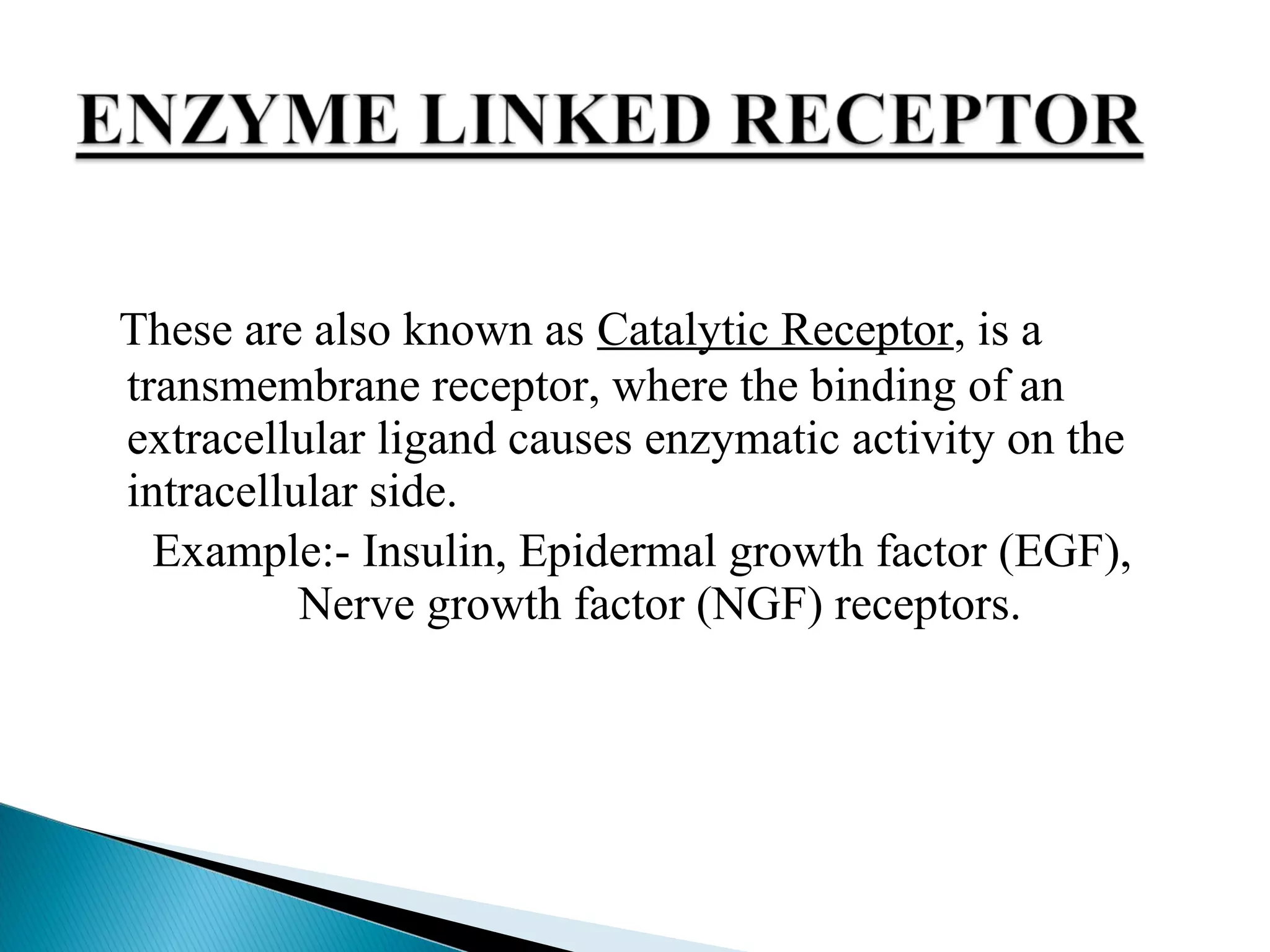
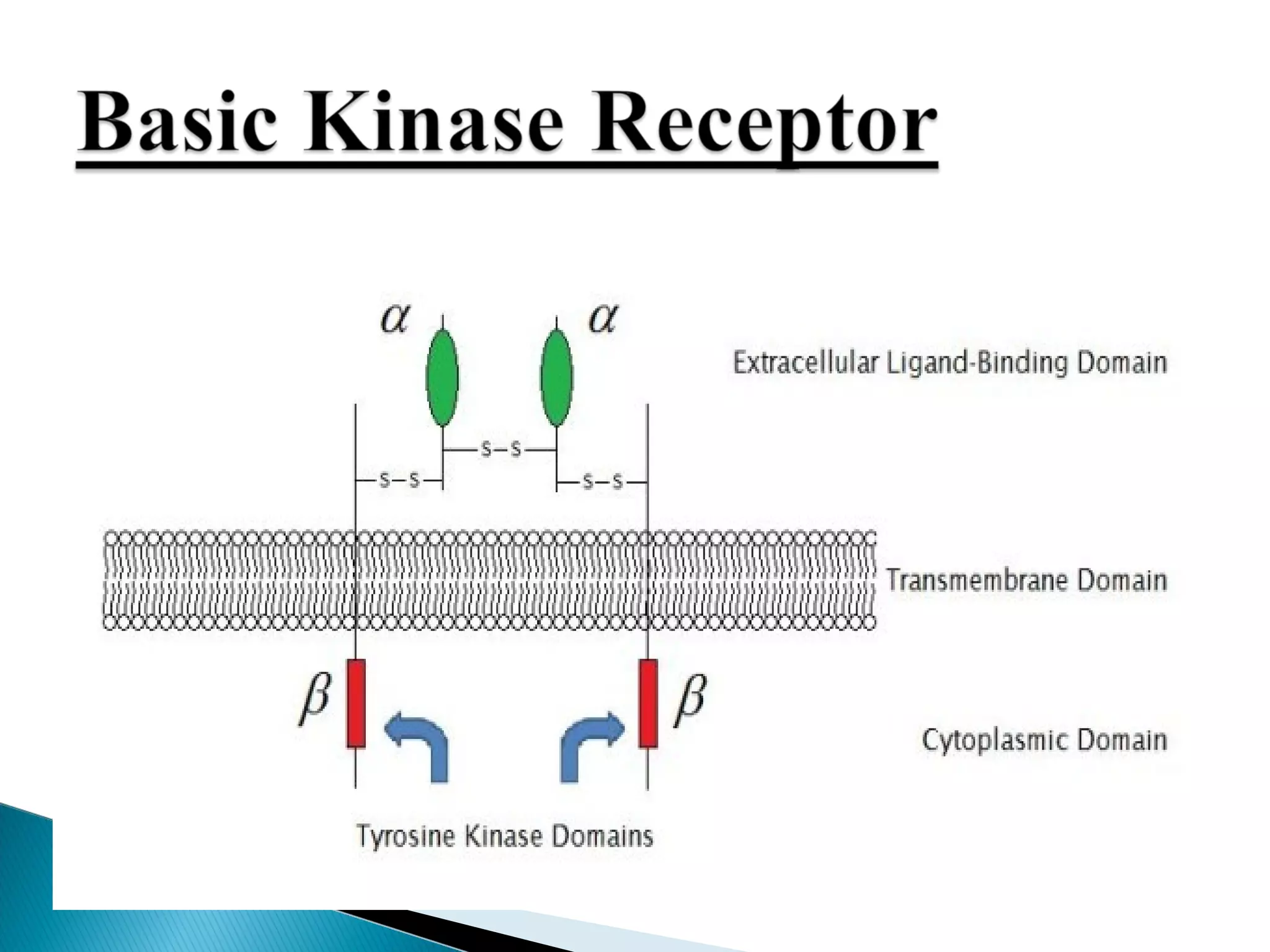
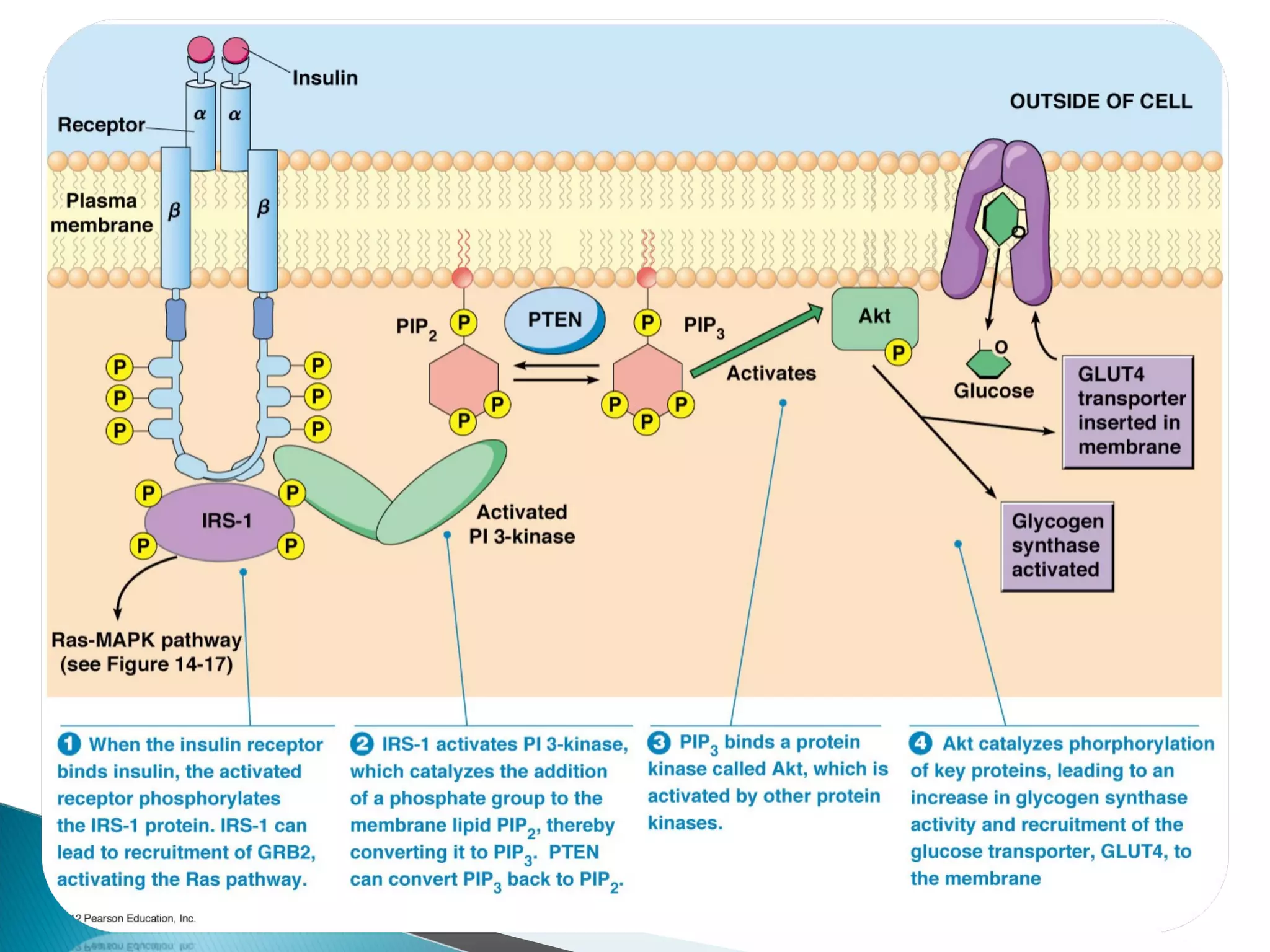
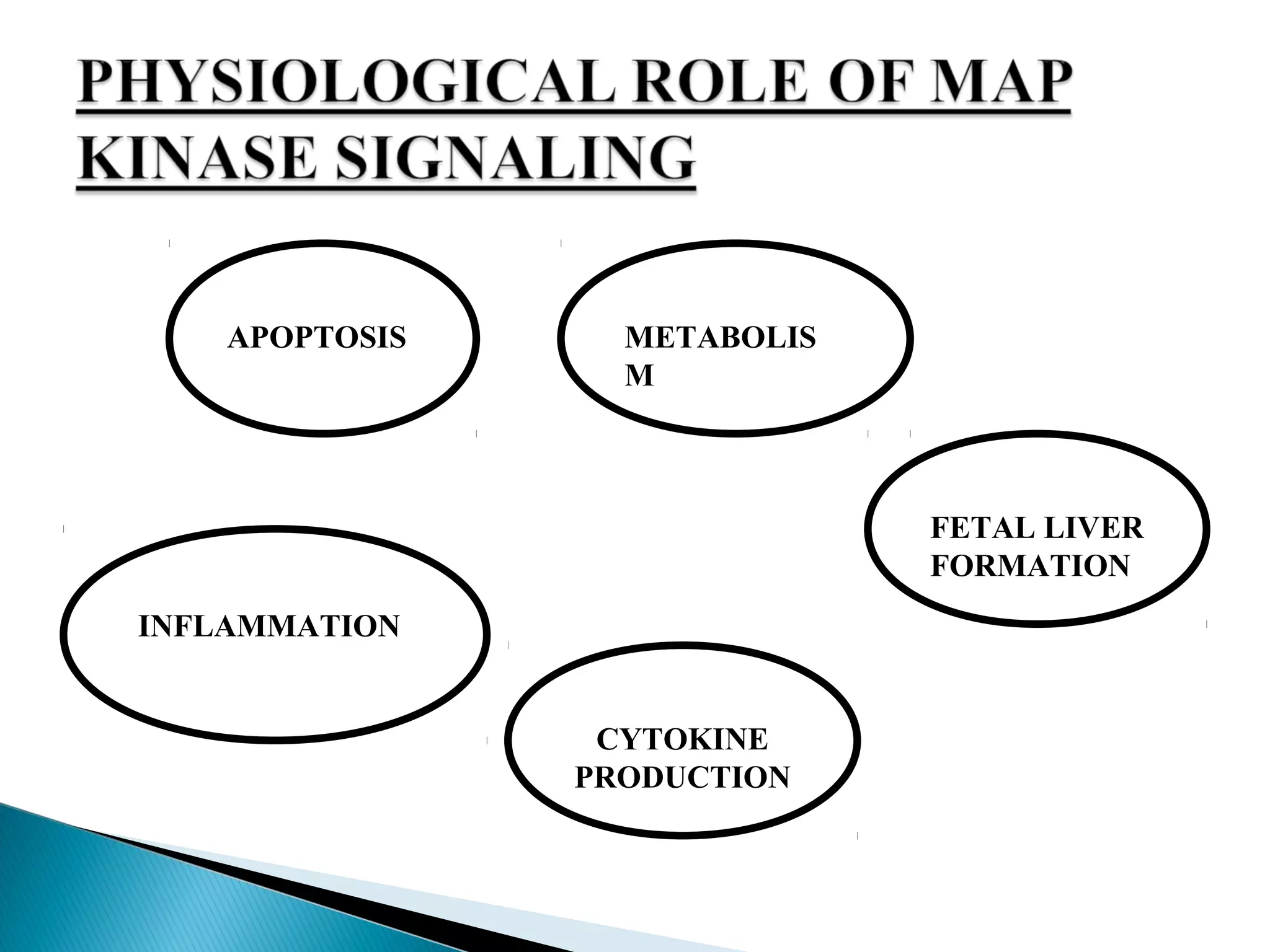
This document discusses receptors and their downstream signaling pathways, including JAK-STAT and MAPK pathways. It defines receptors and describes different receptor types like G protein-coupled and enzyme-linked receptors. It then focuses on the JAK-STAT pathway, identifying its components like JAK kinases and STAT transcription factors, and drugs that target this pathway for conditions like rheumatoid arthritis. Finally, it examines the MAPK pathway, identifying the MAP kinase families involved in key cellular processes and examples of drugs that inhibit parts of this pathway.