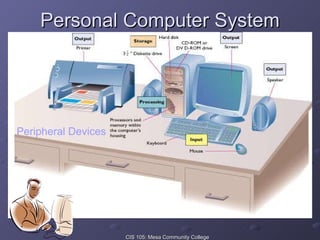
This document provides an overview of computers, including their fundamental characteristics, benefits, and basic components. It describes what a computer is and how it works by accepting input, processing it, and producing output. The main components are identified as the central processing unit, memory, input/output devices, and storage. Common benefits of computers are listed as increased productivity, better decision making, and reduced costs. Networking and the internet are explained, including how they allow sharing of resources globally. Various terms are defined, such as data, information, software, hardware, and computer classifications.























![Electronic Mail E-mail Transmission of messages via a computer network. Electronic mail software enables you to create, send, receive, forward, etc. email message. For example: Outlook E-mail address is a combination of a username and domain name. For example: [email_address] For free email accounts try www.hotmail.com For more information on the Web and email, go to www.learnthenet.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/one-computersoverview-091201020039-phpapp01/85/One-Computers-Overview-25-320.jpg)




