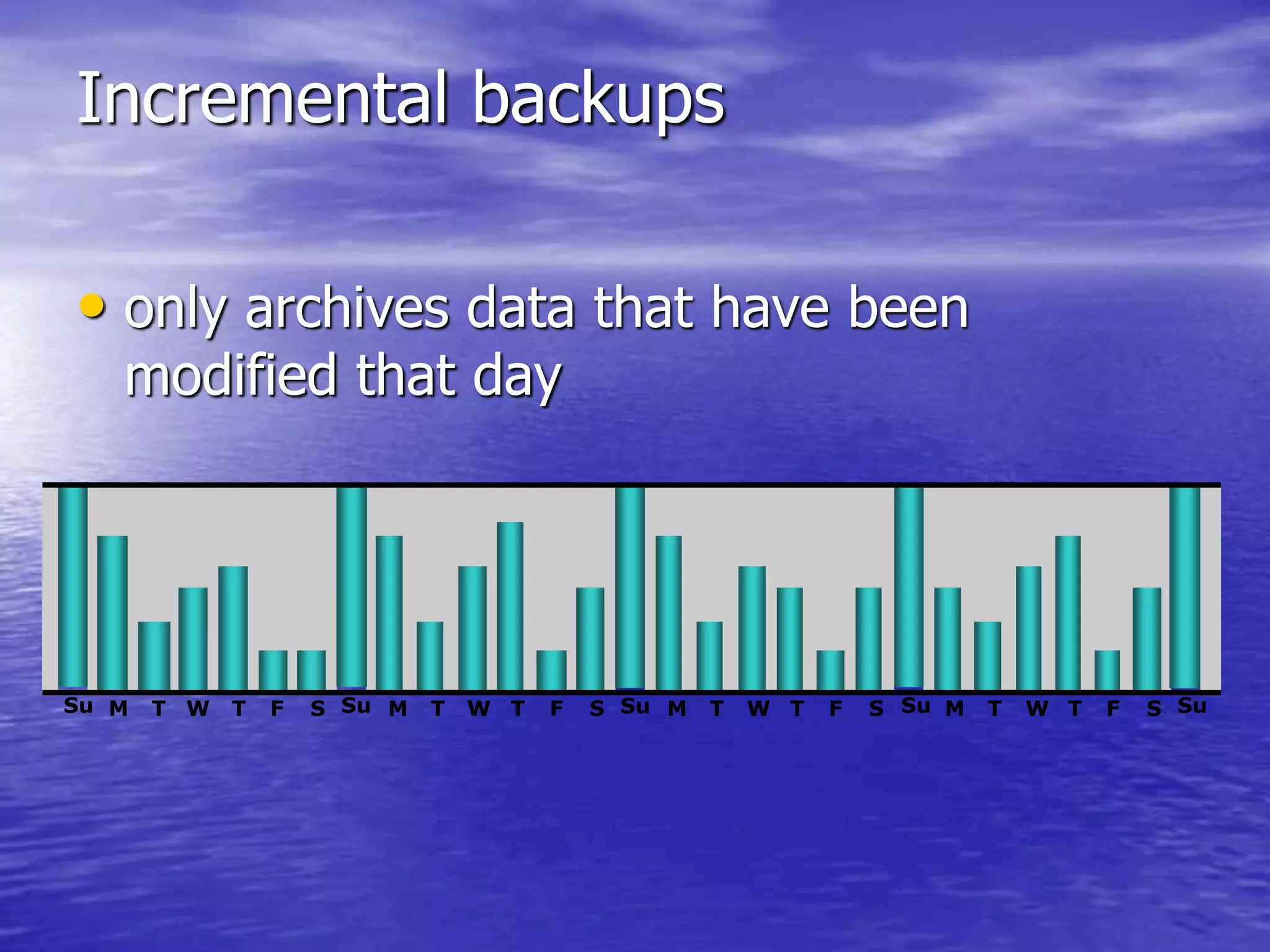
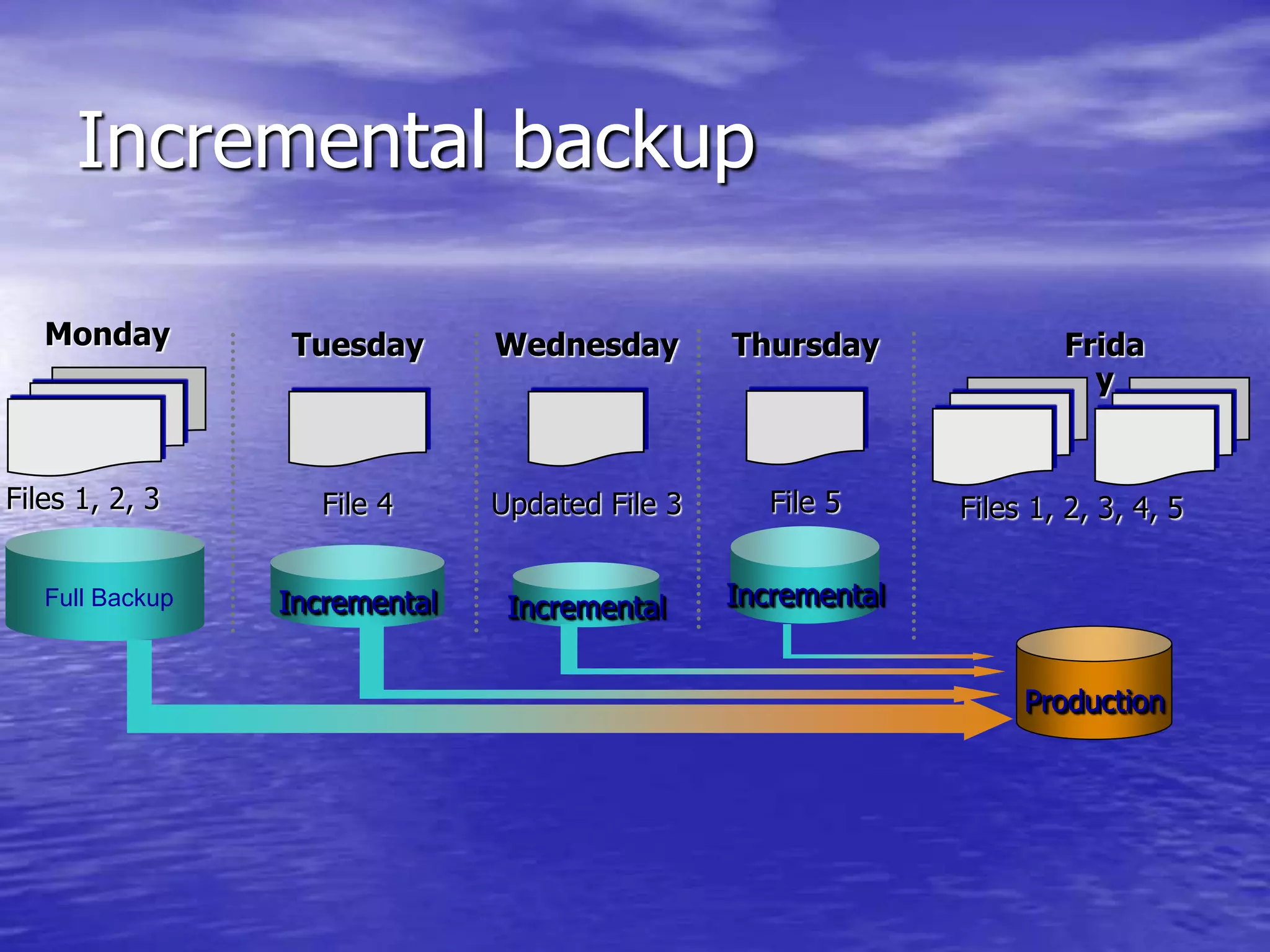
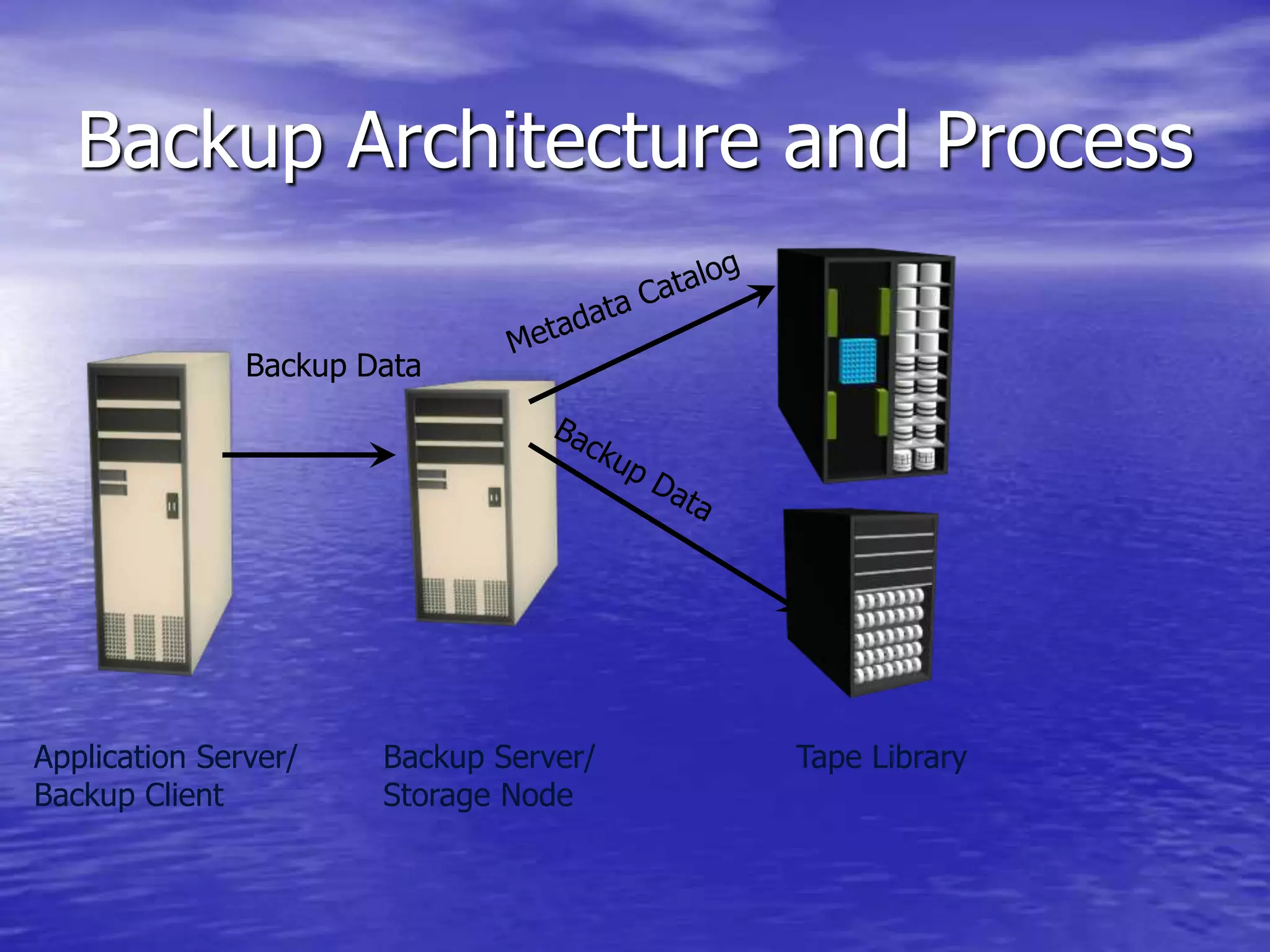
