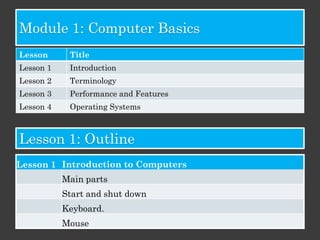
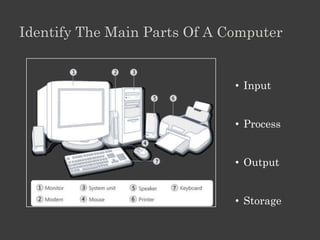
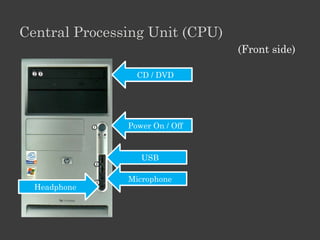
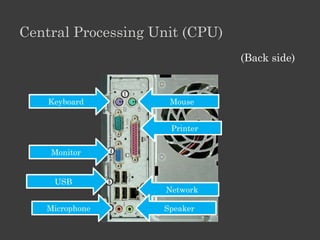
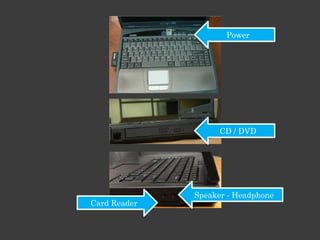
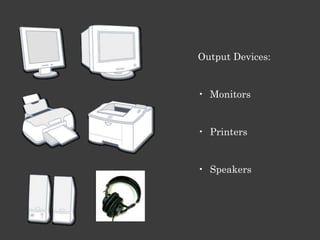
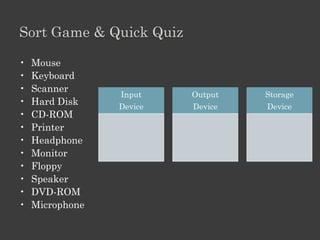
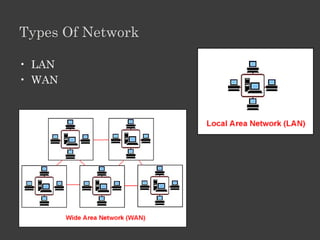
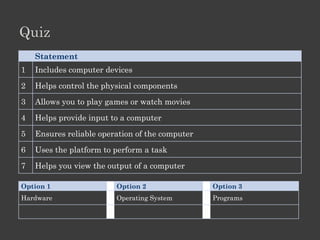
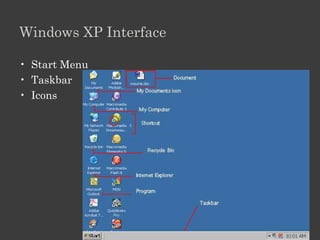
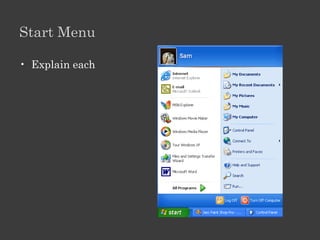
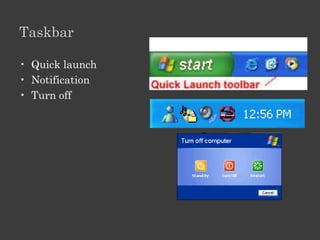
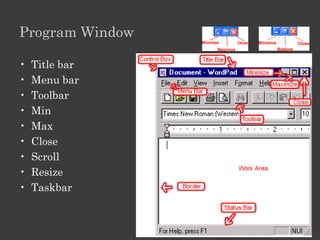
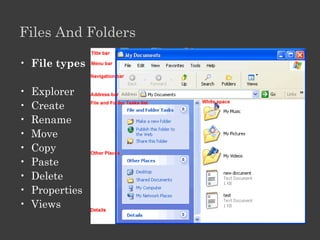
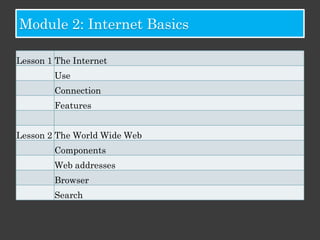
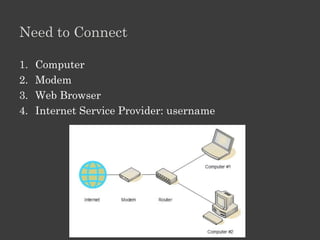
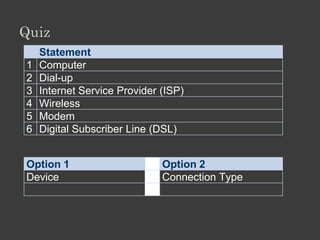
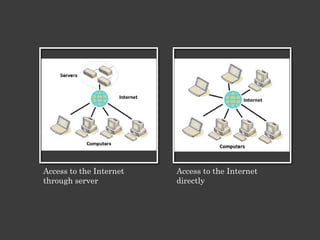
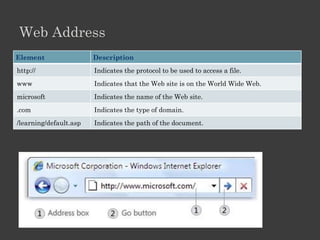
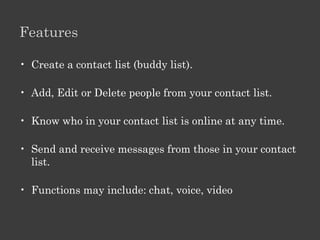
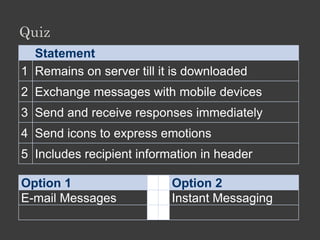
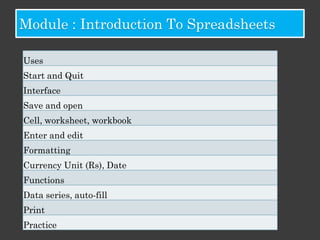
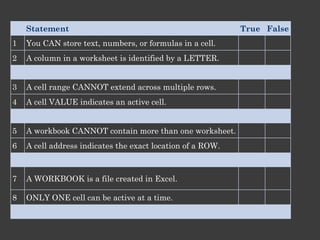
The document outlines an Alpha Tech Program trainer kit that aims to remove fear, be simple and fun, and teach computer basics like operating systems, the internet, email, and digital media through modules that cover topics such as word processing, spreadsheets, and presentations. The trainer kit includes lessons on computer parts, starting and shutting down computers, using keyboards and mice, basic terminology, and introduces functions of operating systems, the internet, email, and instant messaging.