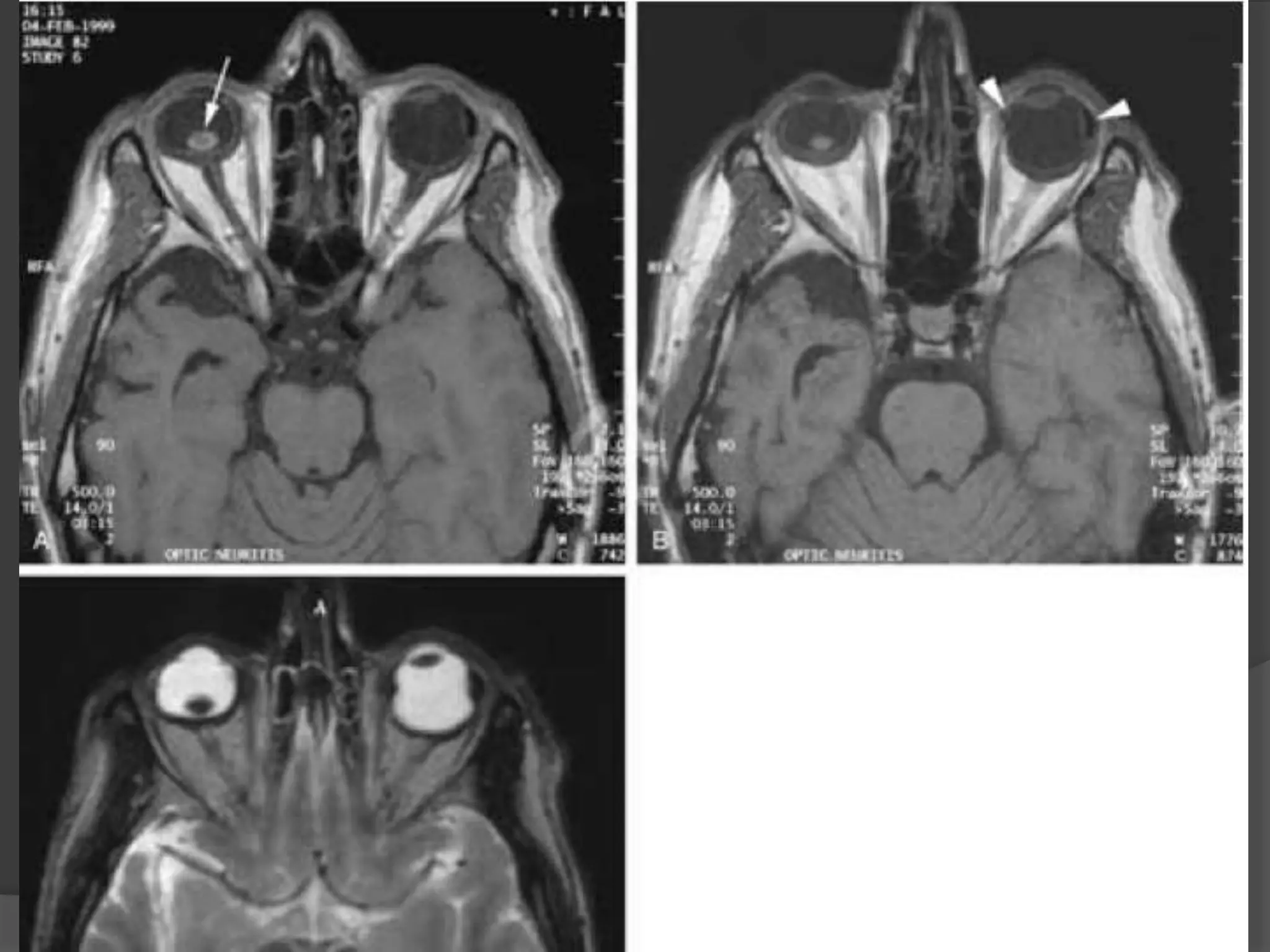
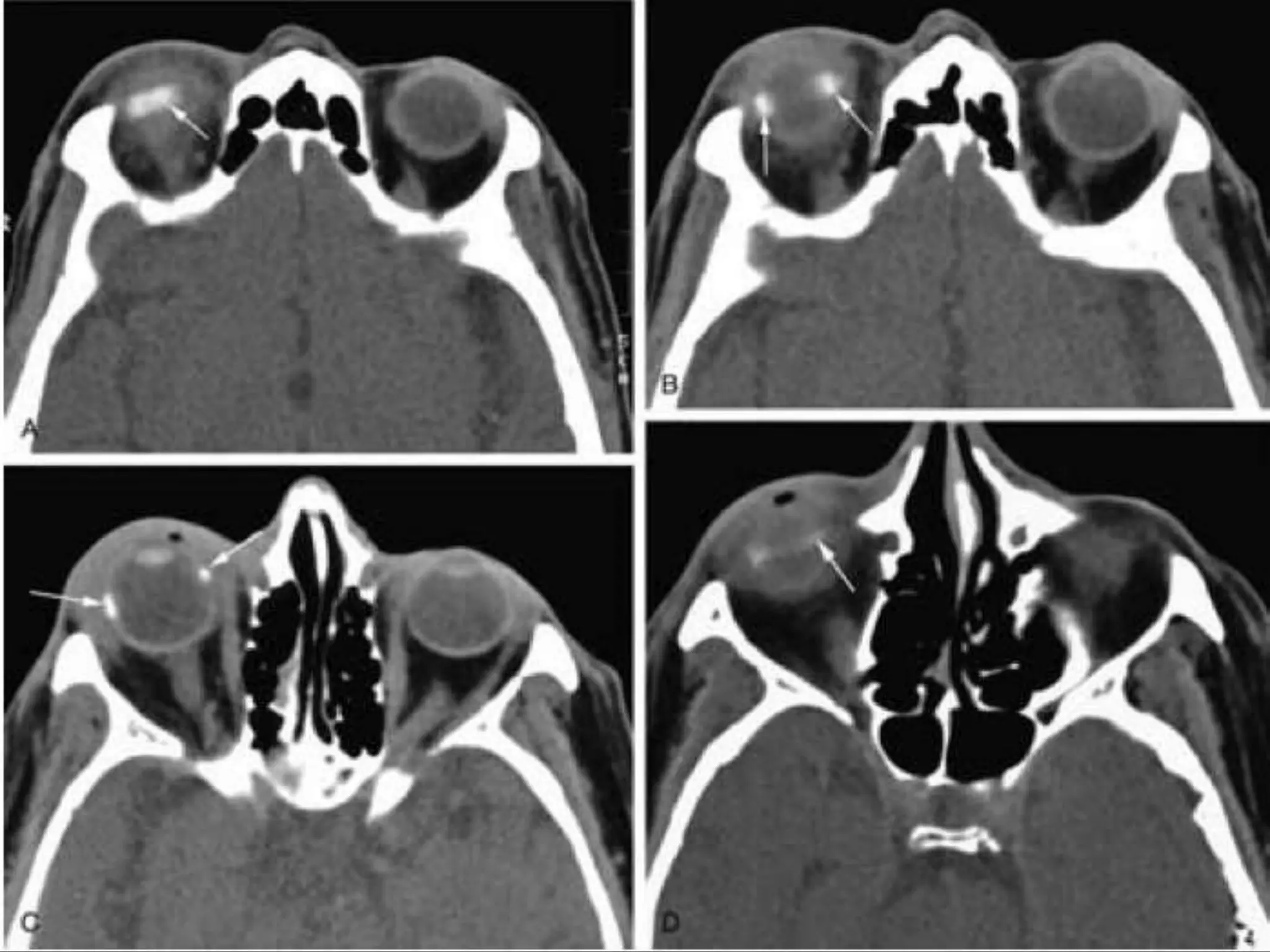
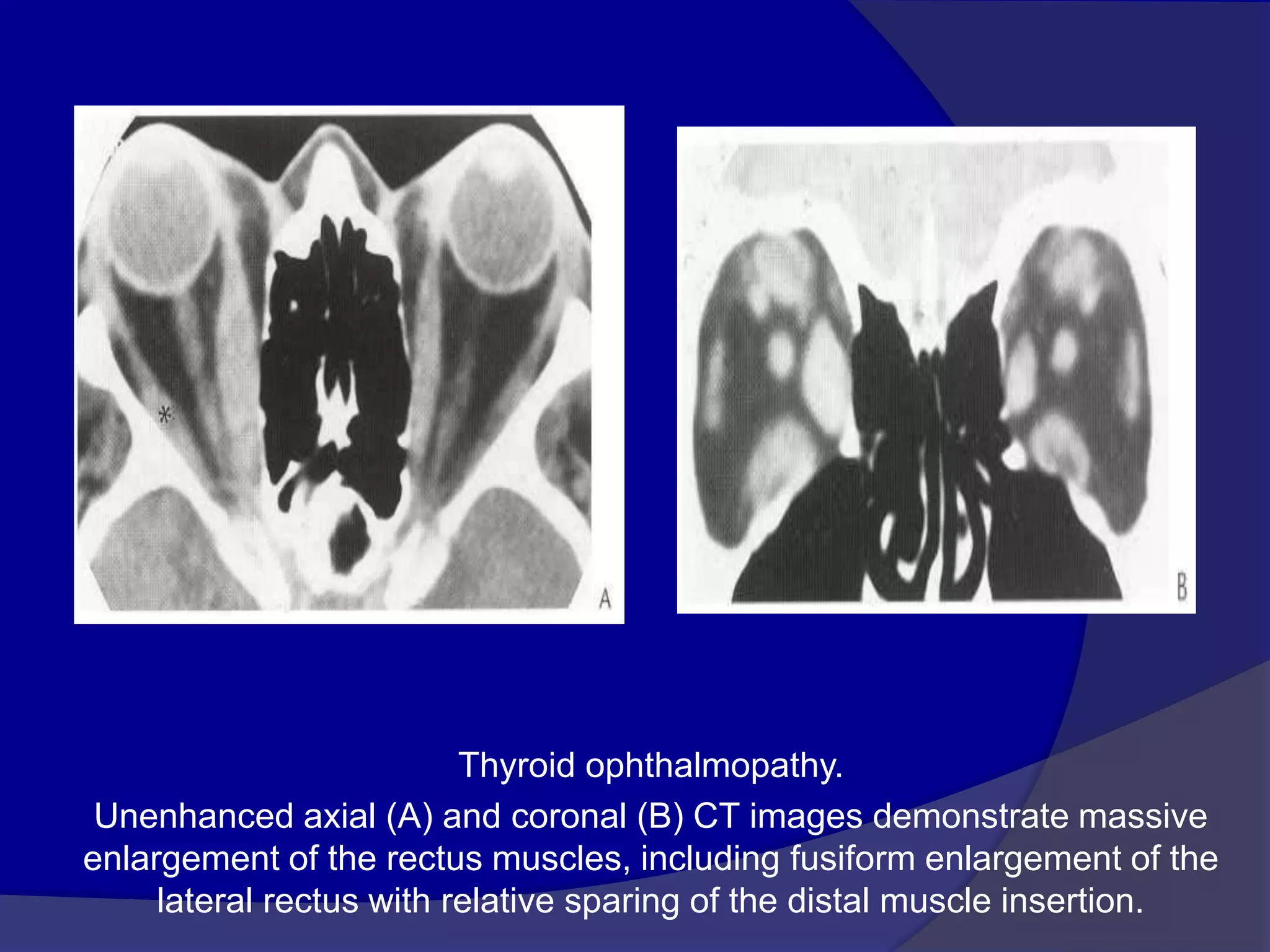