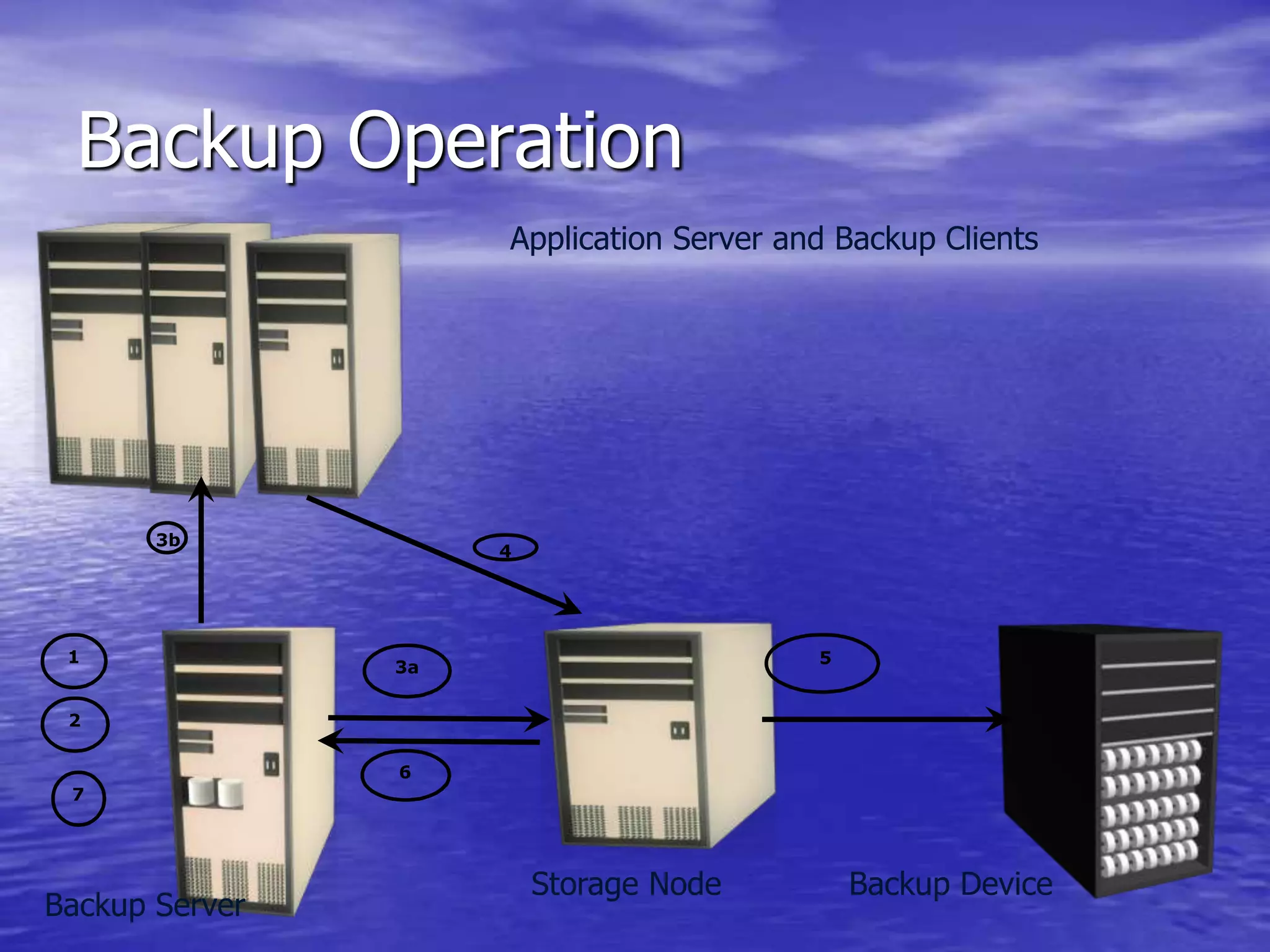
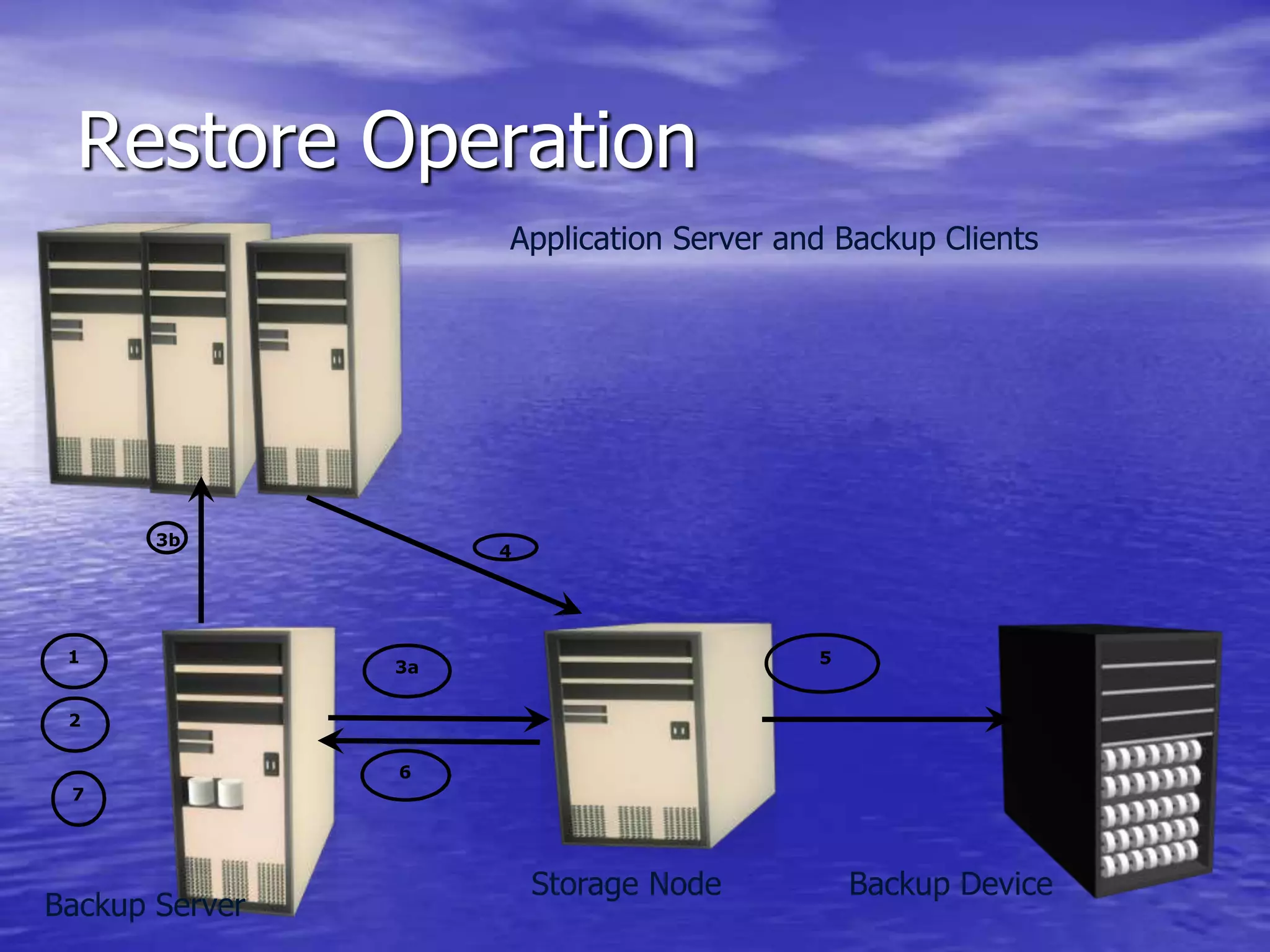
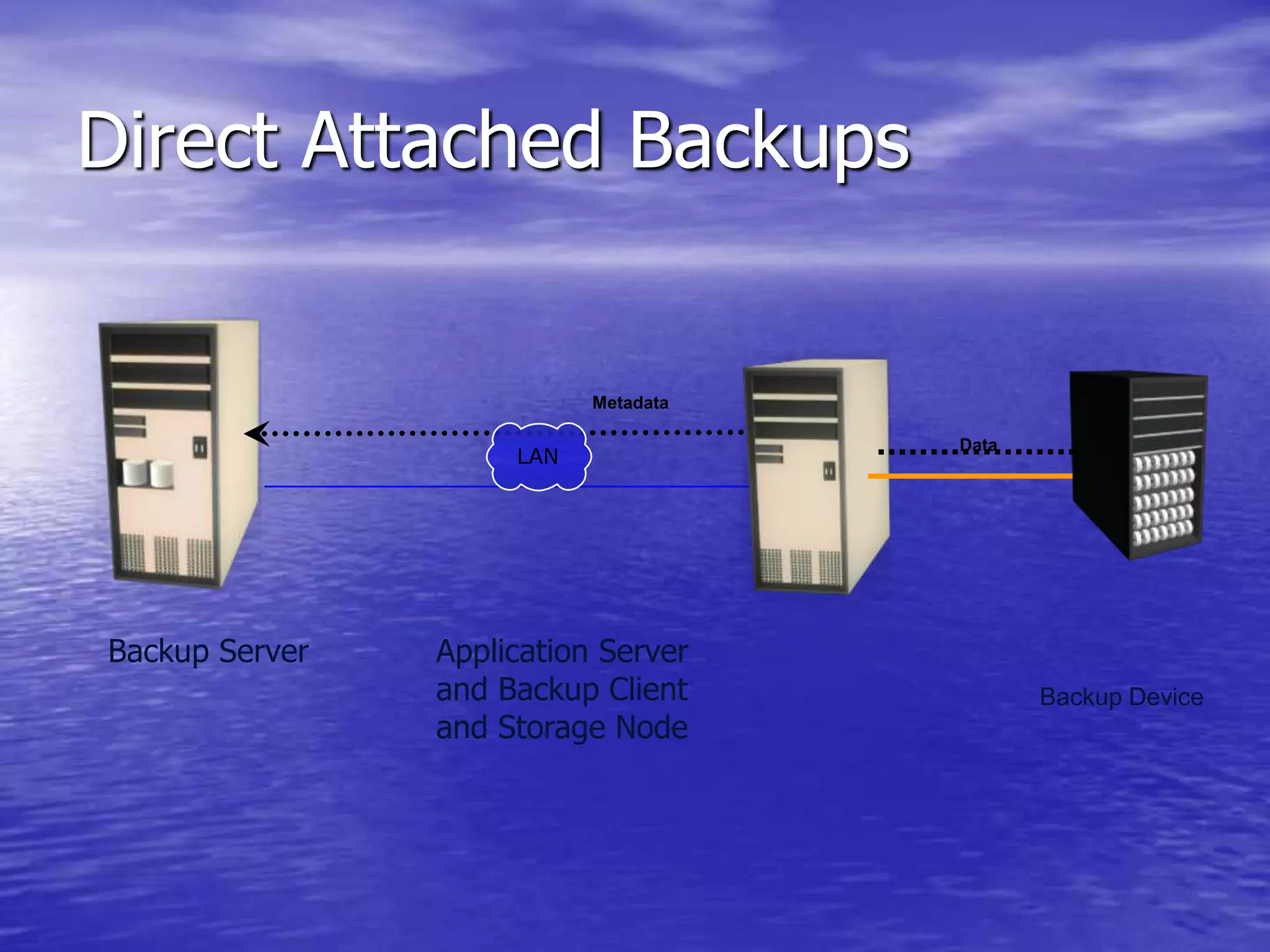
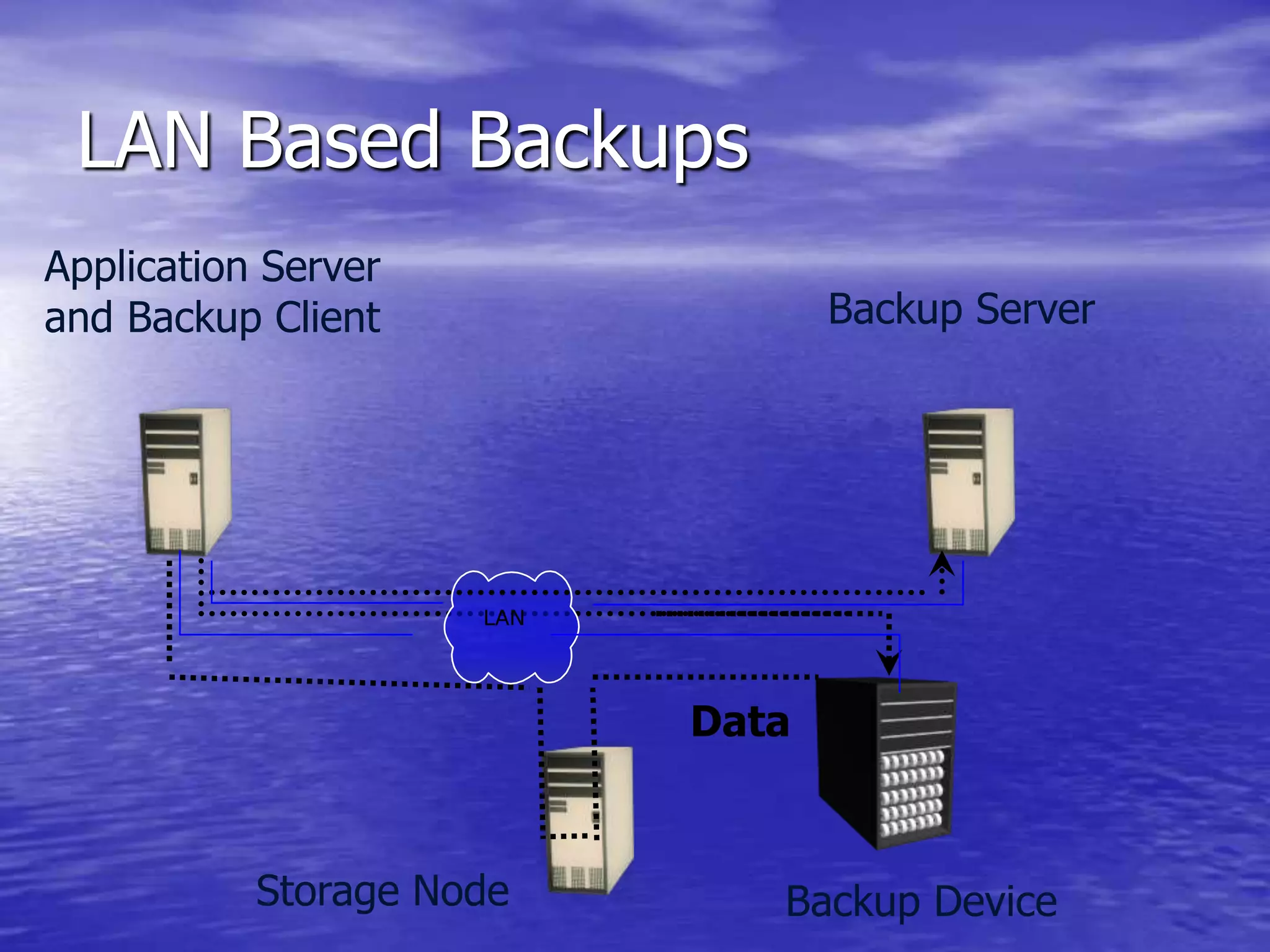
