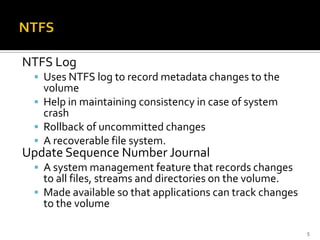
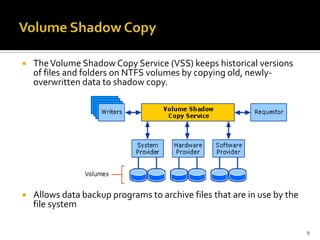
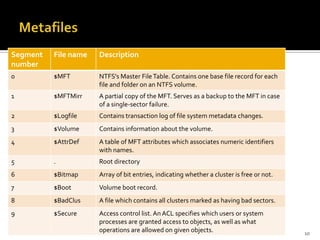
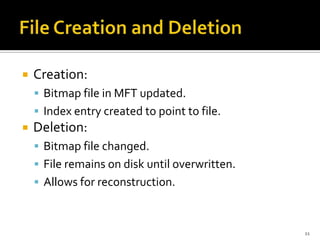
The document discusses digital forensics and evidence extraction from NTFS computers. It describes how NTFS works, including features like the master file table, alternate data streams, volume shadow copies, and more. It explains that deleted or hidden data can potentially be uncovered by examining registry entries, volume shadow copies, unallocated space in the MFT, and clusters marked as bad.