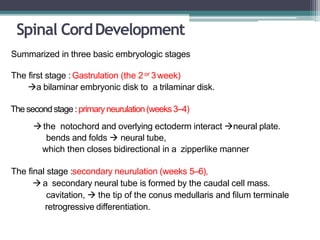
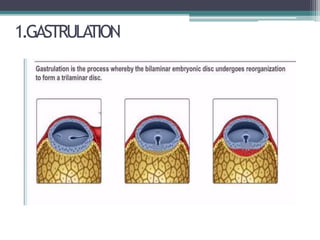
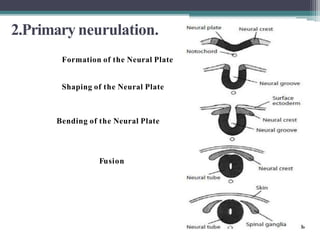
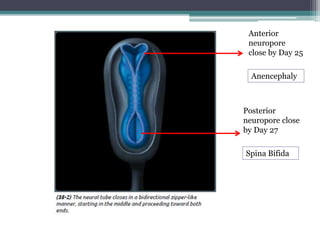
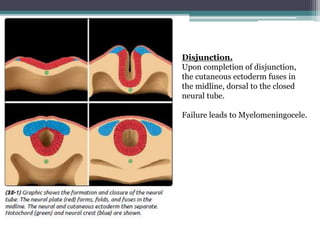
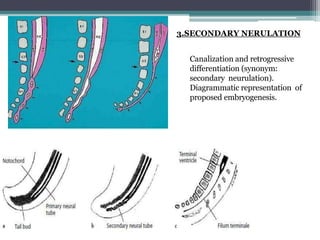
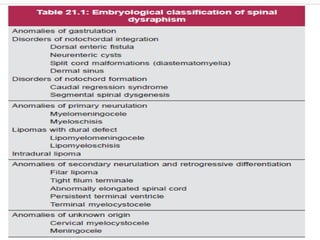
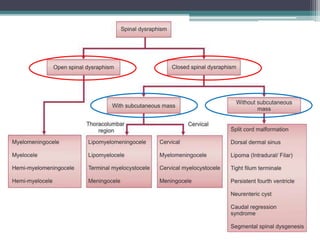
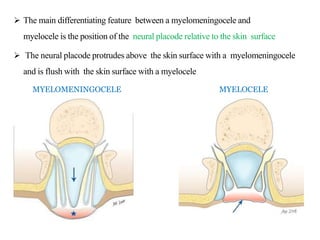
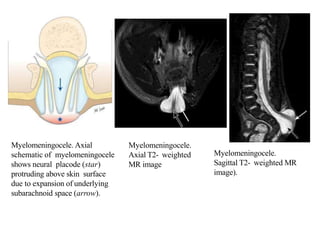
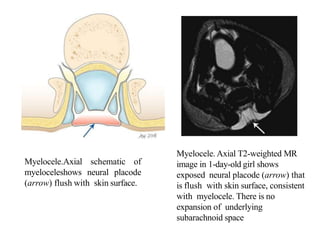
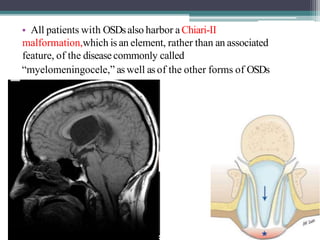
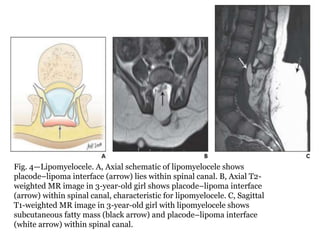
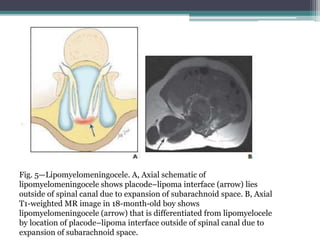
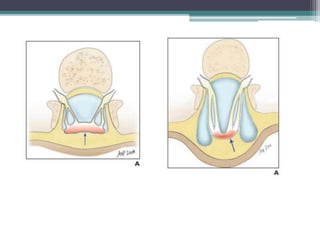
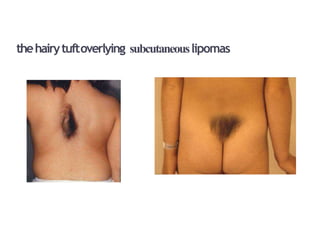
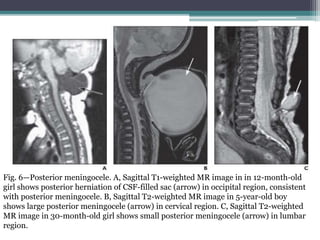
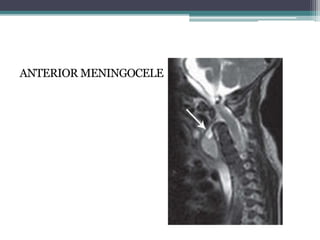
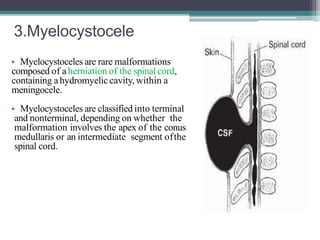
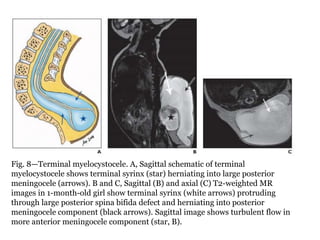
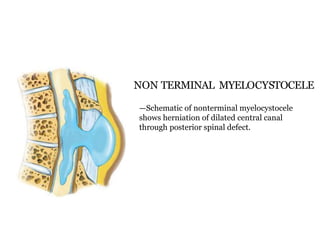
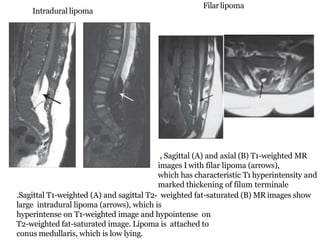
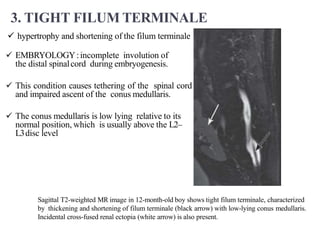
