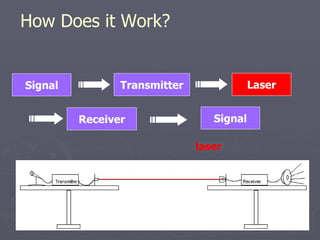
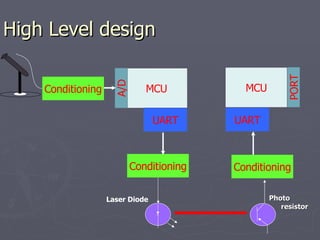
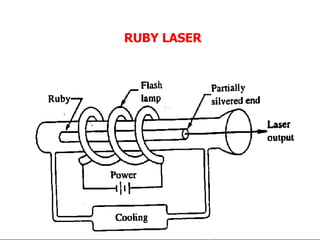
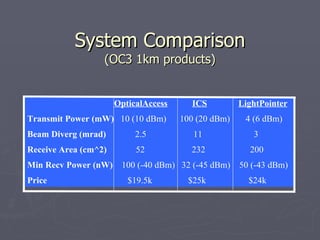
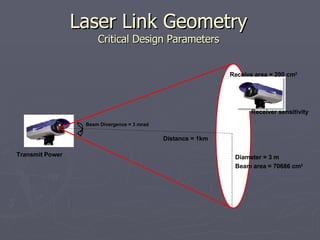
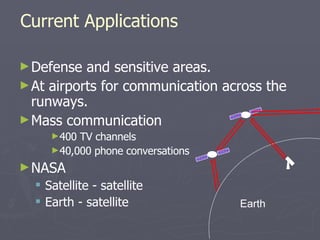
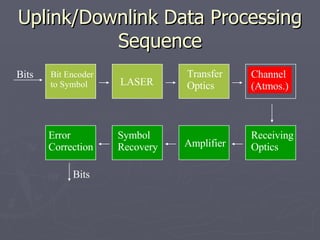
Laser communication uses lasers to transmit information through free space instead of fiber optic cables. It works similarly to fiber optics but transmits the beam through the atmosphere instead of cables. The transmitter converts signals into laser light and the receiver includes a telescope to capture the beam and detectors to convert it back into signals. Laser communication has advantages over radio frequency and fiber optics for applications where laying cable is not possible or practical such as for satellites, remote areas, and emergencies due to its high bandwidth, directivity, security, and smaller antenna size.