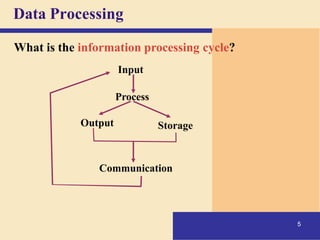
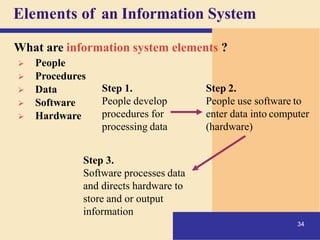
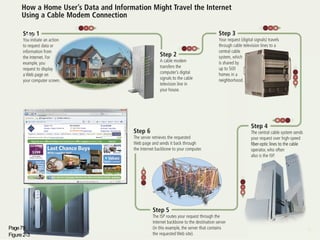
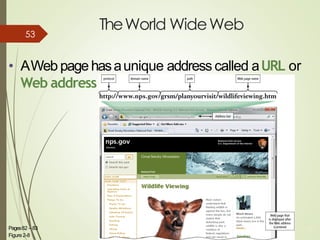
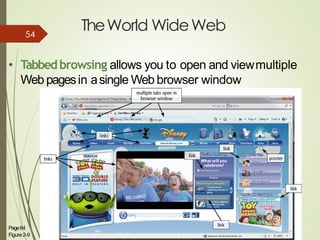
This document provides an overview of computers and the internet in 3 main sections:
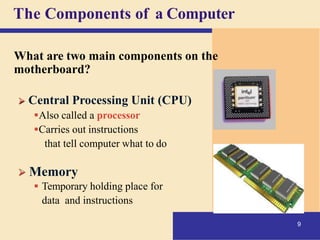
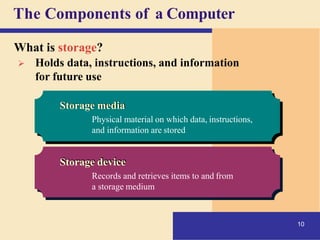
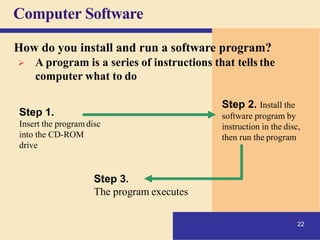
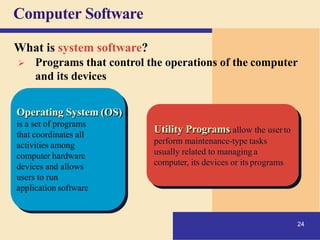
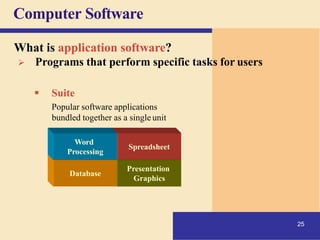
1) It defines what a computer is and describes the basic components of a computer system including the central processing unit, memory, storage, input/output devices, and how they work together.
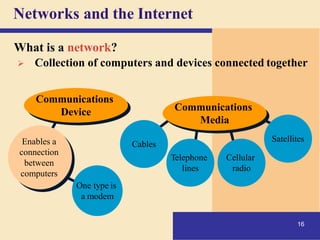
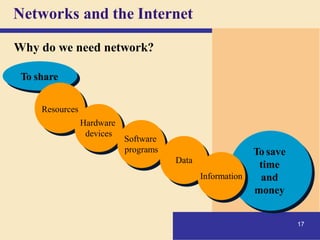
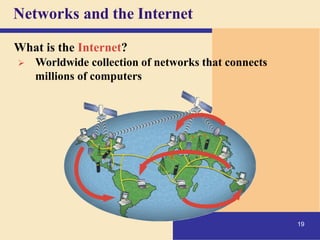
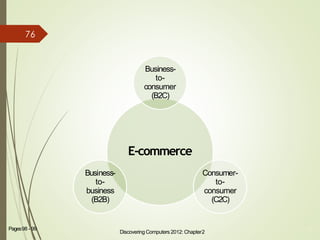
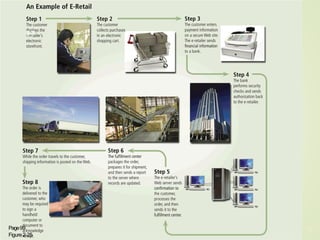
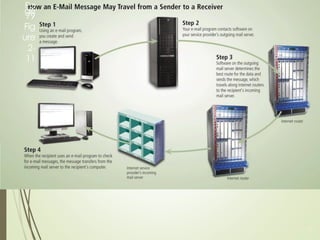
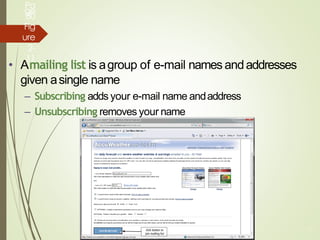
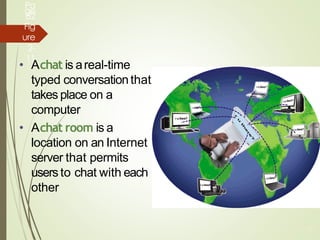
2) It explains what networks and the internet are, how they connect computers, and key technologies that enable communication like servers, IP addresses, and wireless networks. Important internet applications like email, instant messaging, and e-commerce are also outlined.
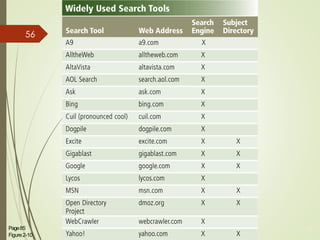
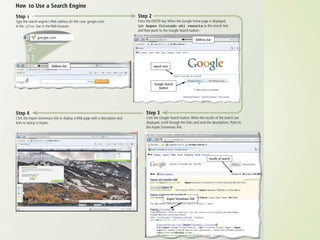
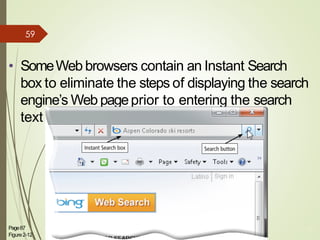
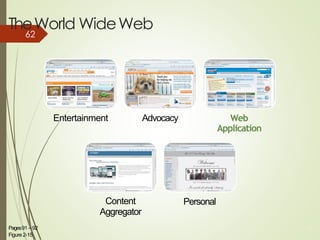
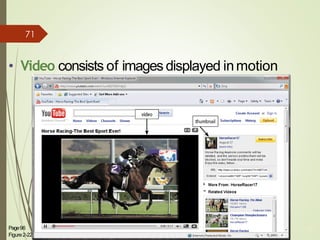
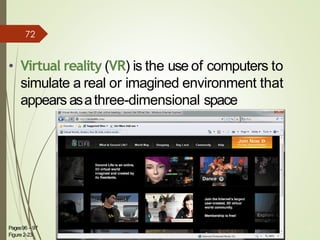
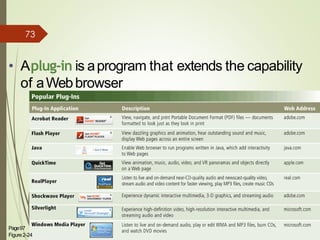
3) It describes the development and functionality of the World Wide Web including browsers, web servers, web pages, URLs, search engines, multimedia, and different types of websites. The impact and opportunities of