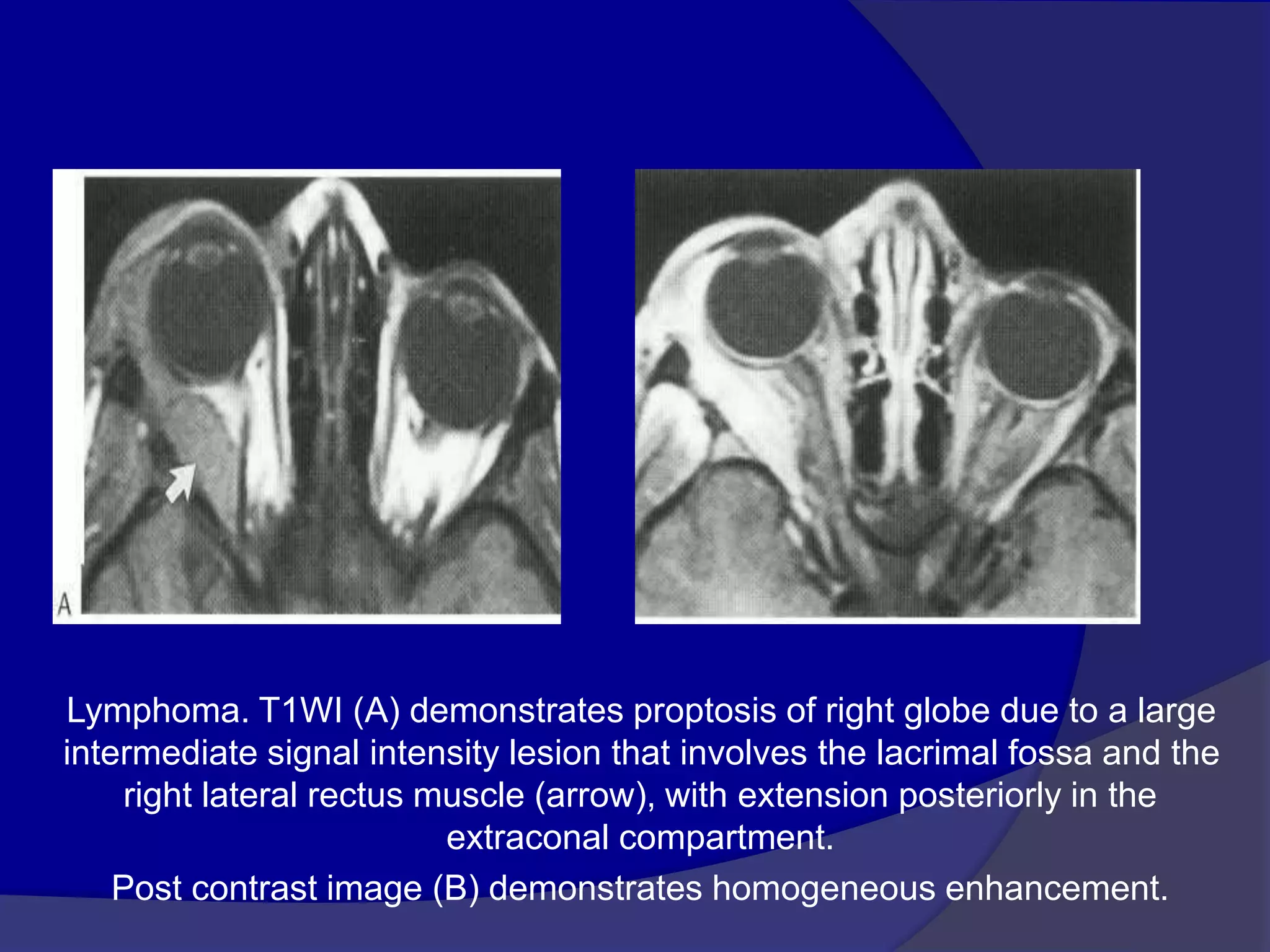
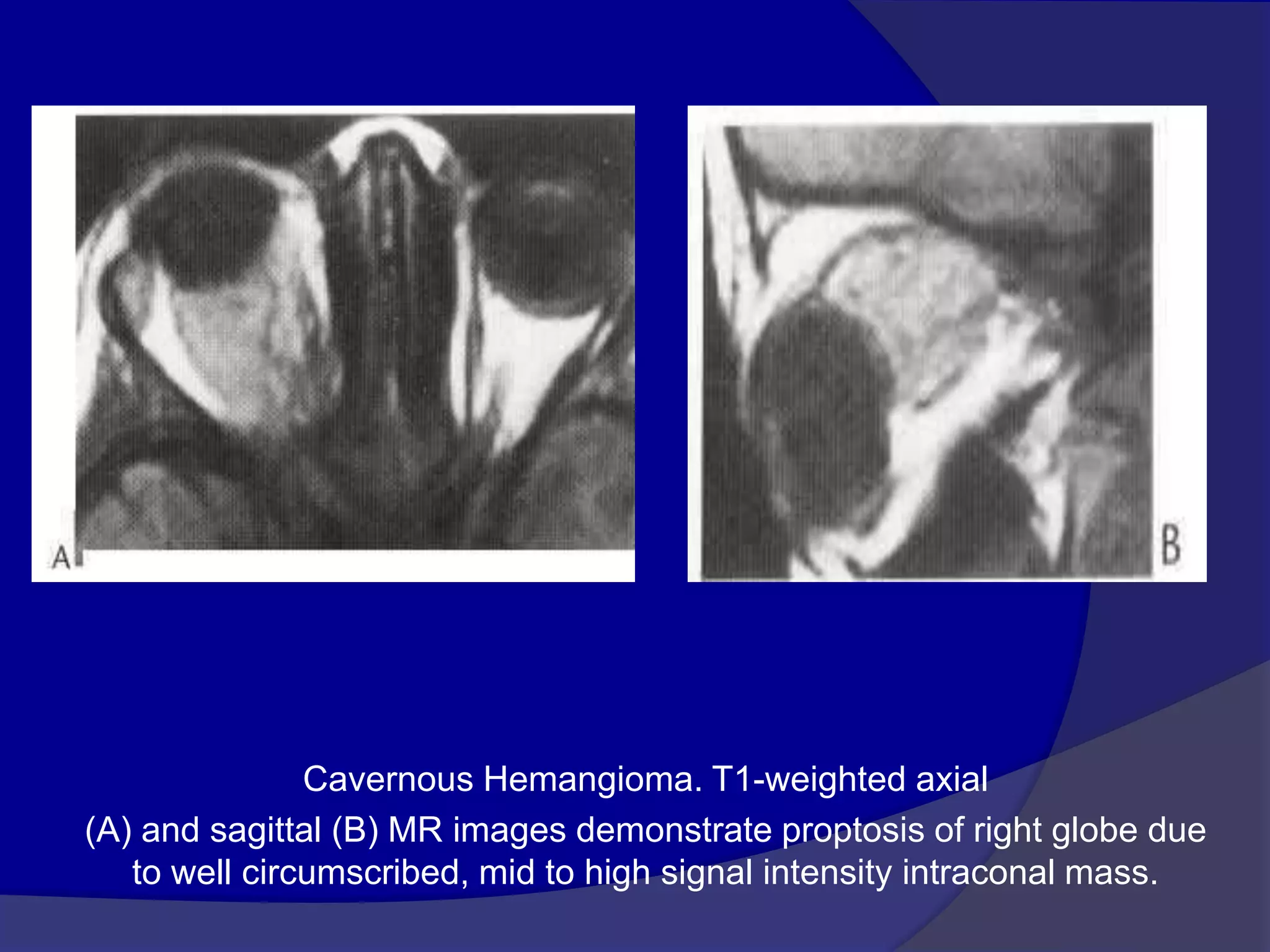
