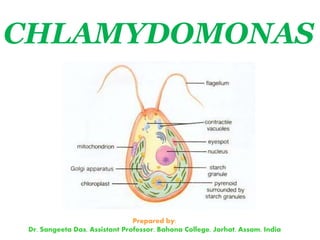
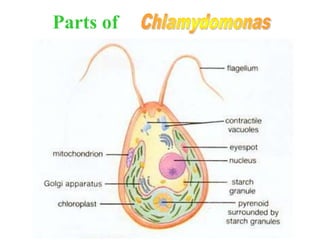
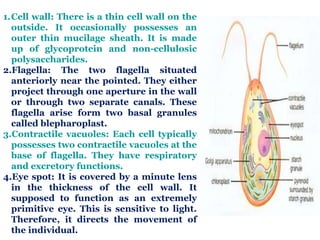
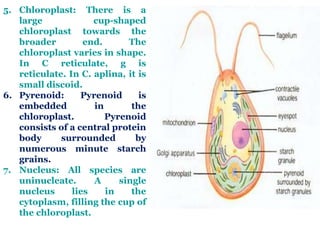
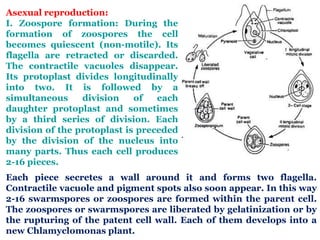
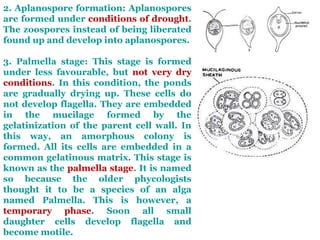
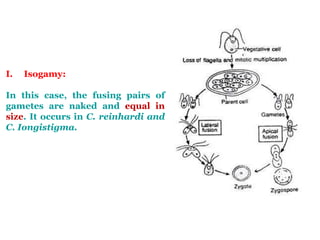
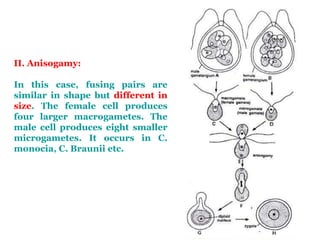
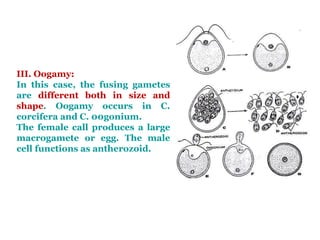
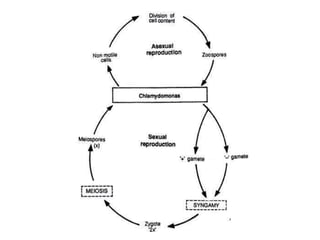
Chlamydomonas is a single-celled green alga that is found in fresh water environments like ponds, ditches, and wet soil. It reproduces both asexually through the production of zoospores and sexually through isogamy, anisogamy, or oogamy depending on the species. The cell contains a cup-shaped chloroplast, pyrenoid, two flagella, contractile vacuoles, and sometimes an eye spot. Chlamydomonas is used as a model organism in research due to its simple structure and life cycle.