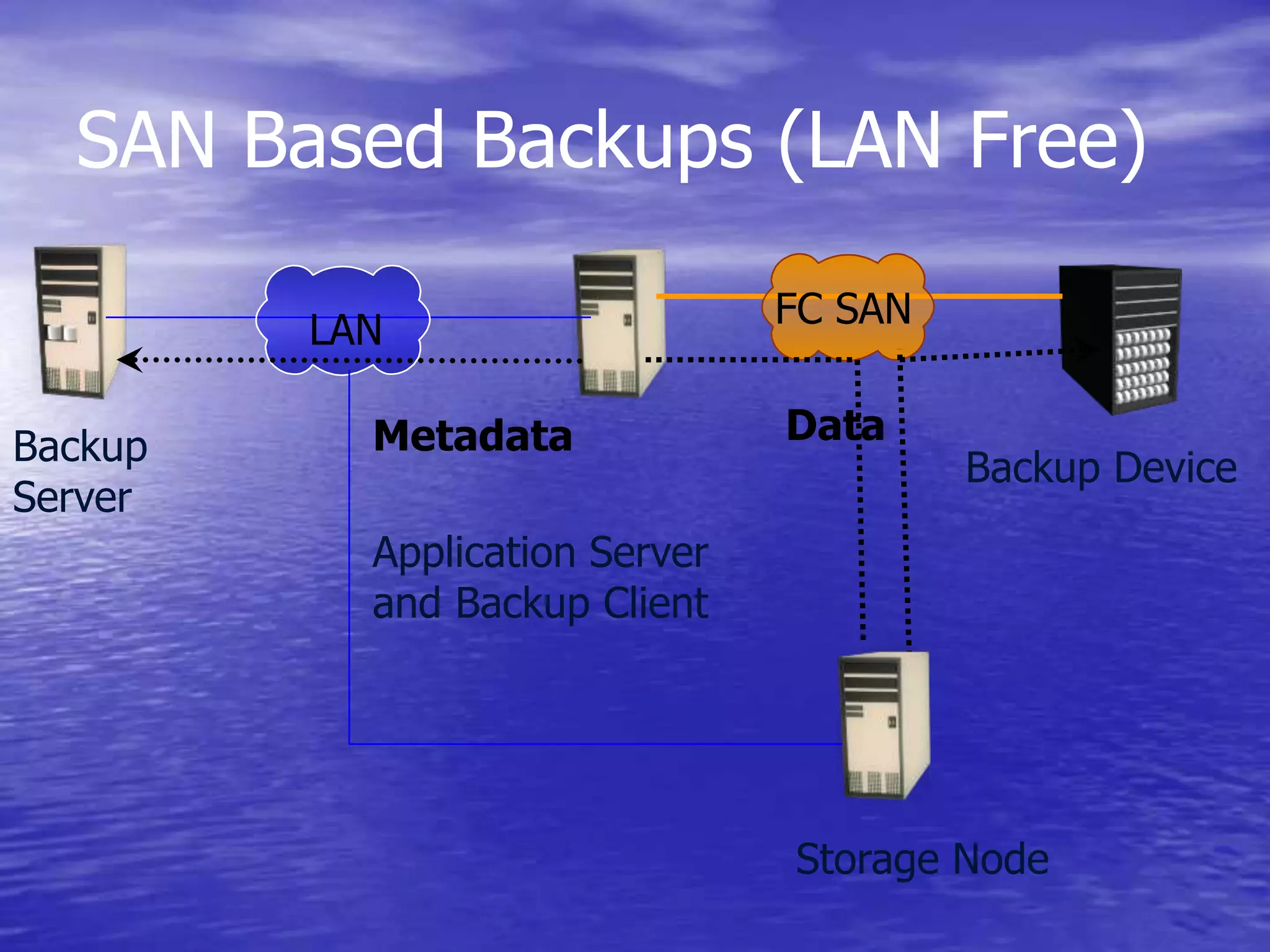
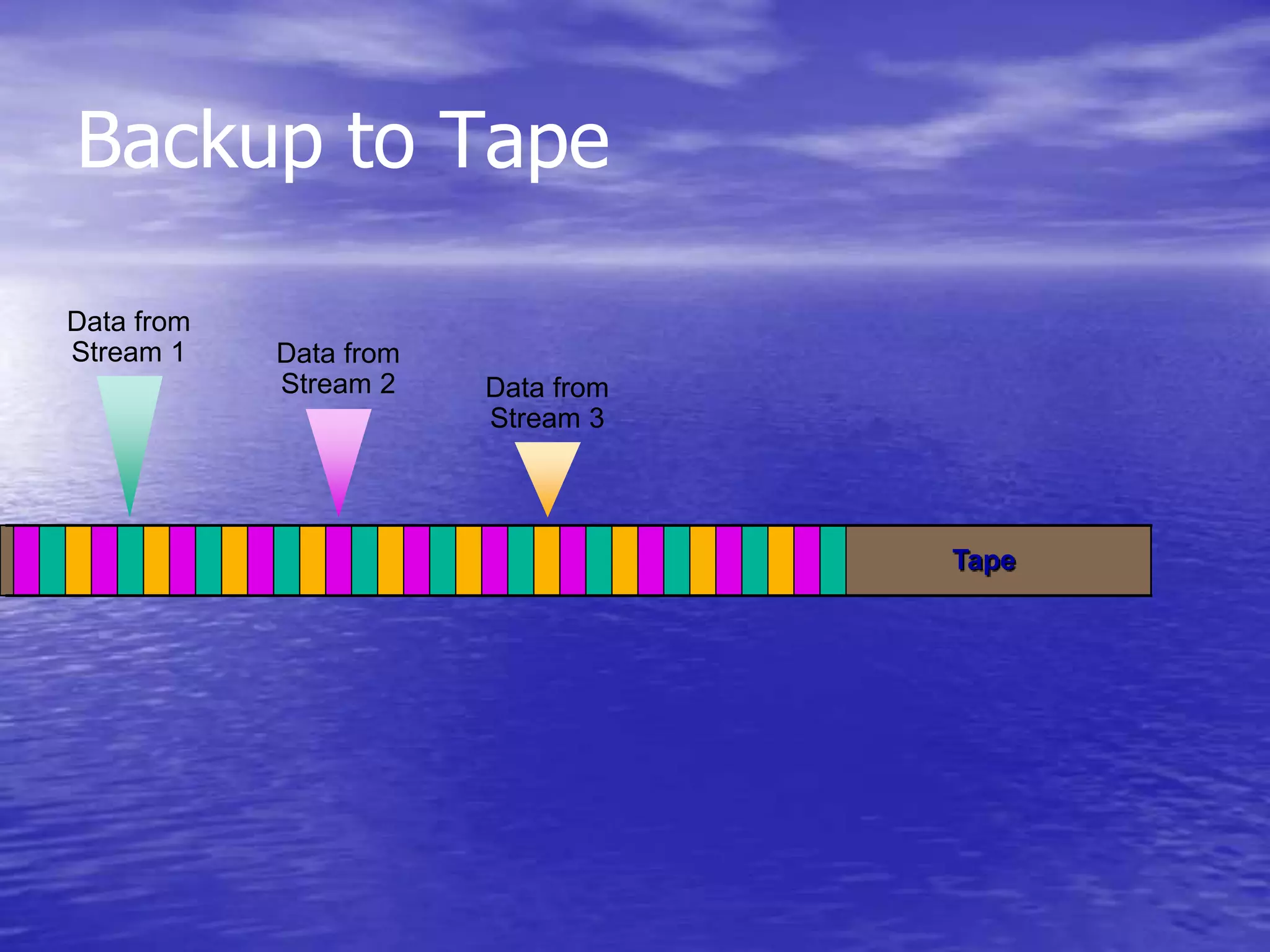
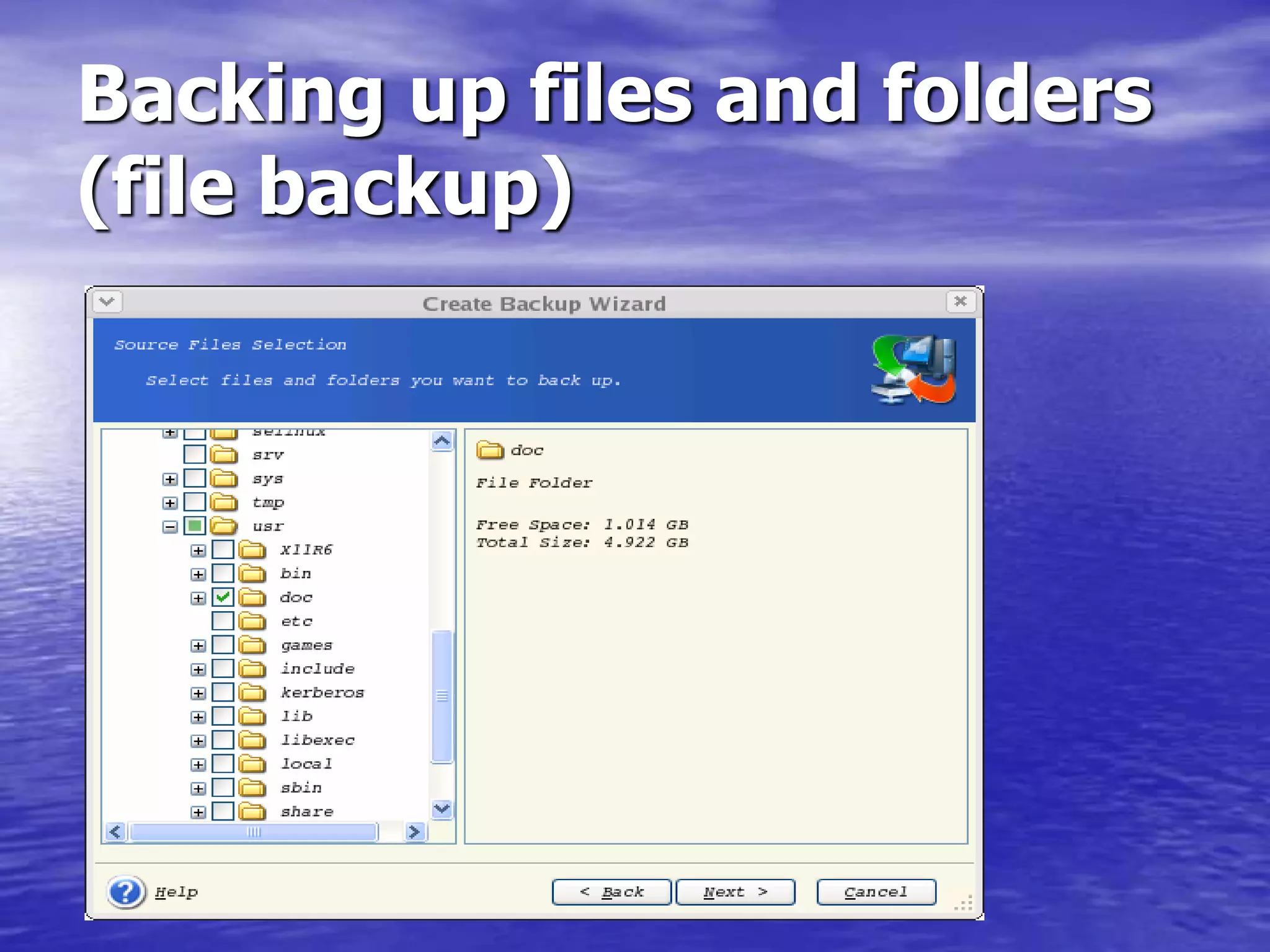