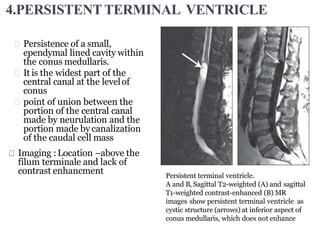
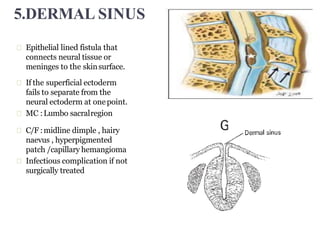
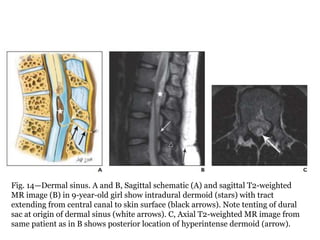
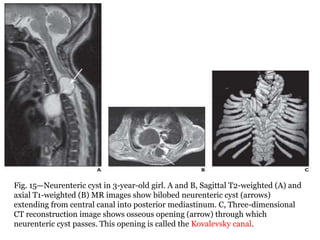
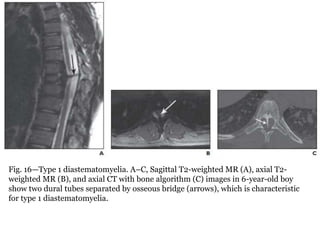
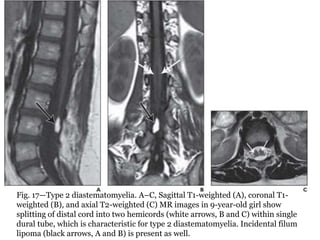
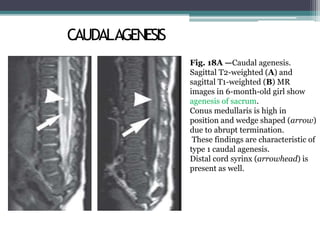
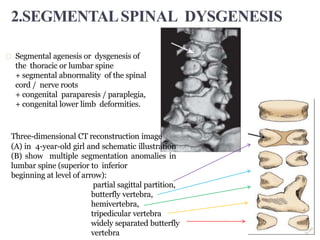
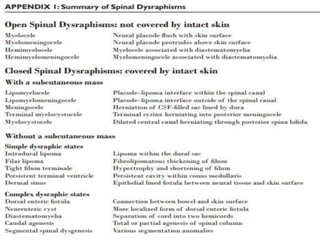
Dr. Pooja discusses various types of spinal dysraphism seen on imaging. She describes open spinal dysraphisms like myelomeningocele and myelocele which involve defects in closure of the neural tube. Closed spinal dysraphisms include lipomas, meningoceles, myelocystoceles, tight filum terminale, and dermal sinuses. Complex dysraphic states arise from disorders of midline notochordal development and include dorsal enteric fistulas, neurenteric cysts, and diastematomyelia where the spinal cord is split. Imaging plays a key role in characterizing these lesions preoperatively.