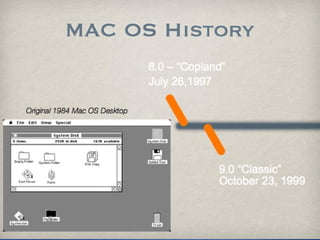
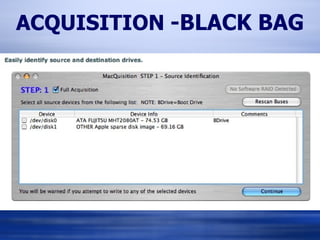
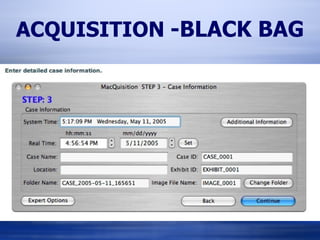
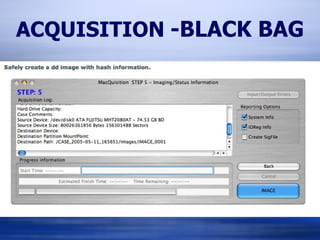
The document provides information on analyzing Macintosh computers for digital forensics purposes. It discusses the file systems, operating systems, and applications used by Macs and how to acquire disk images and examine key artifacts. Specific topics covered include acquiring memory using Target Disk Mode, disabling disk arbitration, analyzing browser data from Safari, Firefox, Internet Explorer, and AOL, and examining email from applications like Mail, Entourage and AOL. Forensic tools mentioned include dd, dcfldd, Emailchemy, and the Safari Tools browser analyzer.













































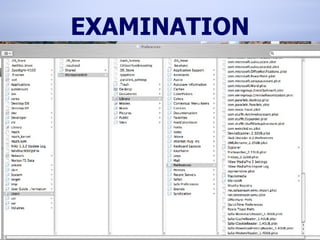


































![Command Line Find + Grep examples for filenames: “ find [path to evidence] -depth | grep “keyword” | tee [path/filename of log] | cpio -pdm [path to output/extract to]” “ find [path to evidence] -depth | grep -f [path/filename of multiple terms] | tee [path/filename of log] | cpio -pdm [path to output/extract to]”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mac-forensics-1227544996610043-9/85/Mac-Forensics-86-320.jpg)
![Command Line Find + Grep examples for contents: “ find [path to evidence] -depth -type f -exec grep -abHirl “keyword” {} \; | tee [path/filename of log] | cpio -pdm [path to output/extract to]” “ find [path to evidence] -depth -type f -exec grep -abHirlf [path/filename of multiple terms] {} \; | tee [path/filename of log] | cpio -pdm [path to output/extract to]”](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mac-forensics-1227544996610043-9/85/Mac-Forensics-87-320.jpg)
