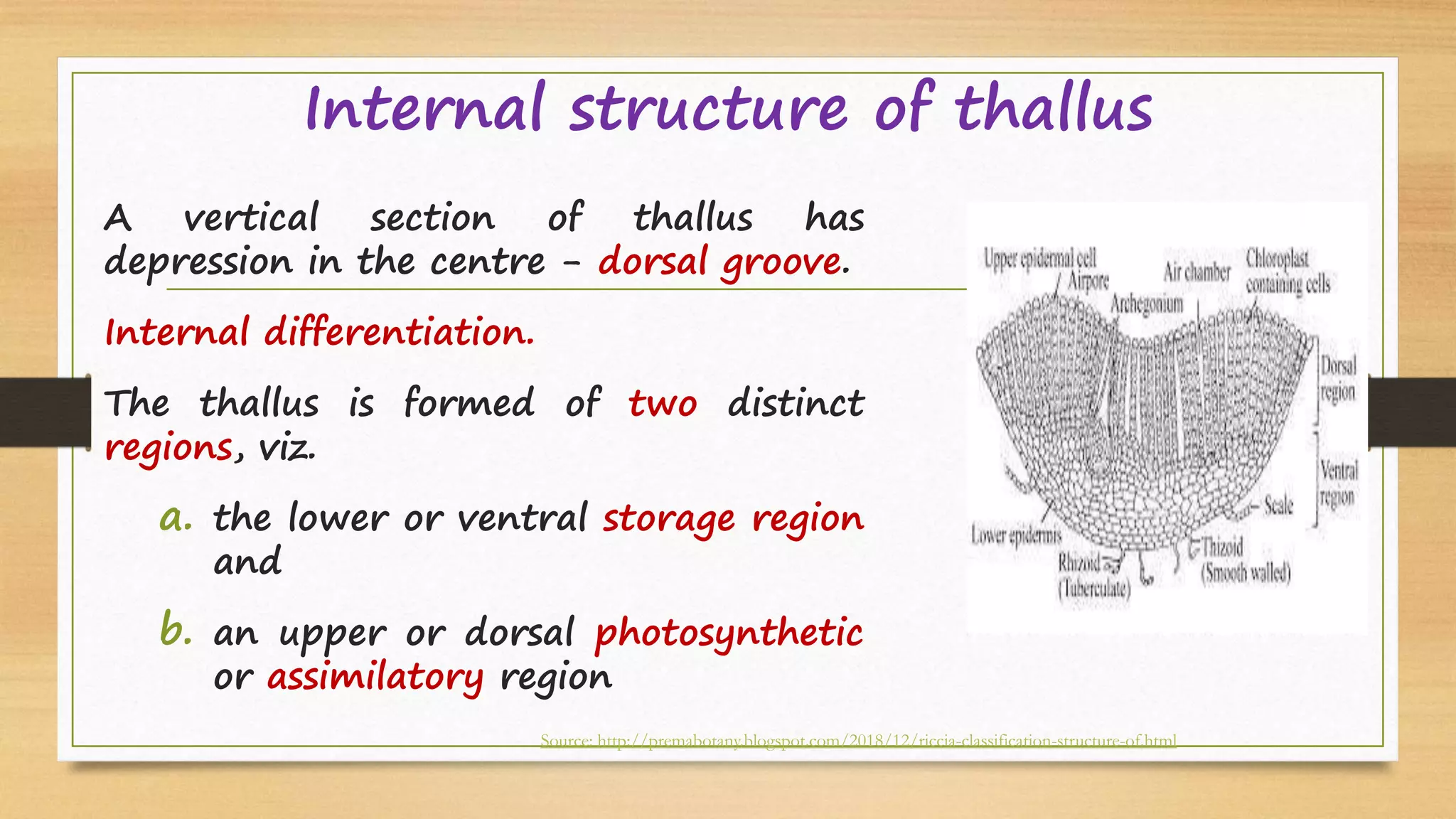
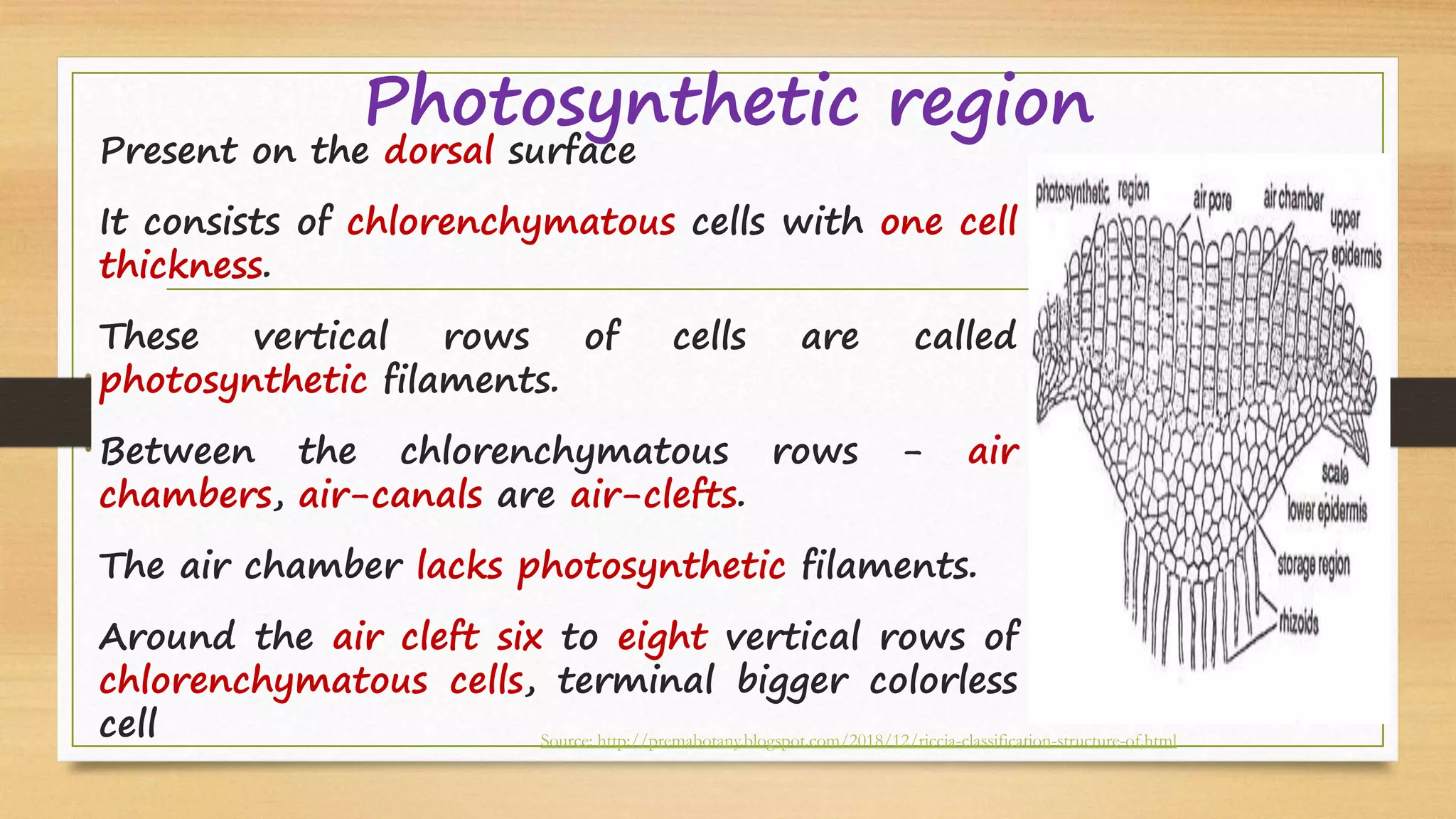
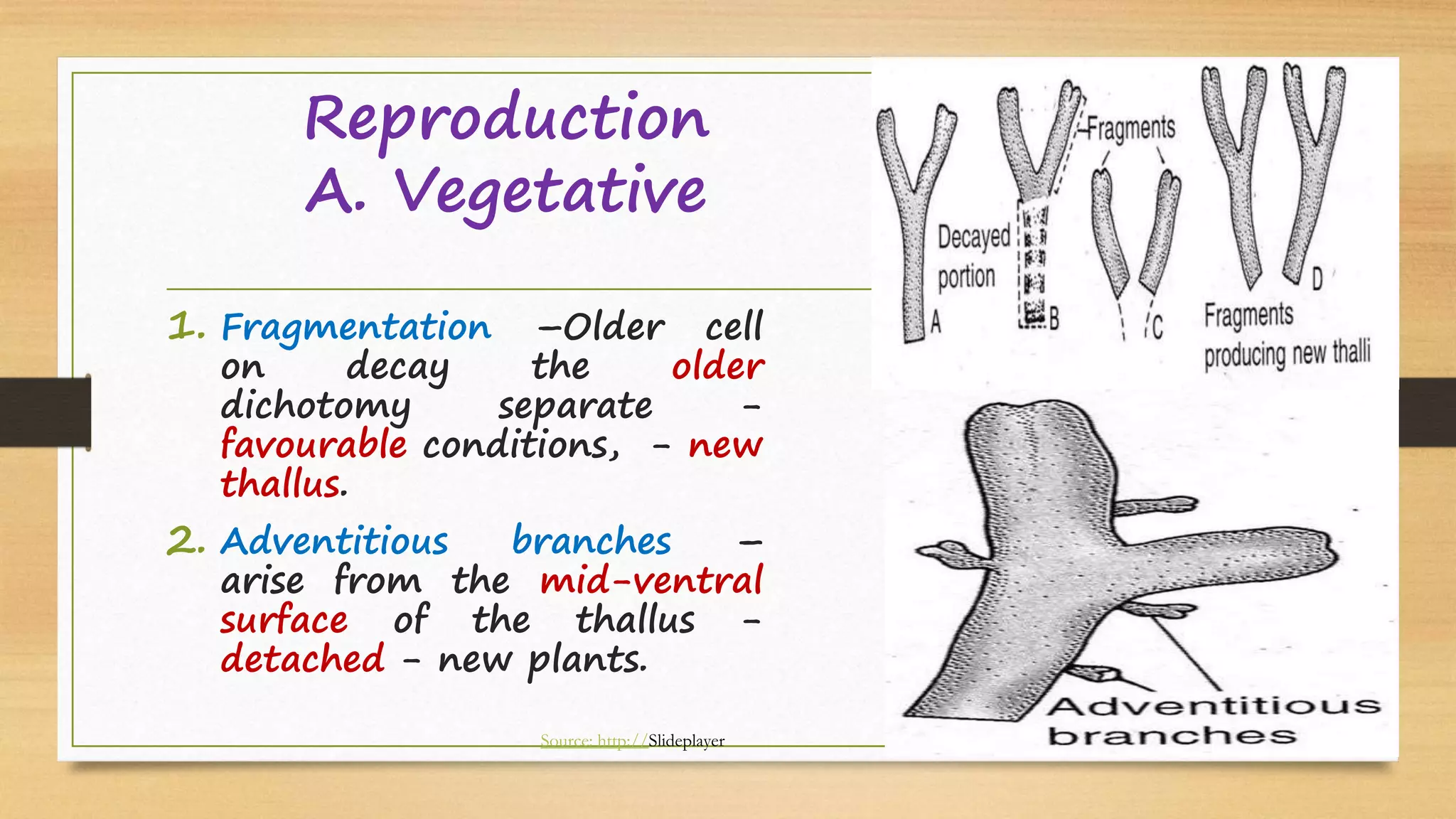
