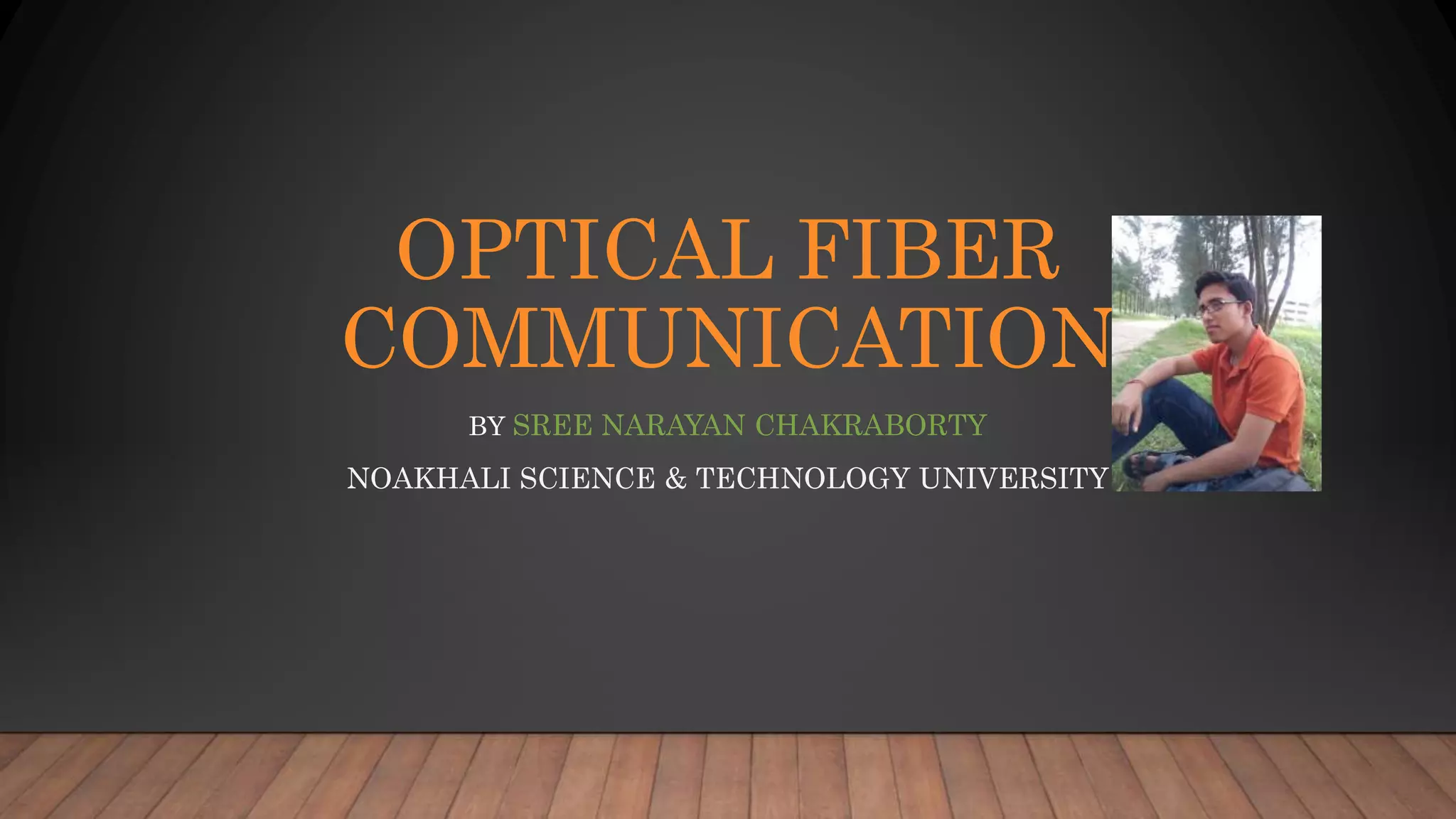
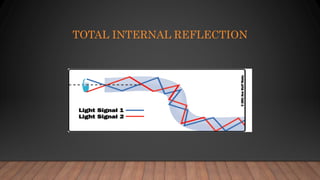
Optical fiber communication uses glass or plastic fibers to transmit light signals for communication over long distances. Light propagates down the fiber core through total internal reflection. Optical fibers have advantages over copper cables like higher bandwidth, lighter weight, and immunity to electromagnetic interference. There are two main types of optical fibers - single-mode fibers for long distances and multi-mode for local networks. Optical fiber communication systems have enabled modern telecommunications infrastructure.