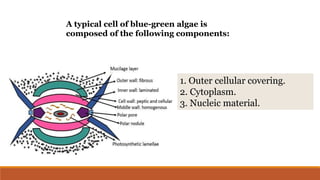
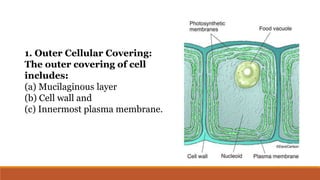
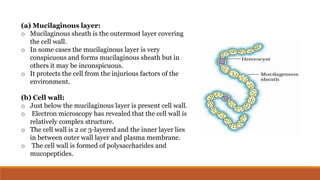
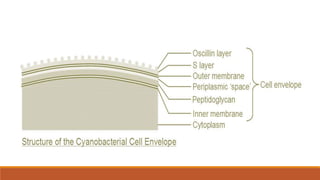
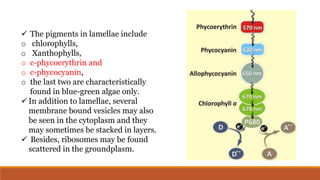
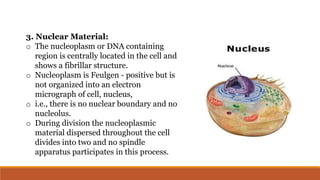
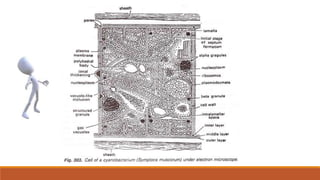
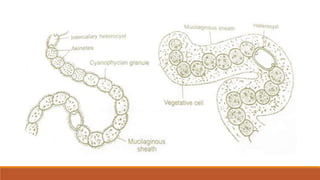
Cyanobacteria are photosynthetic, aquatic bacteria vital for Earth's ecosystems, contributing to nitrogen fixation, shaping evolution, and generating atmospheric oxygen. Their unique structure includes a protective mucilaginous sheath, a complex cell wall, and specific pigments, which make them important in both agriculture and ecological contributions. Nostoc, a type of cyanobacteria, has significant reproductive strategies and ecological roles, including enhancing soil nutrient value, producing biofuels, and potential drug development.