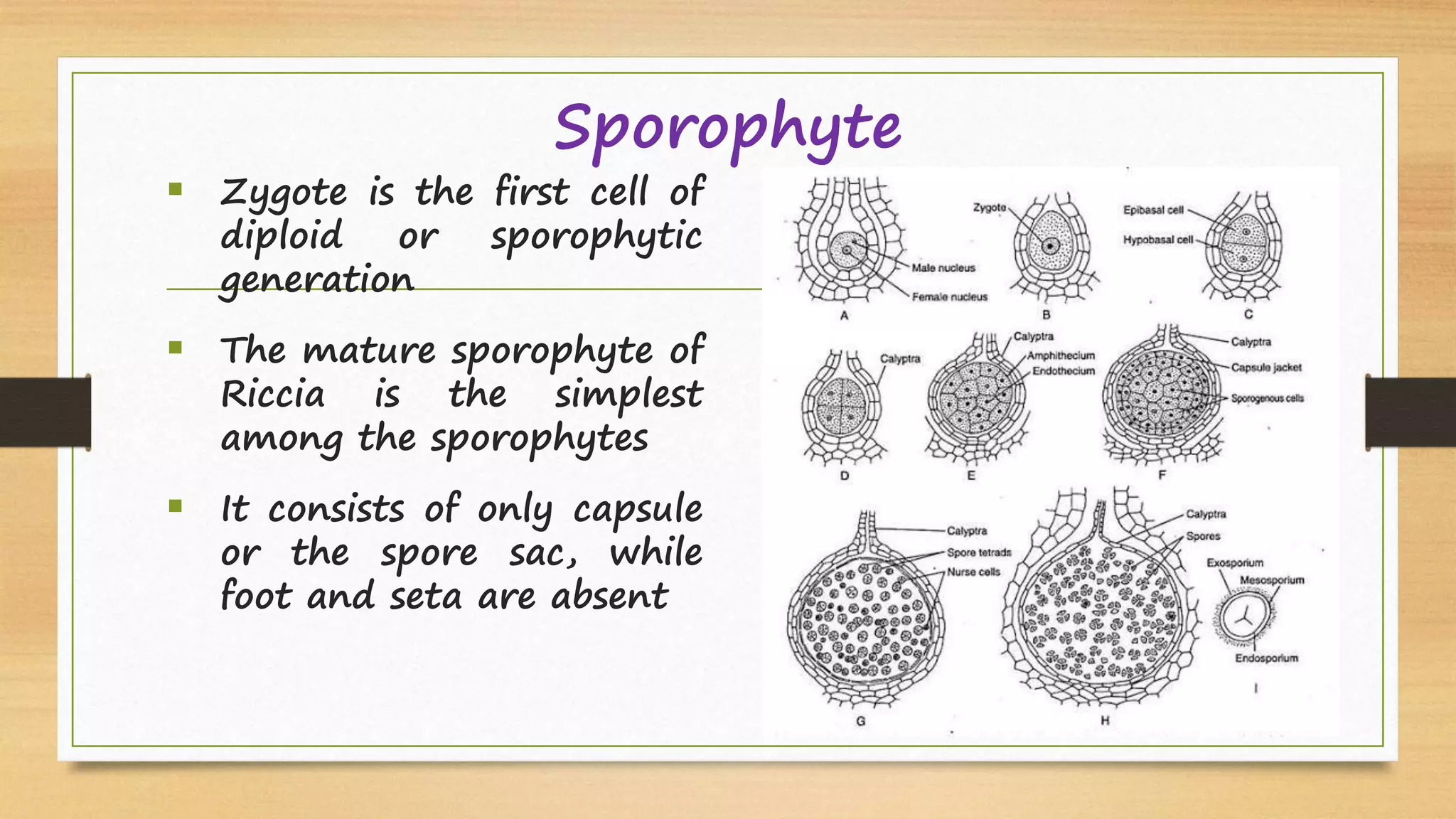
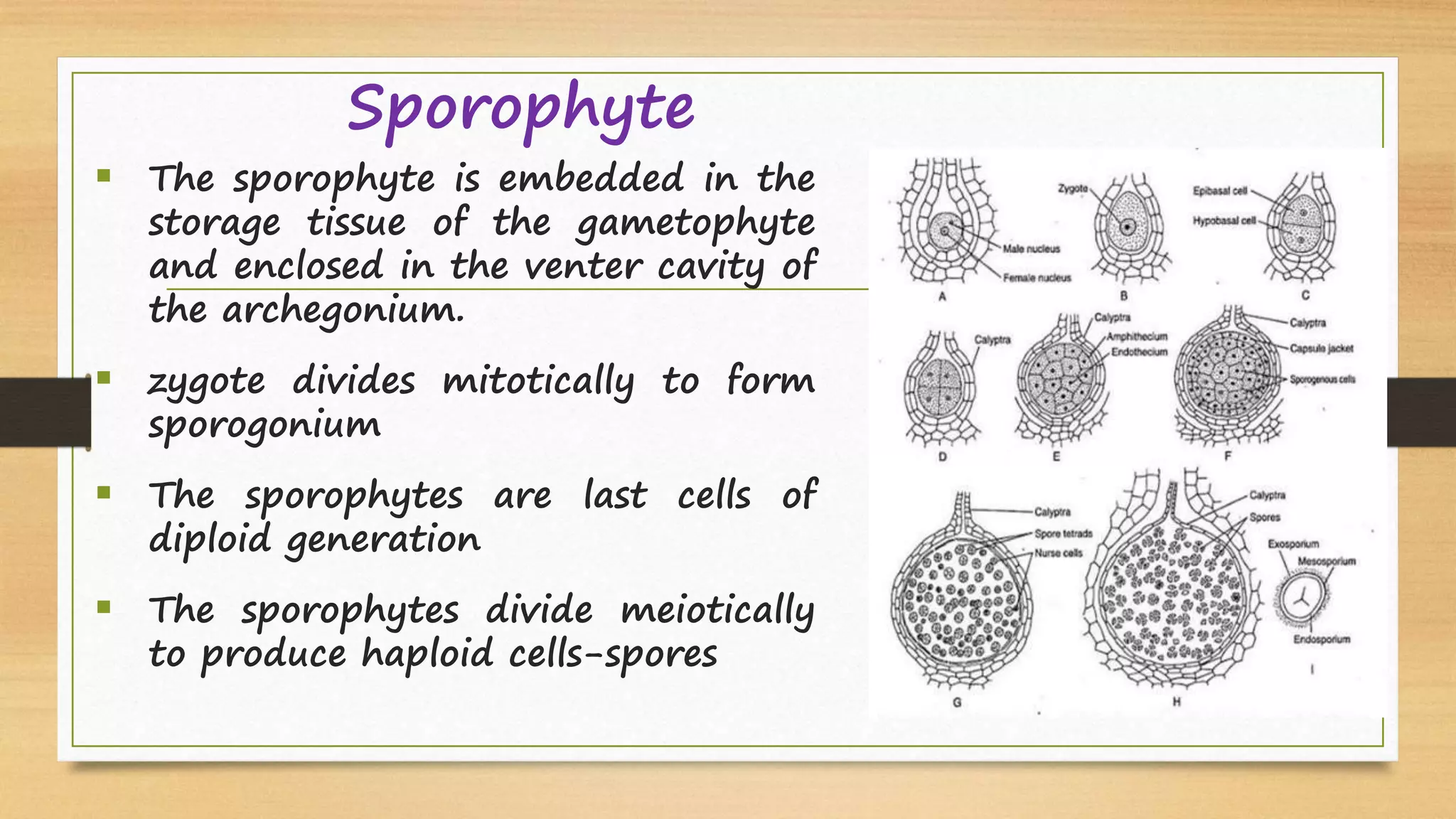
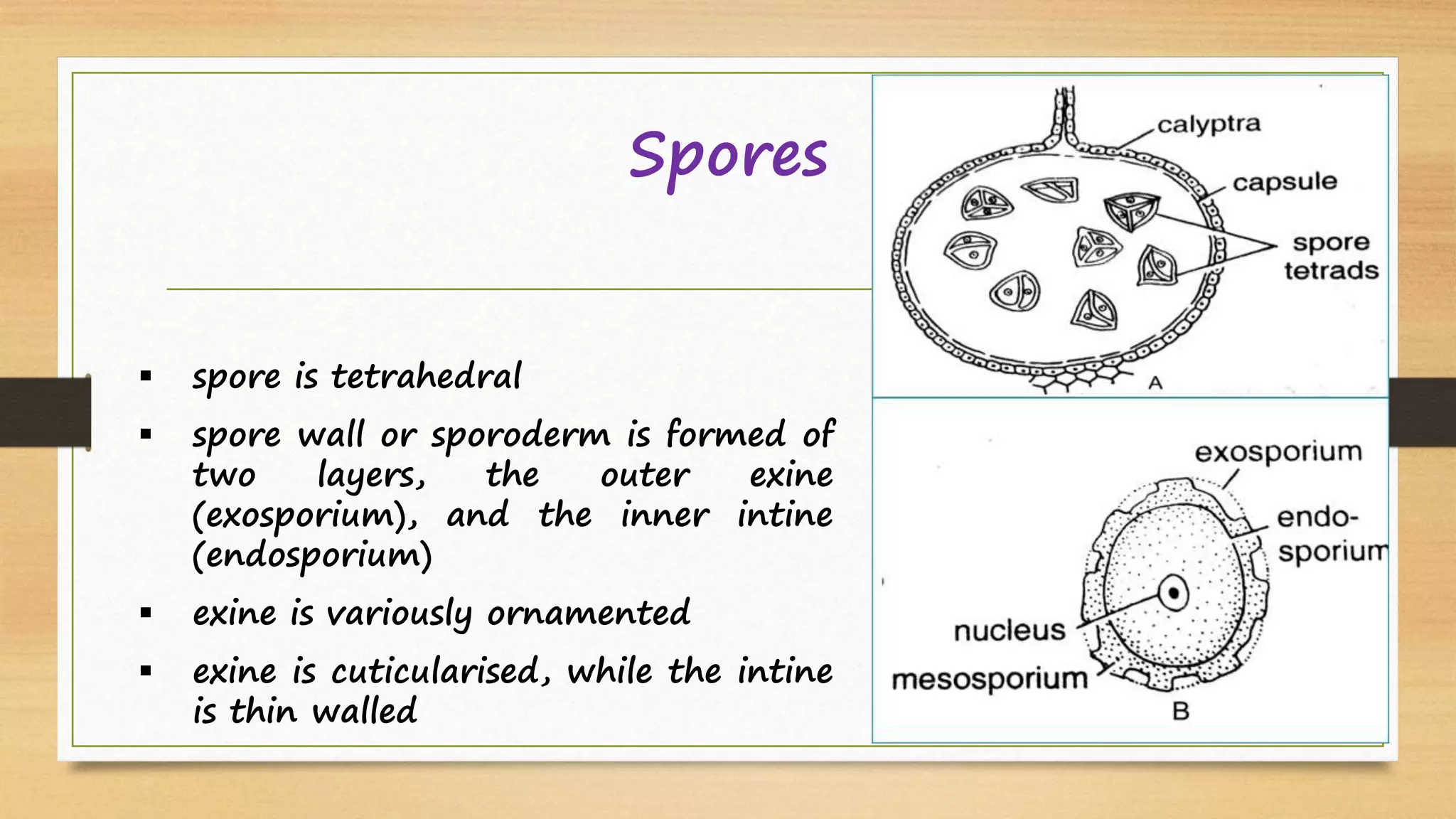