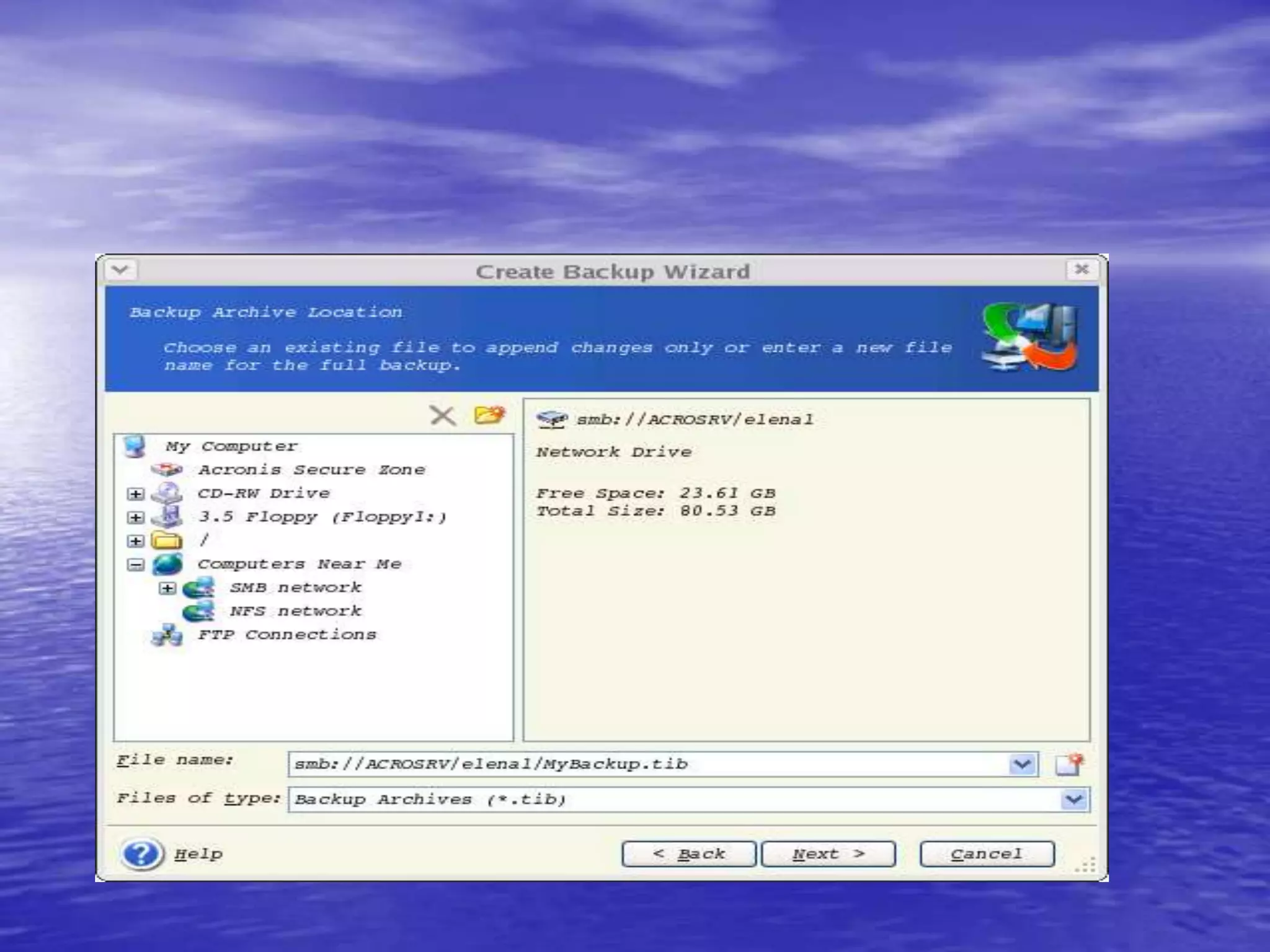
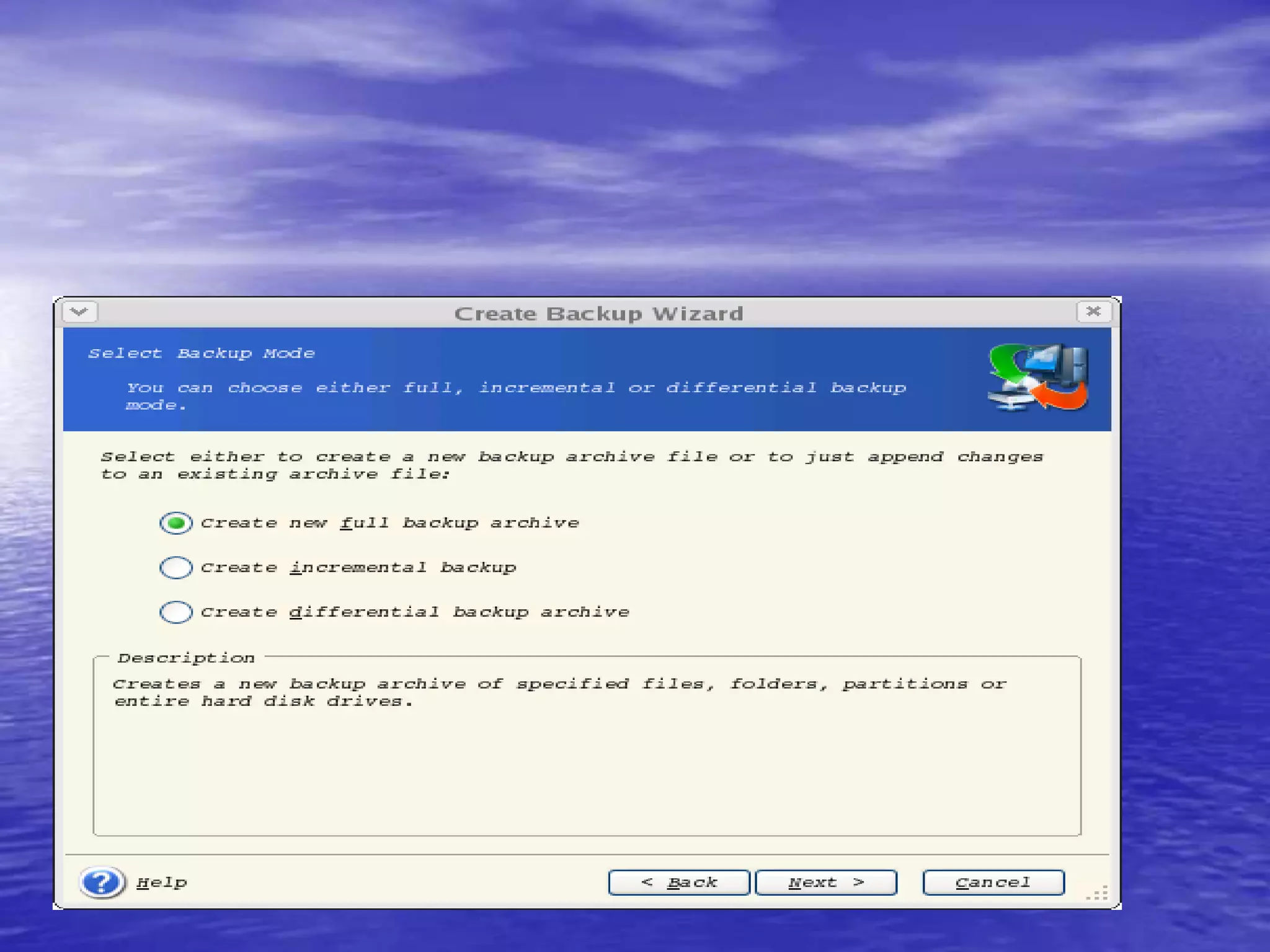
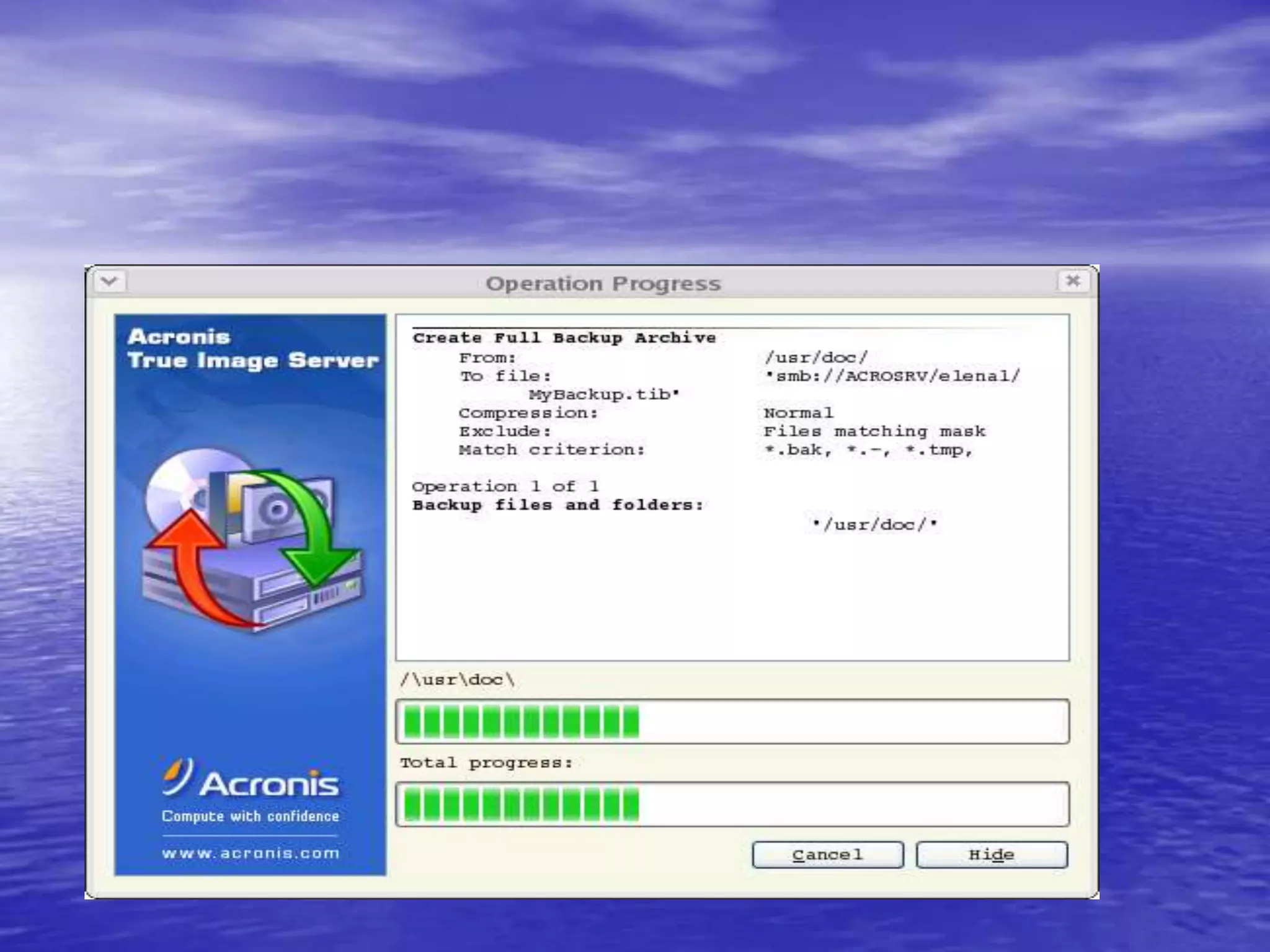
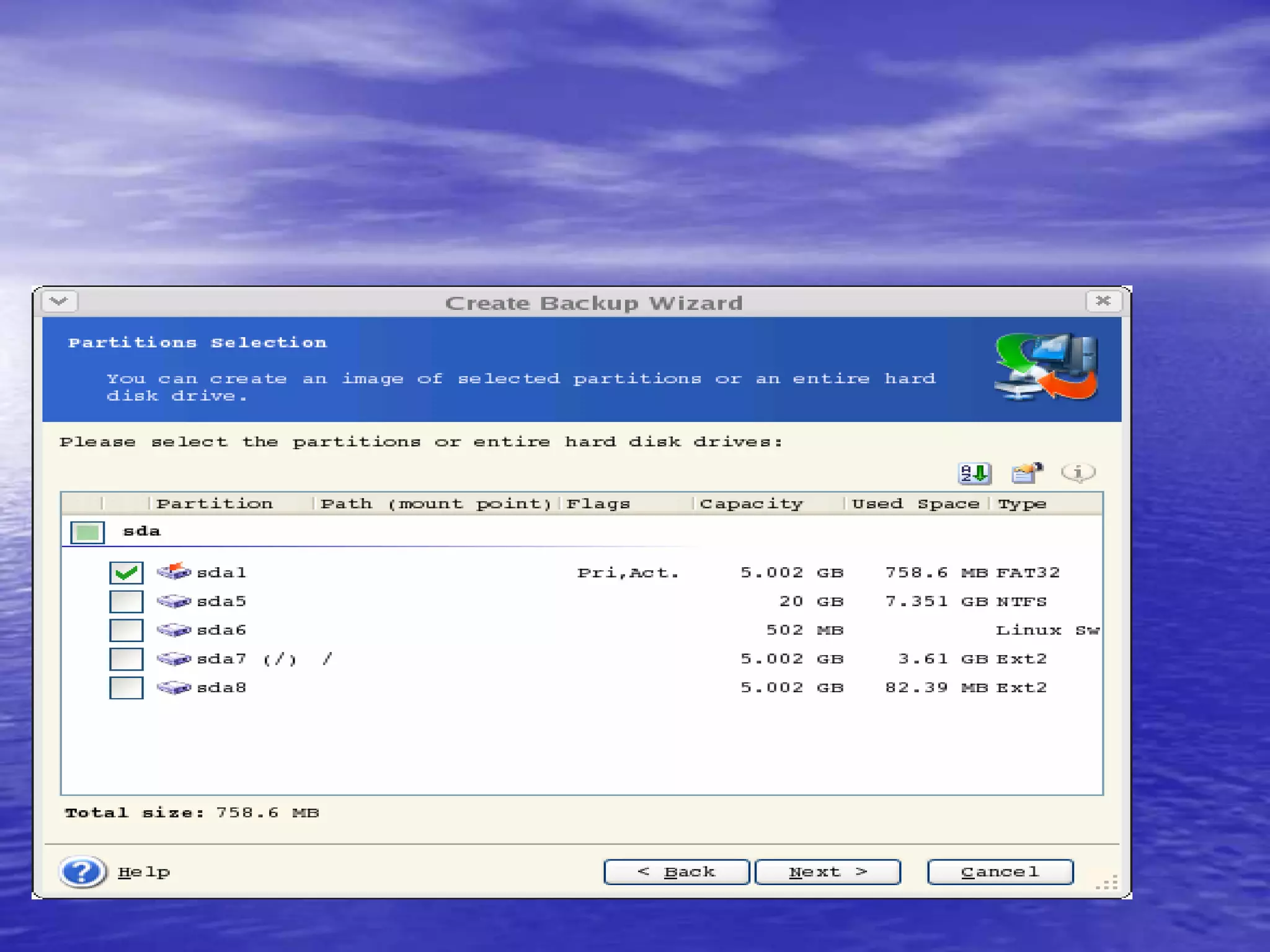
