The document summarizes free space optical communication (FSO). It discusses the operation of FSO links, their advantages over fiber and microwave links, and applications. The key points are:
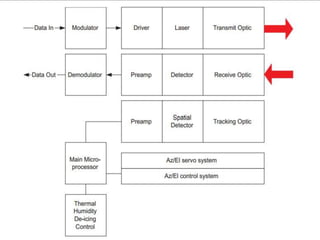
1. An FSO link consists of a transmitter, receiver, and tracking system to direct light beams between nodes. It allows license-free, high-speed connections but is susceptible to weather.
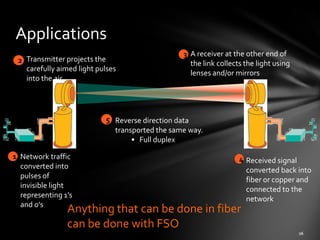
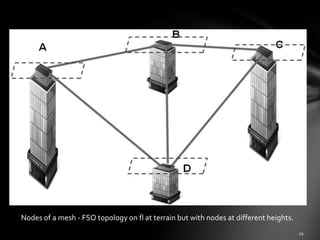
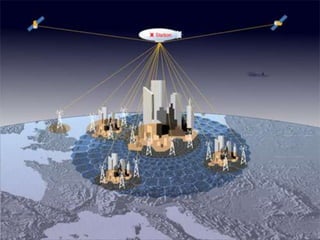
2. Applications include point-to-point links between buildings and potential mesh networks or use on high altitude platforms. Mesh networks provide better coverage but at a higher cost than point-to-point links.
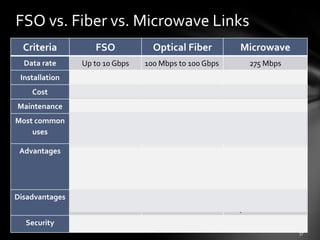
3. Compared to fiber and microwave links, FSO systems have lower costs and power needs but higher data rates and


![Outlines
• Introduction [1]
• Free Space Optical Link Design [2]
• Applications [3]
• FSO vs. Fiber vs. Microwave Links](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespaceopticalcommunication-120621062452-phpapp02/85/Free-space-optical-communication-3-320.jpg)
![Outlines
• Introduction [1]
• Free Space Optical Link Design [2]
• Applications [3]
• FSO vs. Fiber vs. Microwave Links](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespaceopticalcommunication-120621062452-phpapp02/85/Free-space-optical-communication-4-320.jpg)







![Outlines
• Introduction [1]
• Free Space Optical Link Design [2]
• Applications [3]
• FSO vs. Fiber vs. Microwave Links](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespaceopticalcommunication-120621062452-phpapp02/85/Free-space-optical-communication-12-320.jpg)



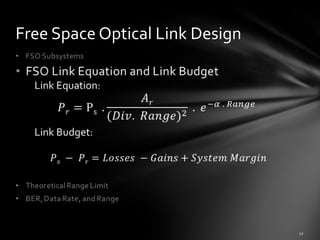

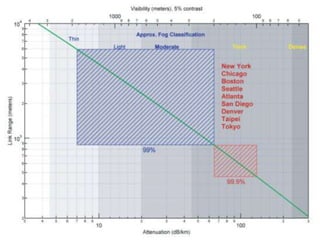

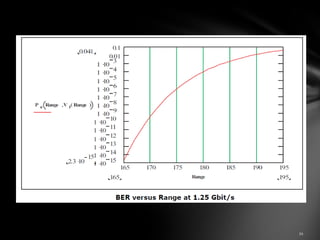
![Outlines
• Introduction [1]
• Free Space Optical Link Design [2]
• Applications [3]
• FSO vs. Fiber vs. Microwave Links](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespaceopticalcommunication-120621062452-phpapp02/85/Free-space-optical-communication-23-320.jpg)









![Outlines
• Introduction [1]
• Free Space Optical Link Design [2]
• Applications [3]
• FSO vs. Fiber vs. Microwave Links](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespaceopticalcommunication-120621062452-phpapp02/85/Free-space-optical-communication-36-320.jpg)
![References
[1] S.V. Kartalopoulos , “ Disaster Avoidance in the Manhattan
Fiber Distributed Data Interface Network , ” Globecom ’
93, Houston, TX, December 2, 1993 .
[2] Scott Bloom, “The Physics of Free Space Optics”, AirFiber, Inc.
[3] “Free-Space Optical Communications on
HAPs”, www.hapcos.org , accessed on : 13-May-2012](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/freespaceopticalcommunication-120621062452-phpapp02/85/Free-space-optical-communication-38-320.jpg)
