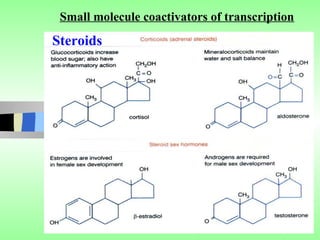
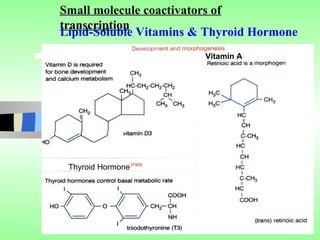
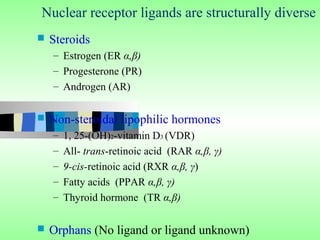
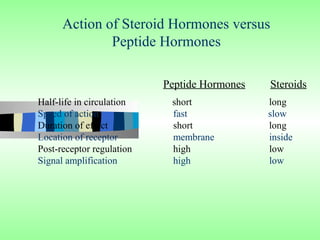
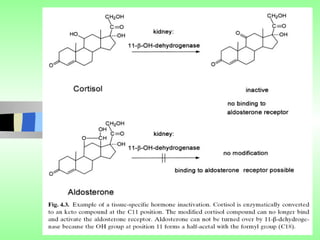
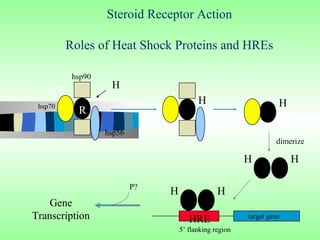
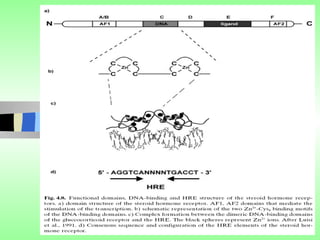
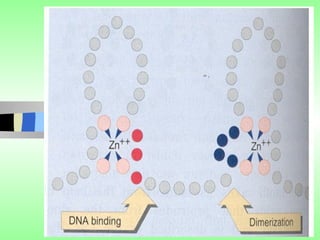
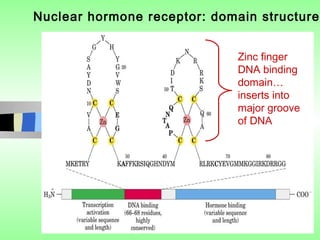
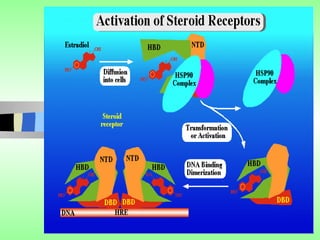
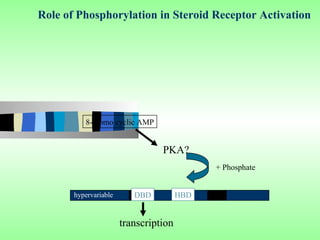
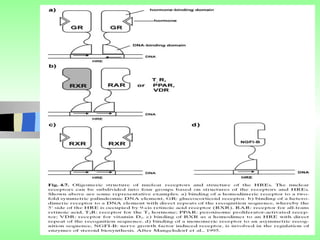
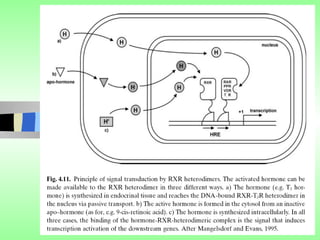
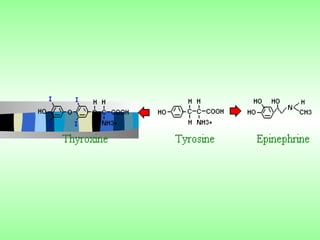
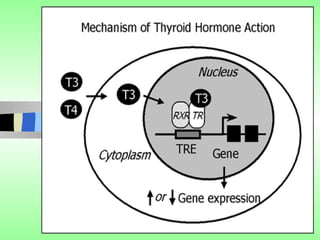
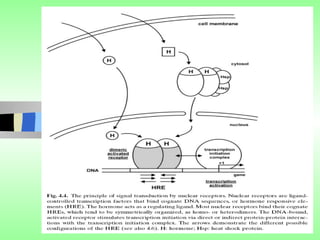
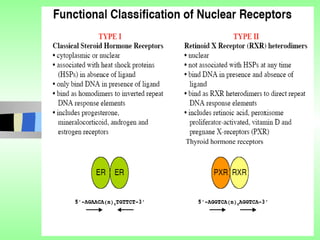
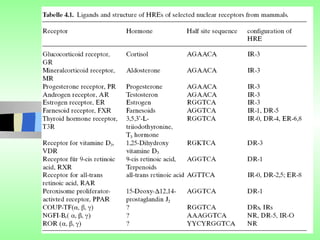
Nuclear receptors regulate gene expression by binding to ligands that pass through the cell membrane via simple diffusion. These receptors are located in the cytoplasm or nucleus and bind small molecule ligands like steroids, lipids, vitamins, and thyroid hormone to function as transcriptional coactivators. Nuclear receptor ligands come in various structures including steroids like estrogen, progesterone, and androgen as well as non-steroidal lipophilic hormones such as vitamin D, retinoic acid, fatty acids, and thyroid hormone. Some receptors have unknown ligands and are called "orphan" receptors. Steroid receptors differ from peptide receptors in their half-life, speed of action, duration of effect, location, and degree of post-receptor regulation