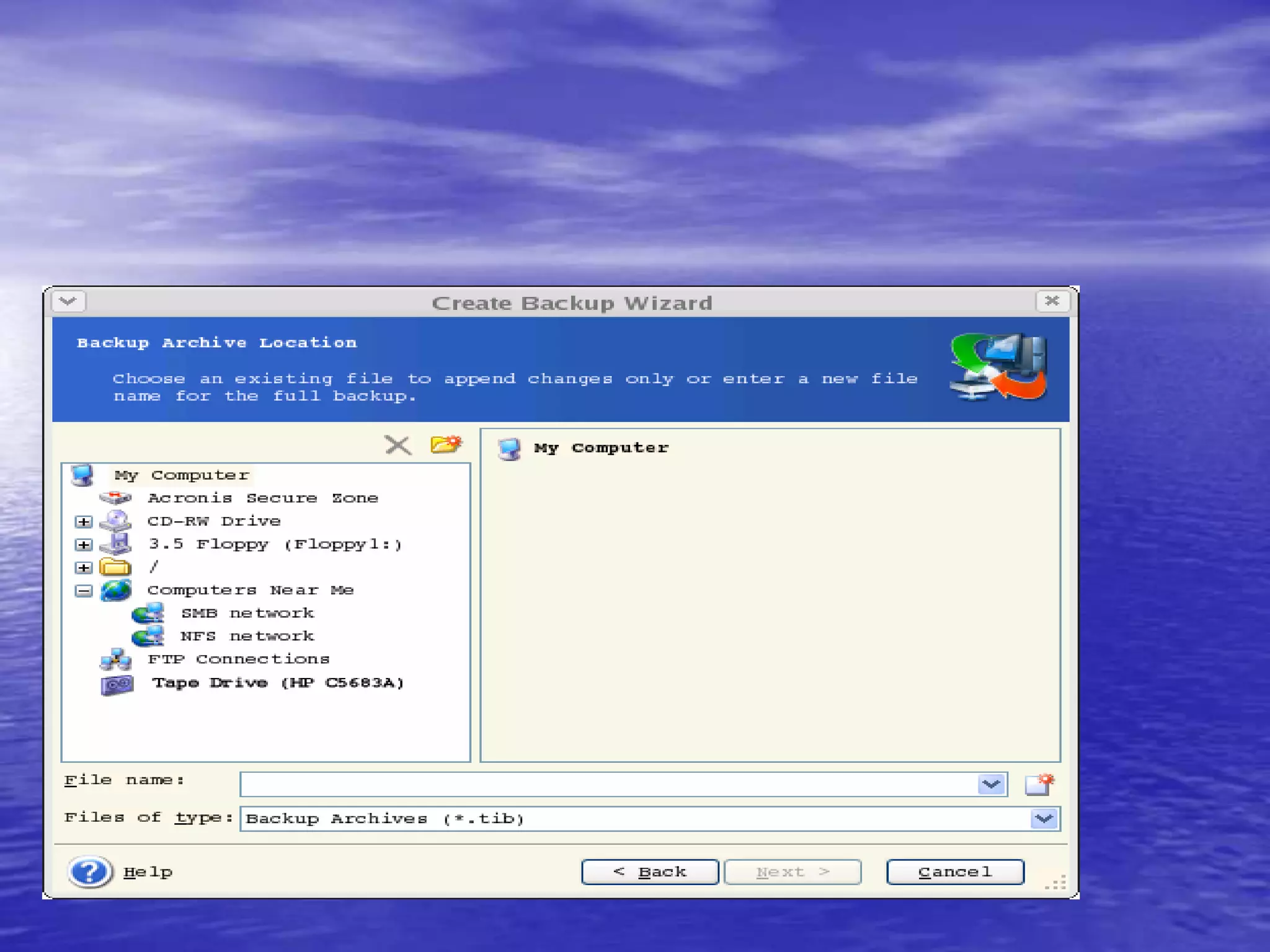
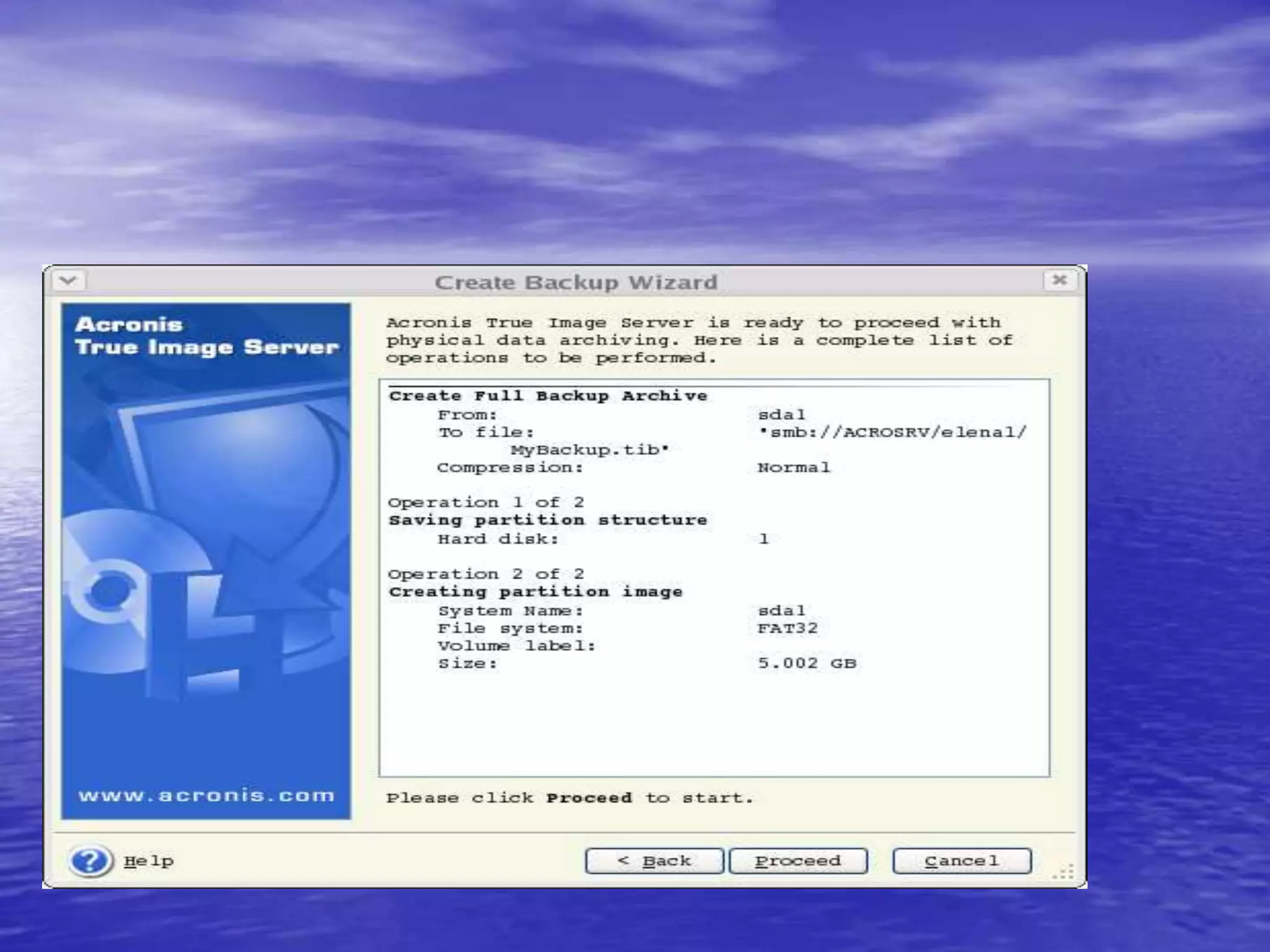
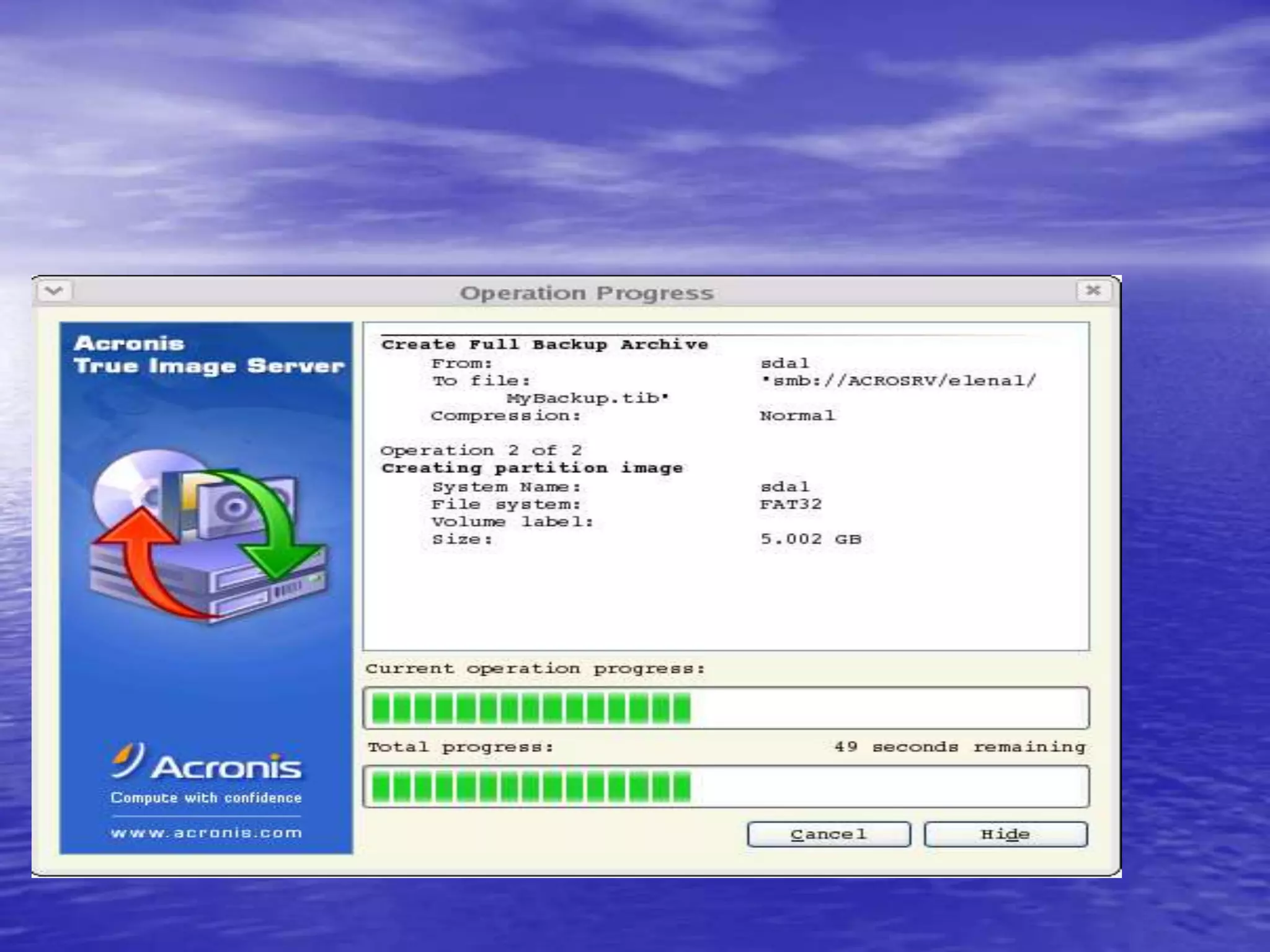
The document is a presentation on file backup strategies by Muskan Soni, aimed at Mr. Devarshi Mehta. It outlines key concepts such as the definition and purposes of backups, types of backups (full, differential, incremental), backup architecture, and recovery procedures. The presentation emphasizes the importance of having a well-documented recovery procedure and explores various backup technologies and processes.