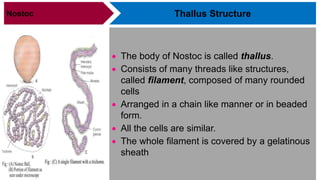
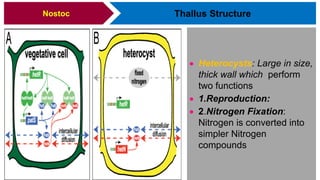
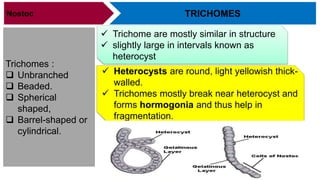
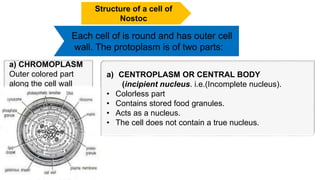
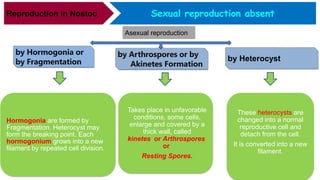
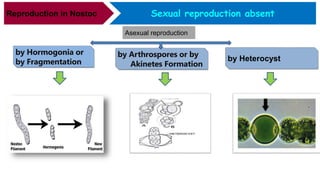
Nostoc is a genus of cyanobacteria that is commonly found in alkaline soils, moist rocks, water ponds, streams, and lakes. The body, or thallus, of Nostoc consists of many filaments made up of rounded cells arranged in a chain. The filaments are embedded in a jelly-like mass and covered by a gelatinous sheath. Cells contain a centroplasm and chromoplasm but not a true nucleus. Nostoc reproduces asexually through fragmentation of filaments, formation of hormogonia, or production of thick-walled resting cells called akinetes. It can fix atmospheric nitrogen and plays an important ecological role through photosynthesis.