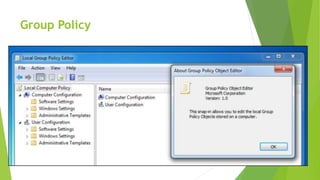
The document provides an overview of systems administration focusing on DNS, Active Directory, and Group Policy within information systems. It defines key terminologies, outlines the structure and function of DNS, including types of lookups and zones, and explains Active Directory and its significance in user and resource management. Additionally, it touches on software publishing versus assigning, detailing the role of Group Policy in managing user environments.