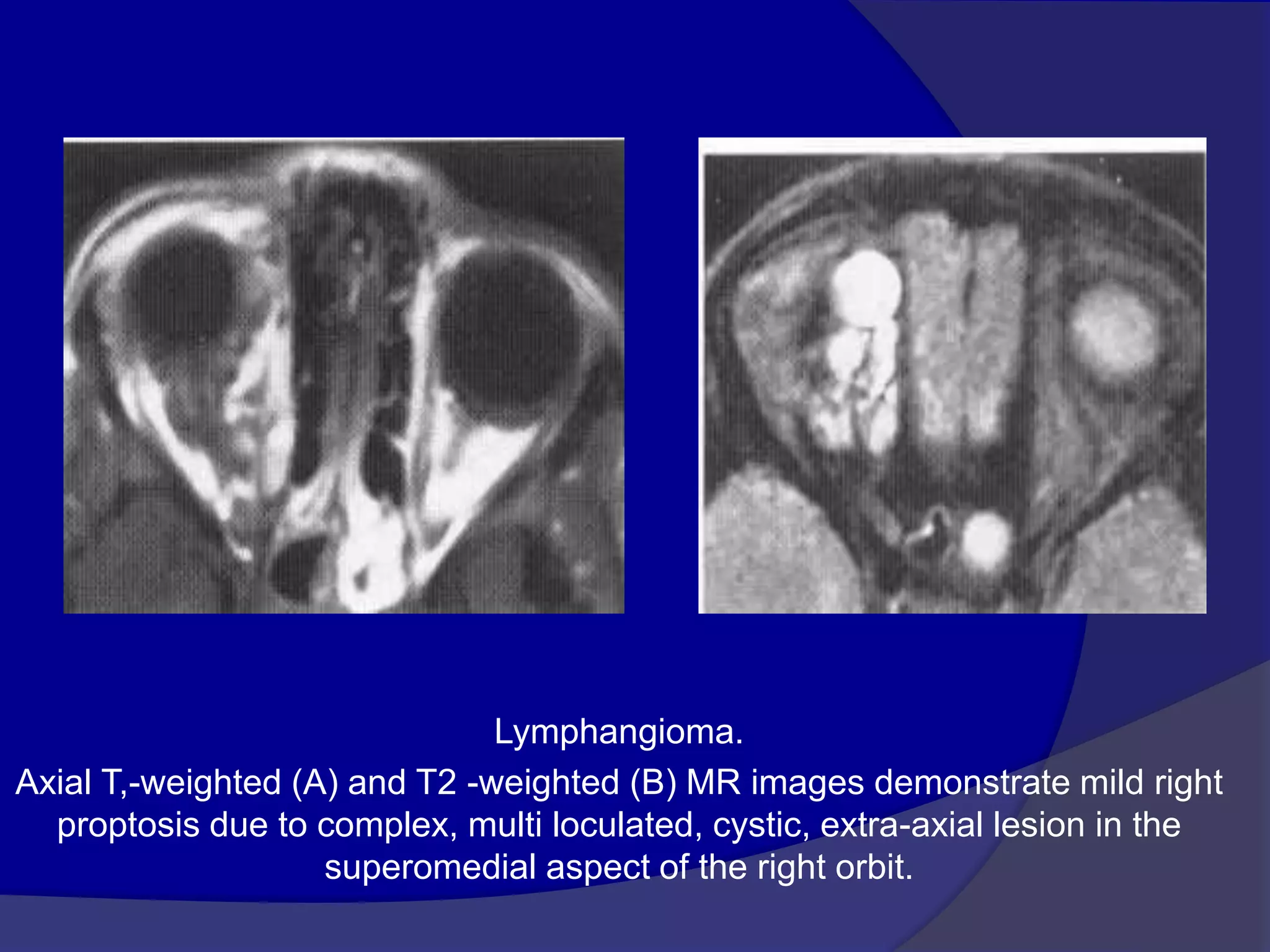
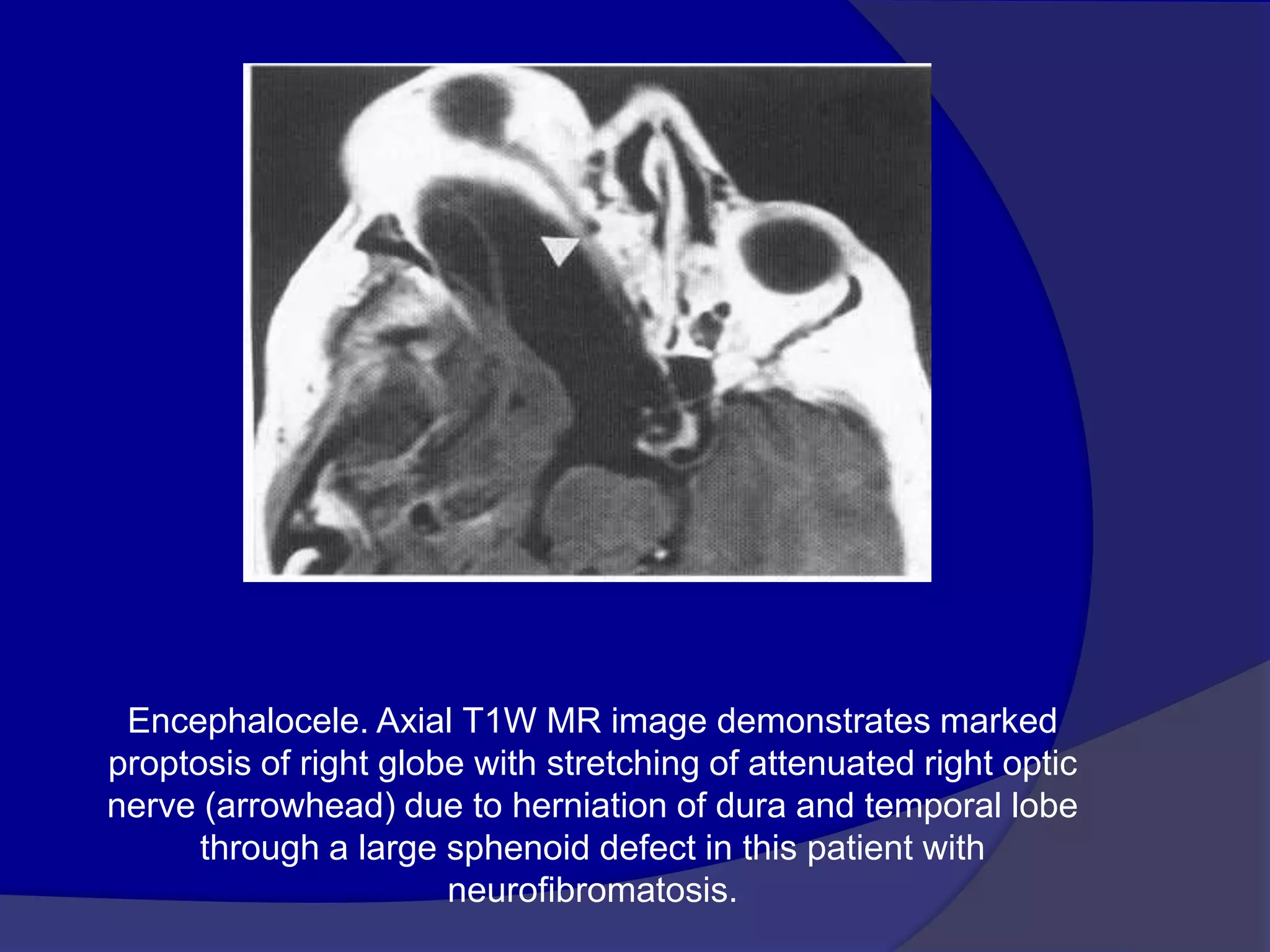
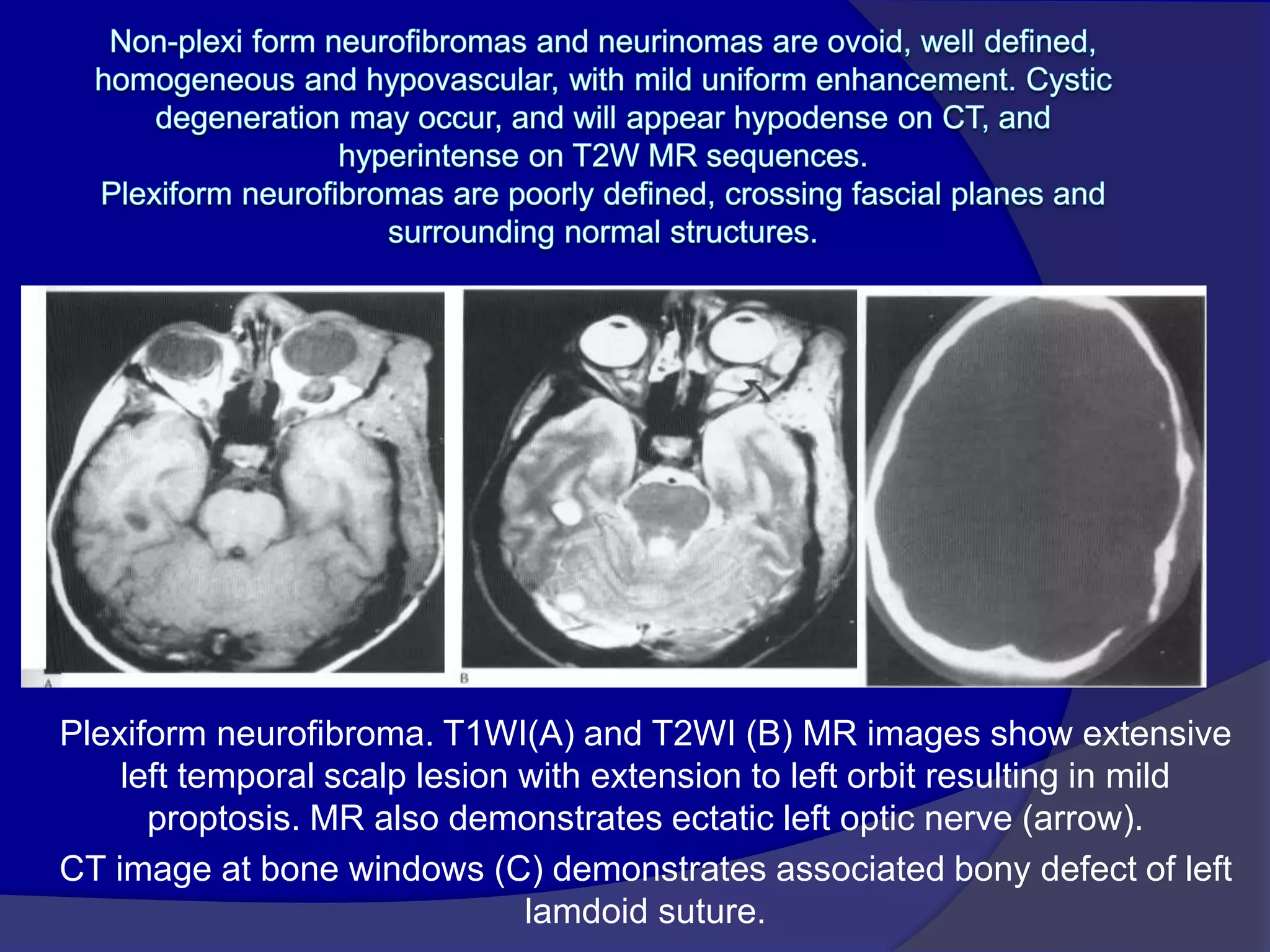
