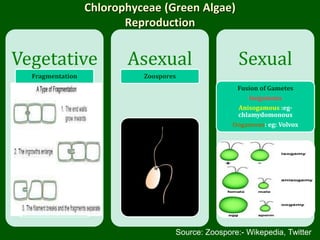
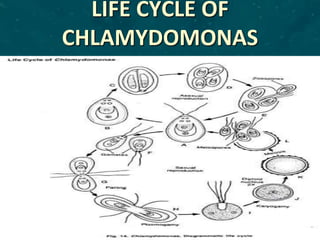
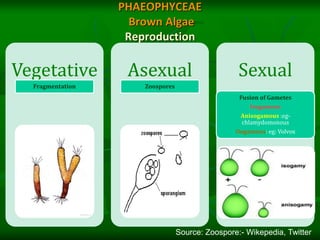
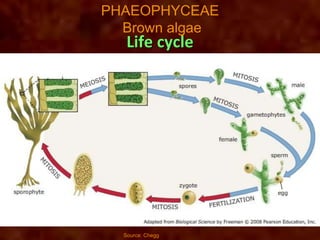
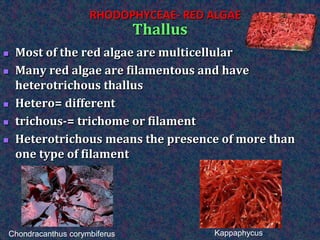
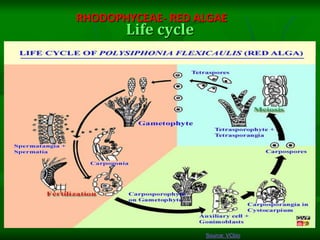
This document discusses the classification and characteristics of algae. It describes the three main groups of algae - Chlorophyceae (green algae), Phaeophyceae (brown algae) and Rhodophyceae (red algae) - based on their dominant pigments, cell structure and life cycles. Key aspects covered include the photosynthetic pigments and organelles of each group, their reproductive mechanisms, importance as food sources, and commercial uses of substances extracted from them like agar and alginates.