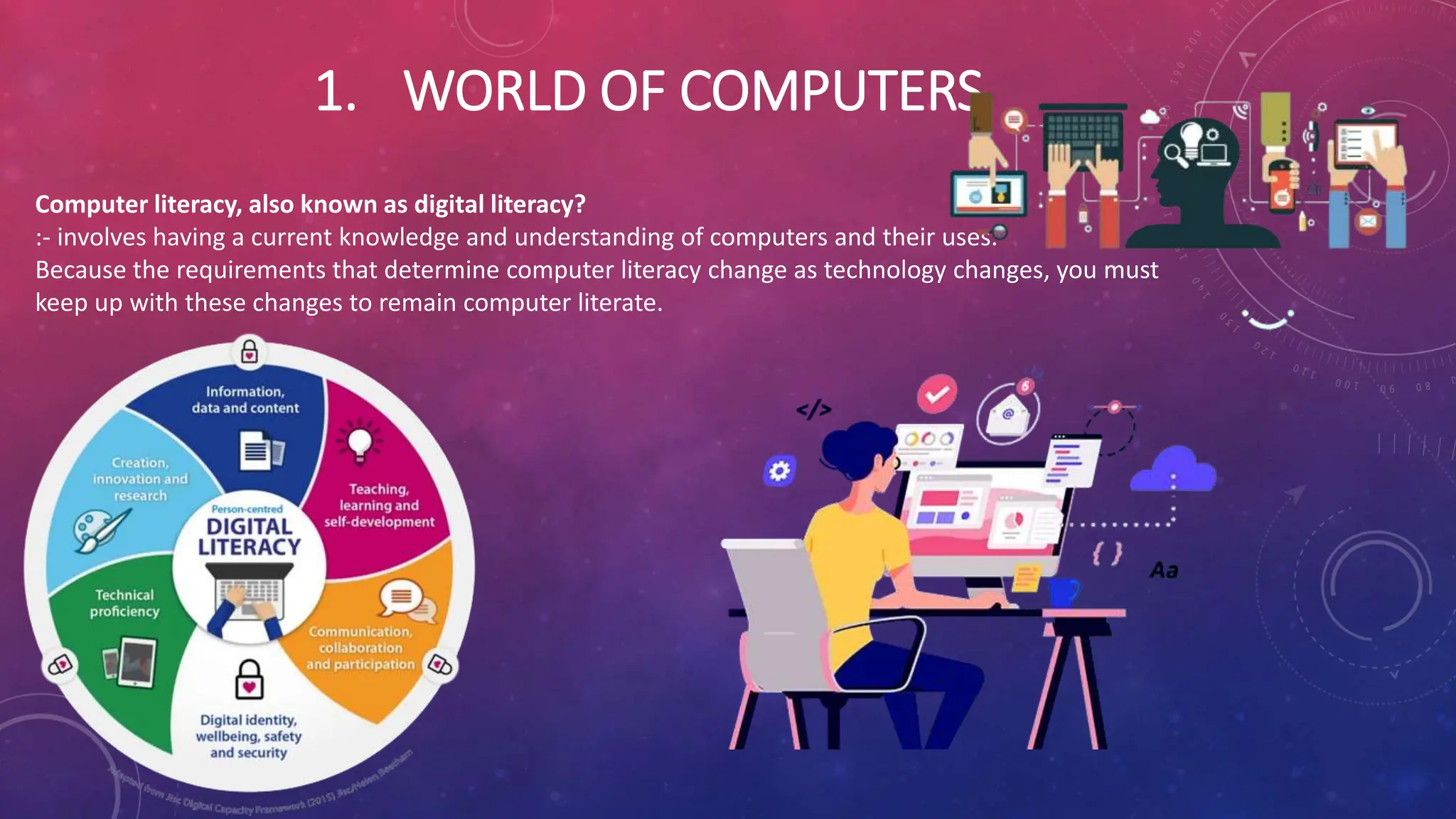
This chapter introduces computers and their basic components. It defines a computer as an electronic device that can accept data as input, process the data, produce output, and store results. The main components of a computer are the system unit, input devices, output devices, storage devices, and communication devices. Examples of input devices include keyboards, mice, and scanners, while common output devices are monitors and printers. The chapter also discusses computer networks, the internet, and how they allow sharing of resources. It introduces concepts such as websites, webpages, web applications, blogs, podcasts, and how they are categorized as Web 2.0 sites.