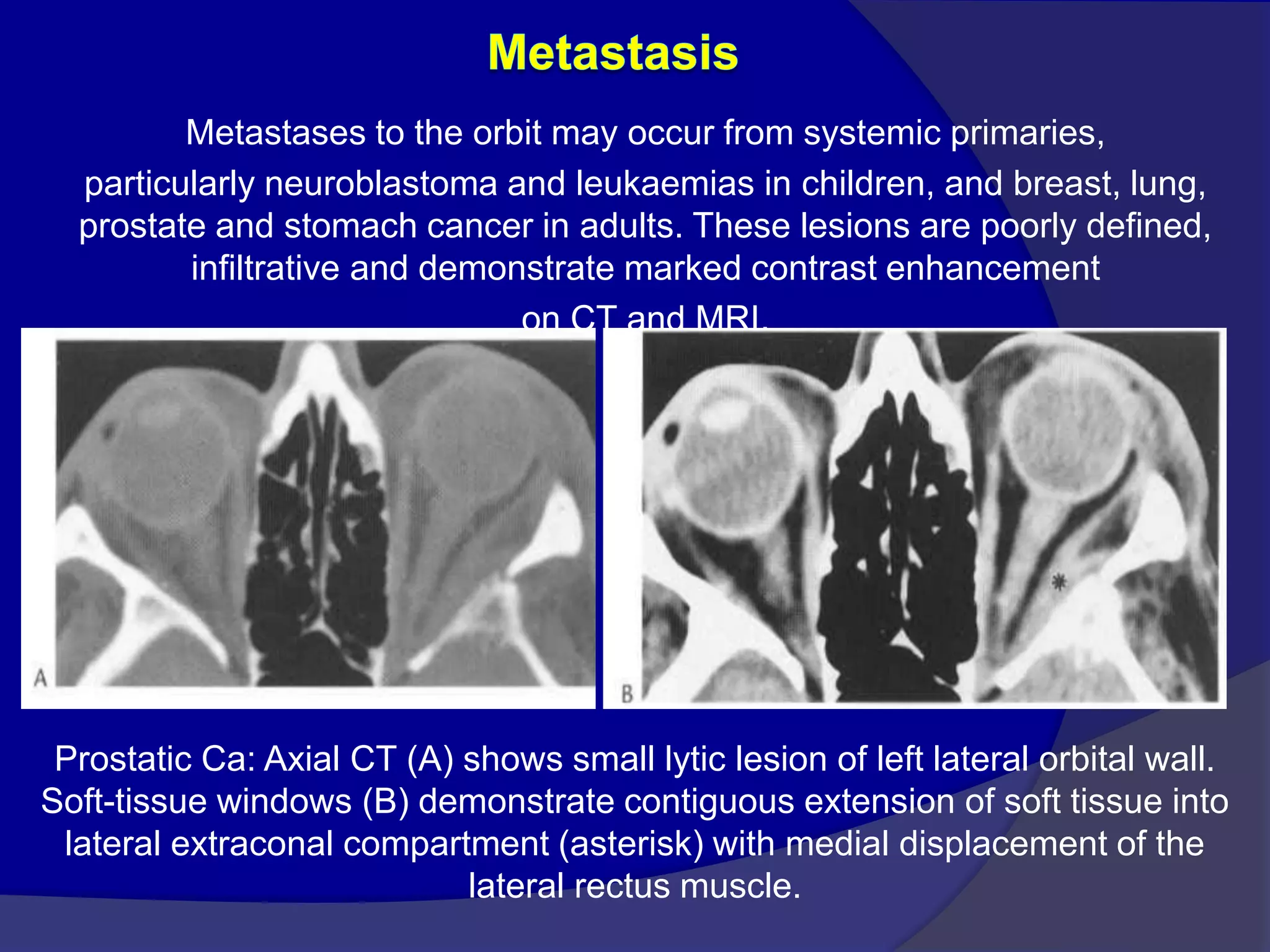
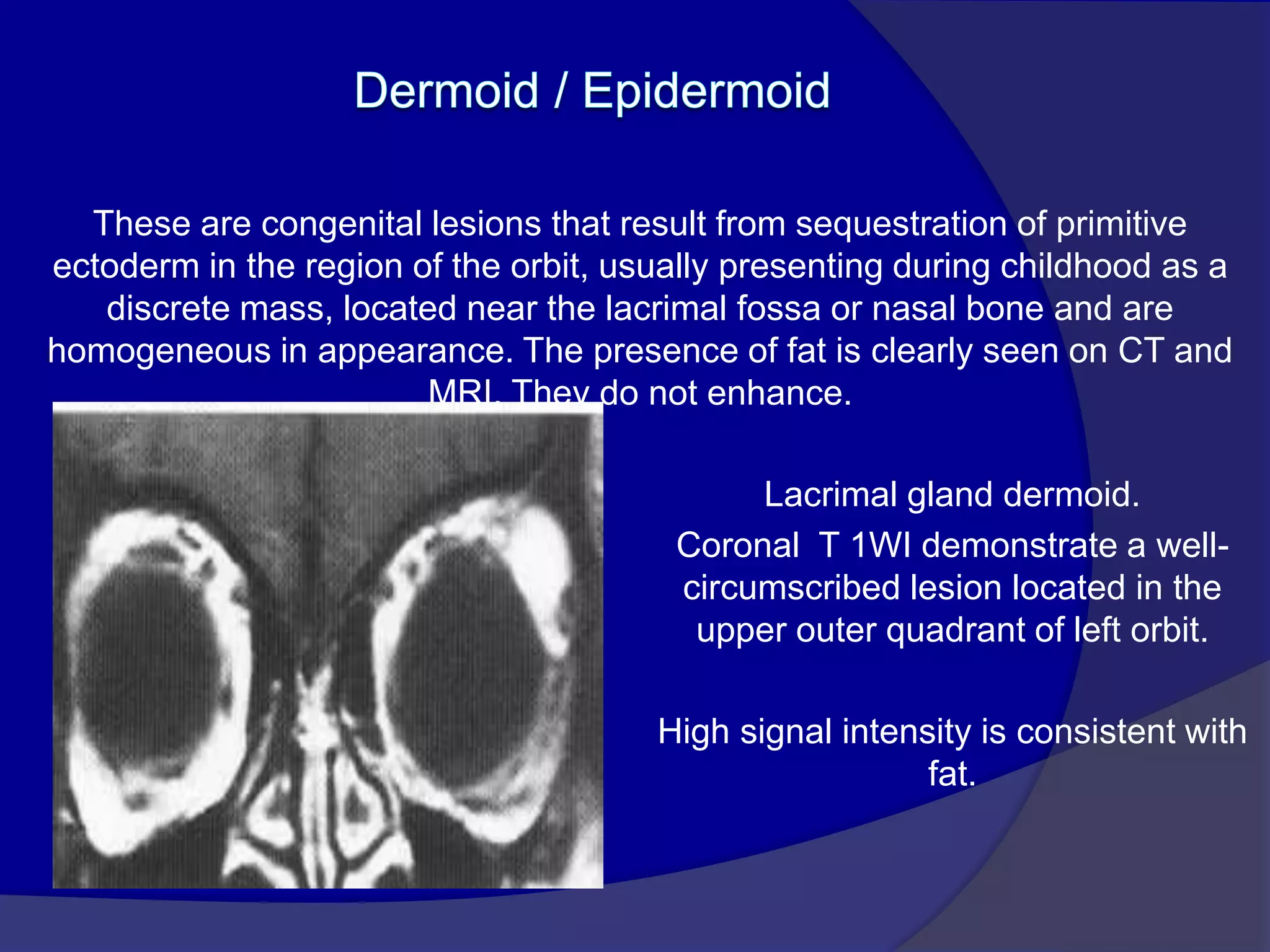
This document summarizes various pathologies that can affect the eye and orbit. It discusses congenital anomalies, infections and inflammations, tumors, trauma, and miscellaneous conditions. For each condition, it provides a brief description and highlights relevant imaging findings on modalities such as CT, MRI, and plain films. Key features that help characterize many lesions include enhancement pattern, presence of calcification, and signal characteristics on different MRI sequences.