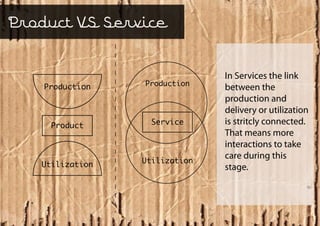
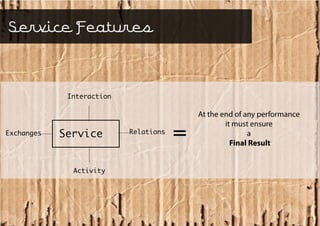
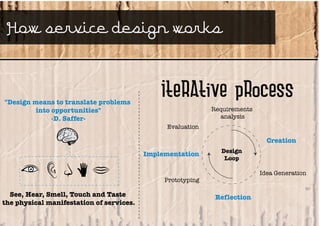
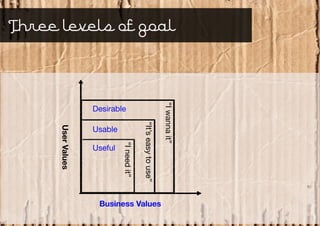
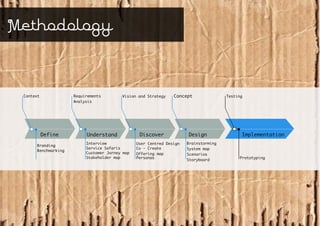
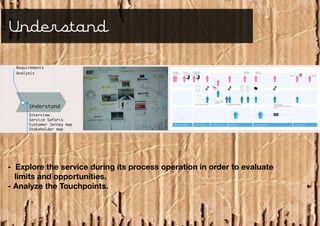
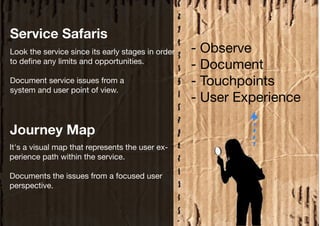
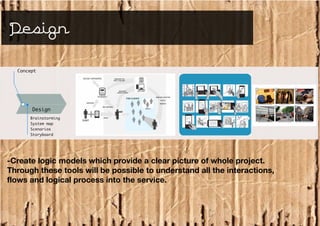
Service design is an interdisciplinary approach that combines tools from various disciplines to create well-designed experiences. It focuses on defining services through requirements analysis, understanding user needs, discovering opportunities through co-creation, designing service concepts, and implementing solutions through prototyping. The goal is to innovate or improve existing services to make them more useful, usable, and desirable for end users.