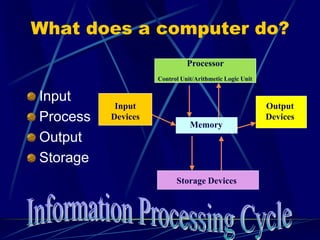
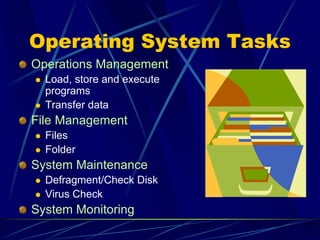
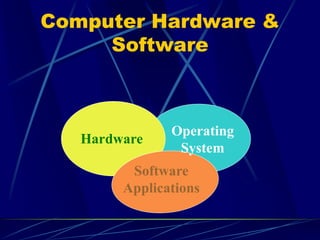
A computer is an electronic device that can accept data as input, process the data, produce output, and store results. It performs these functions under the control of instructions stored in its memory. A computer includes input devices, output devices, a processor, memory, storage, and software. Common computer applications and uses include email, shopping, communication, and accessing information online.