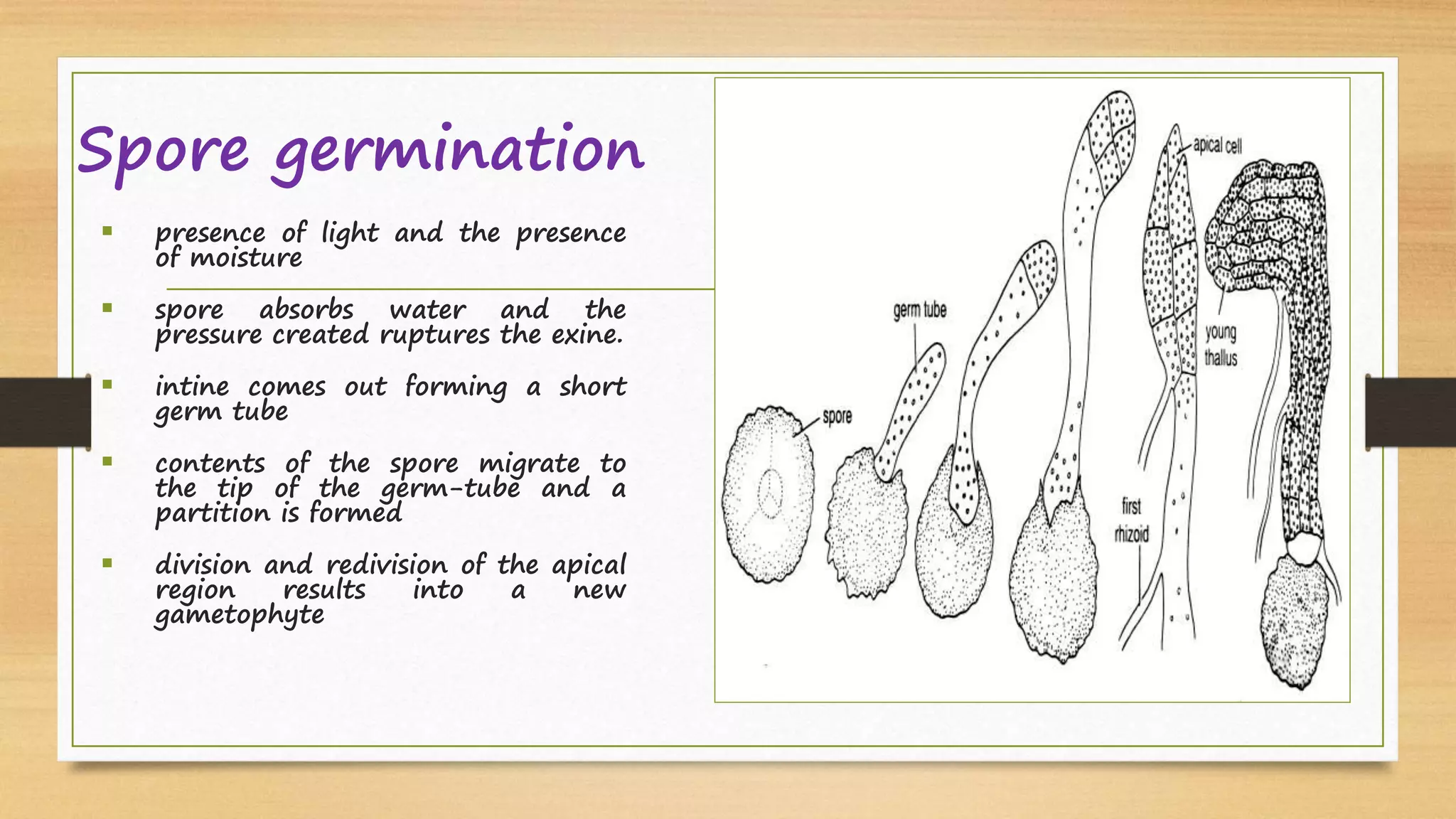
Riccia is a genus of liverworts that includes around 138 species. It mainly grows in damp soil and shady places. The thallus has dichotomous branching forming a circular rosette. It has a ventral storage region and dorsal photosynthetic region. Reproduction can occur vegetatively through fragmentation, adventitious branches, tubers, or persistent apices, or sexually through antheridia and archegonia that produce sperm and eggs. Fertilization results in a sporophyte embedded in the gametophyte that produces spores through meiosis, completing the alternation of generations between haploid gametophyte and diploid sporophyte generations.