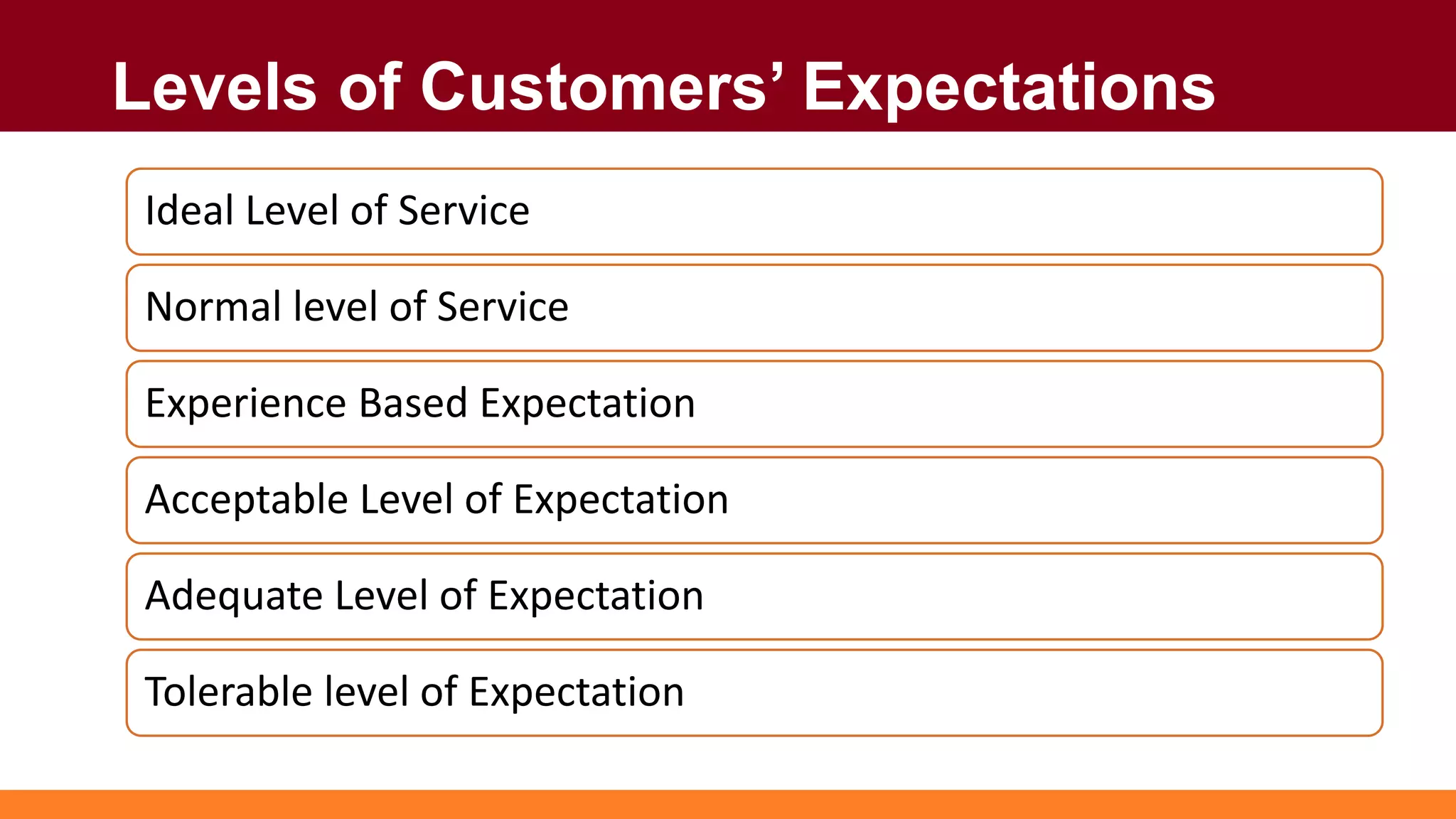
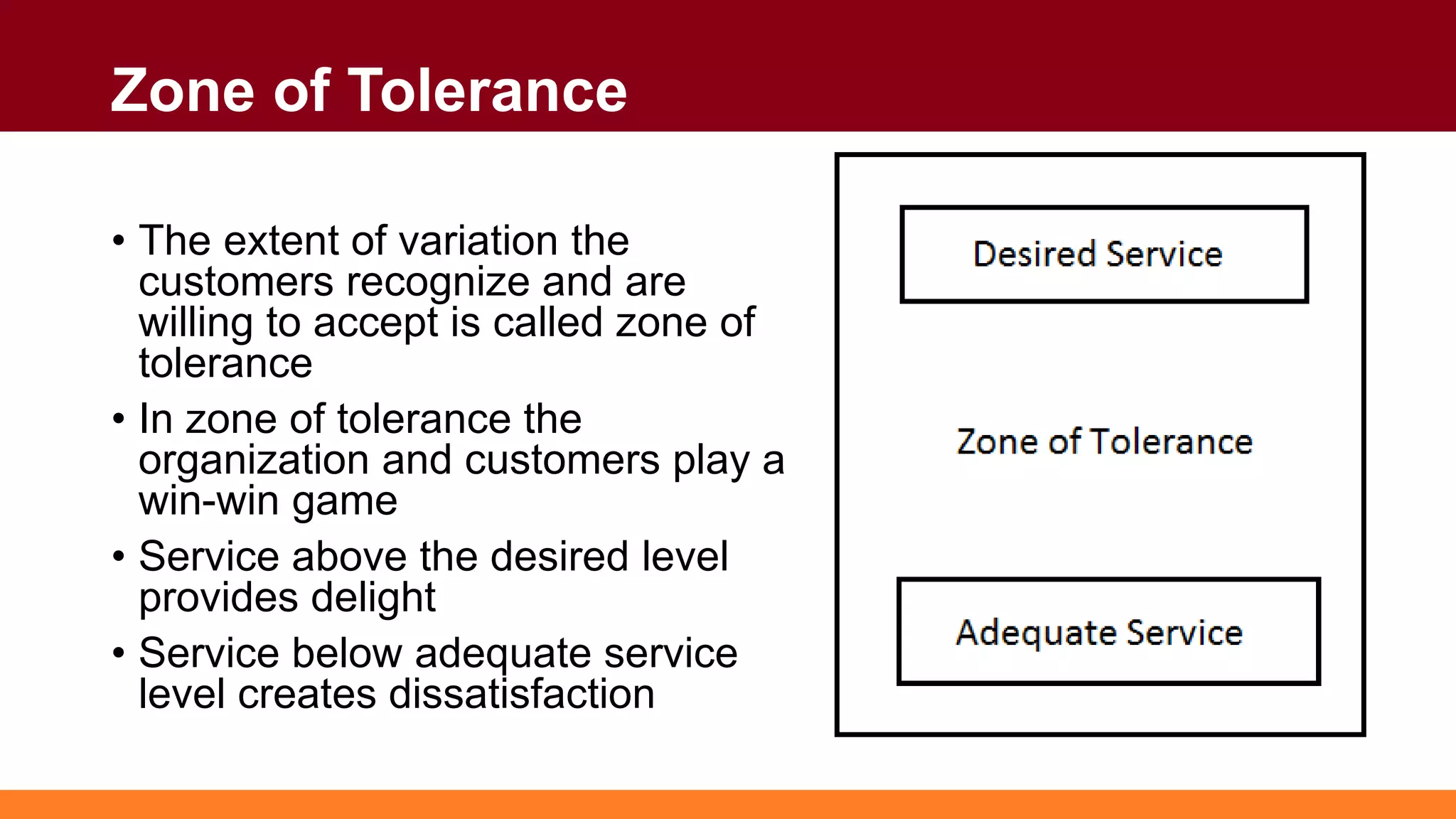
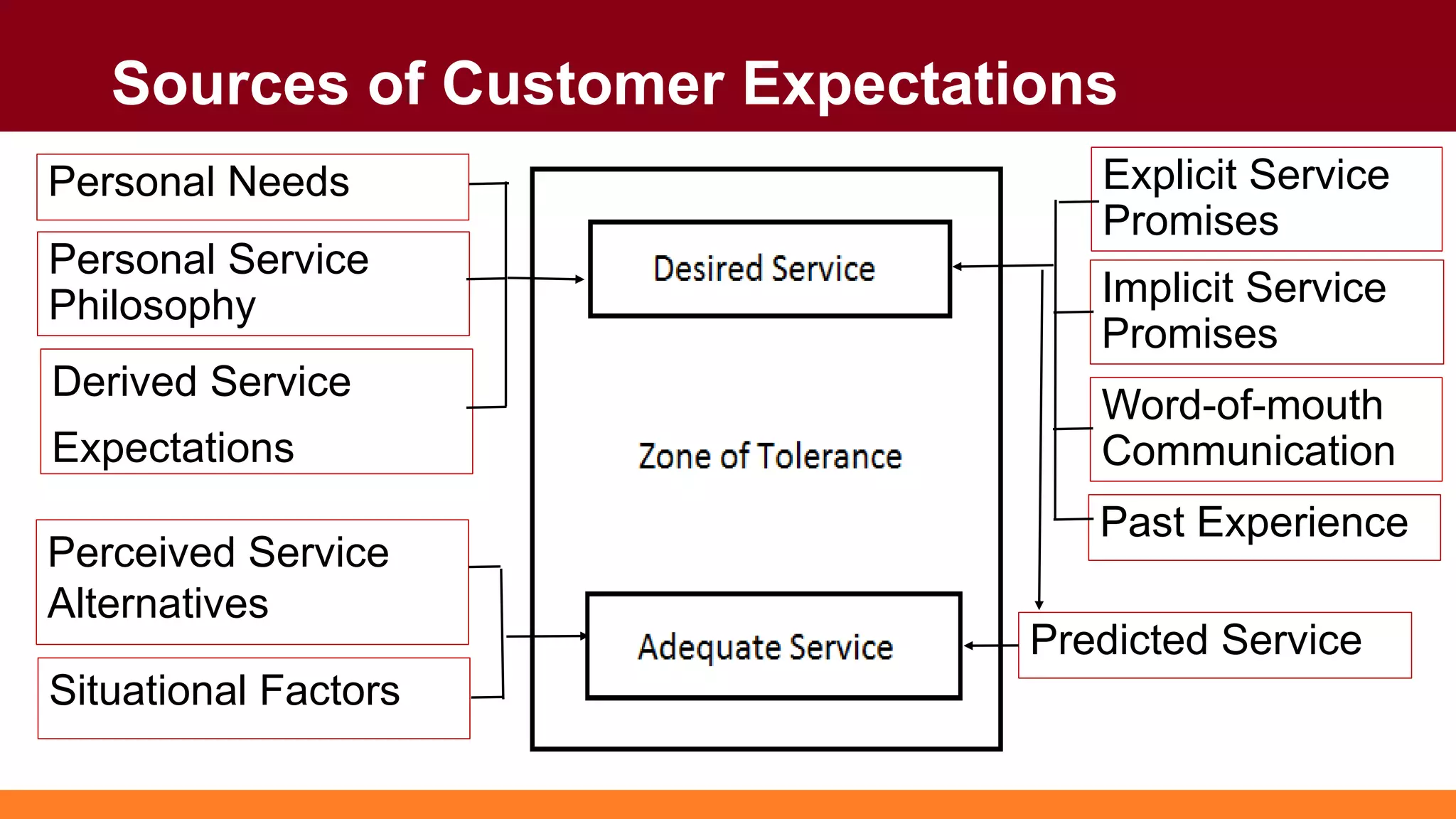
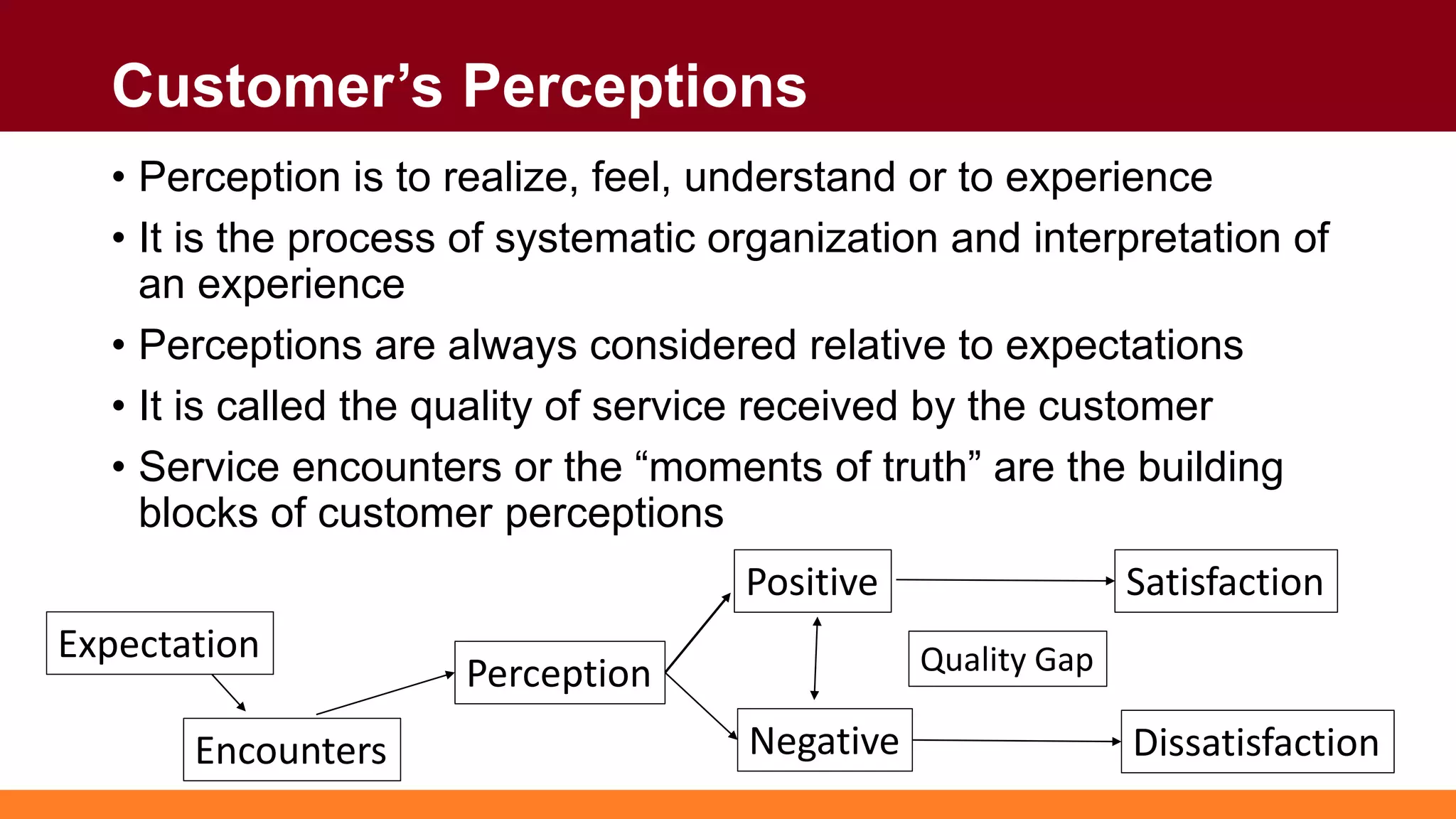
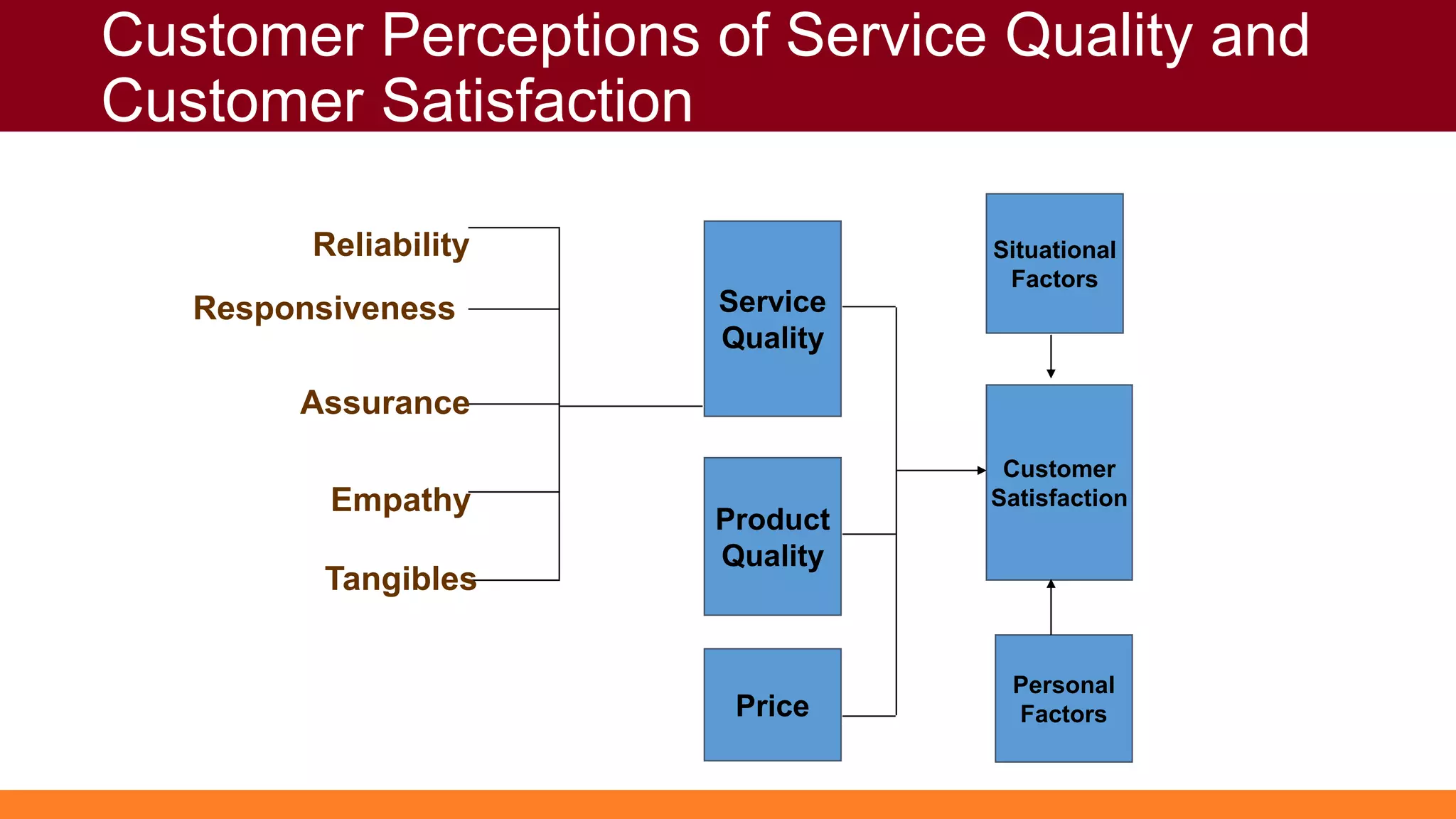
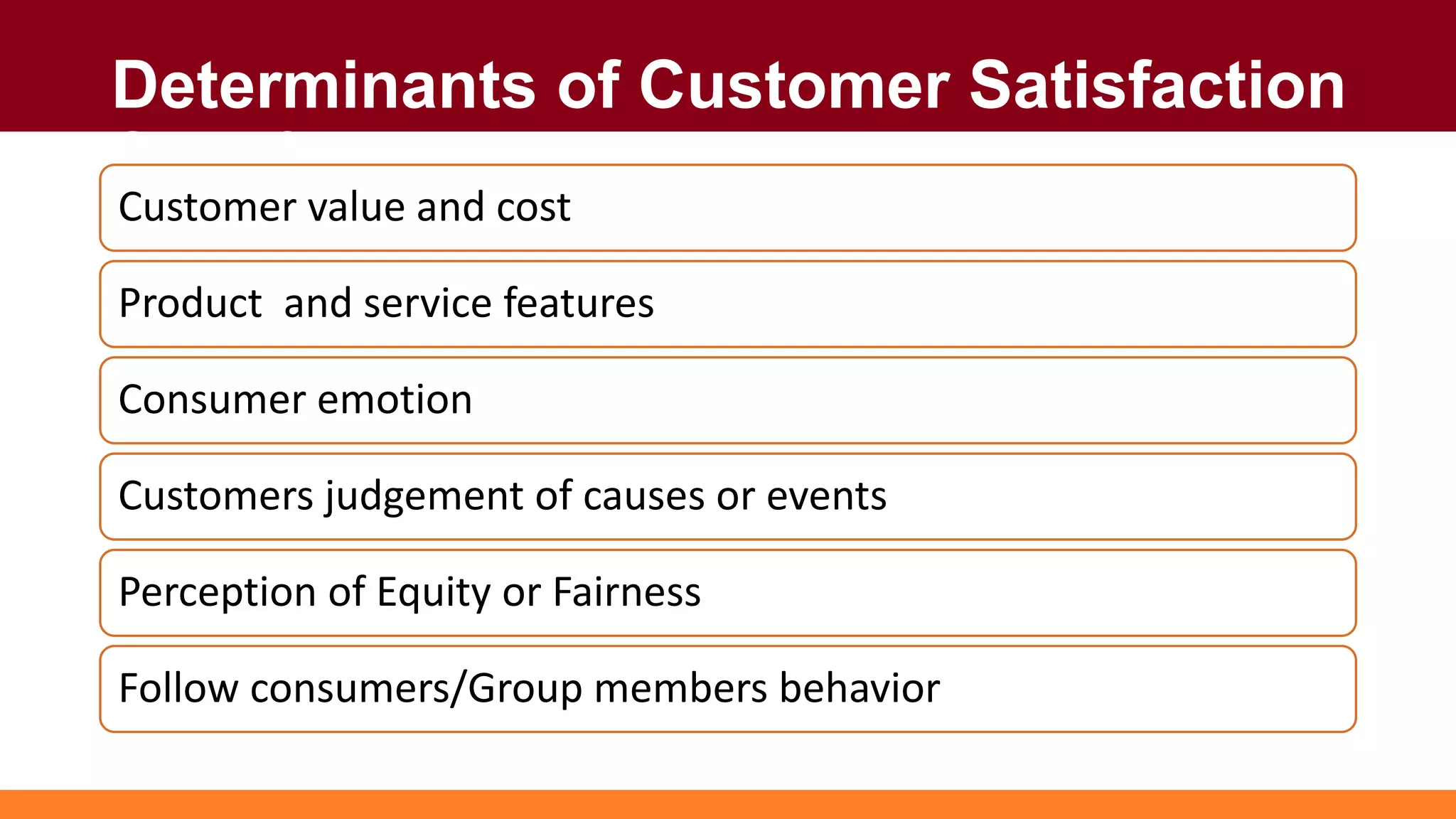
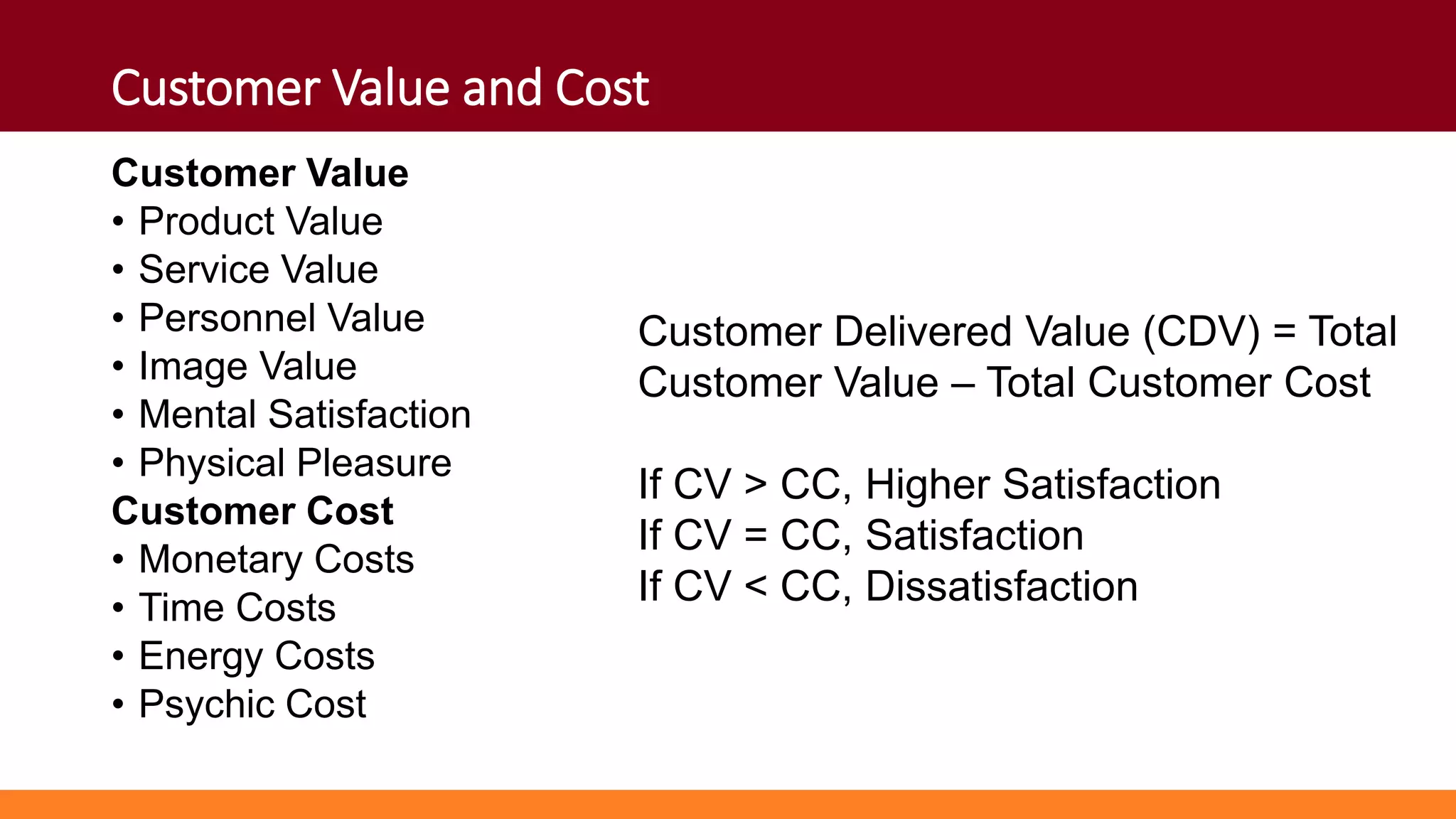
Customers have both expectations and perceptions of the level of service they will receive. Their expectations are influenced by personal needs, past experiences, and promises made by the service provider. Perceptions are formed through service encounters and compared to expectations. If perceptions meet or exceed expectations, the customer will be satisfied. Key aspects of service quality that influence perceptions are reliability, responsiveness, assurance, empathy, and tangibles. Higher customer value relative to costs also leads to greater satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more loyal and help the business grow through positive word-of-mouth.