The document discusses four nonparametric statistical tests:
1. The Wilcoxon Rank Sum Test (also called the Mann-Whitney U Test) compares the medians of two independent samples and is an alternative to the independent t-test.
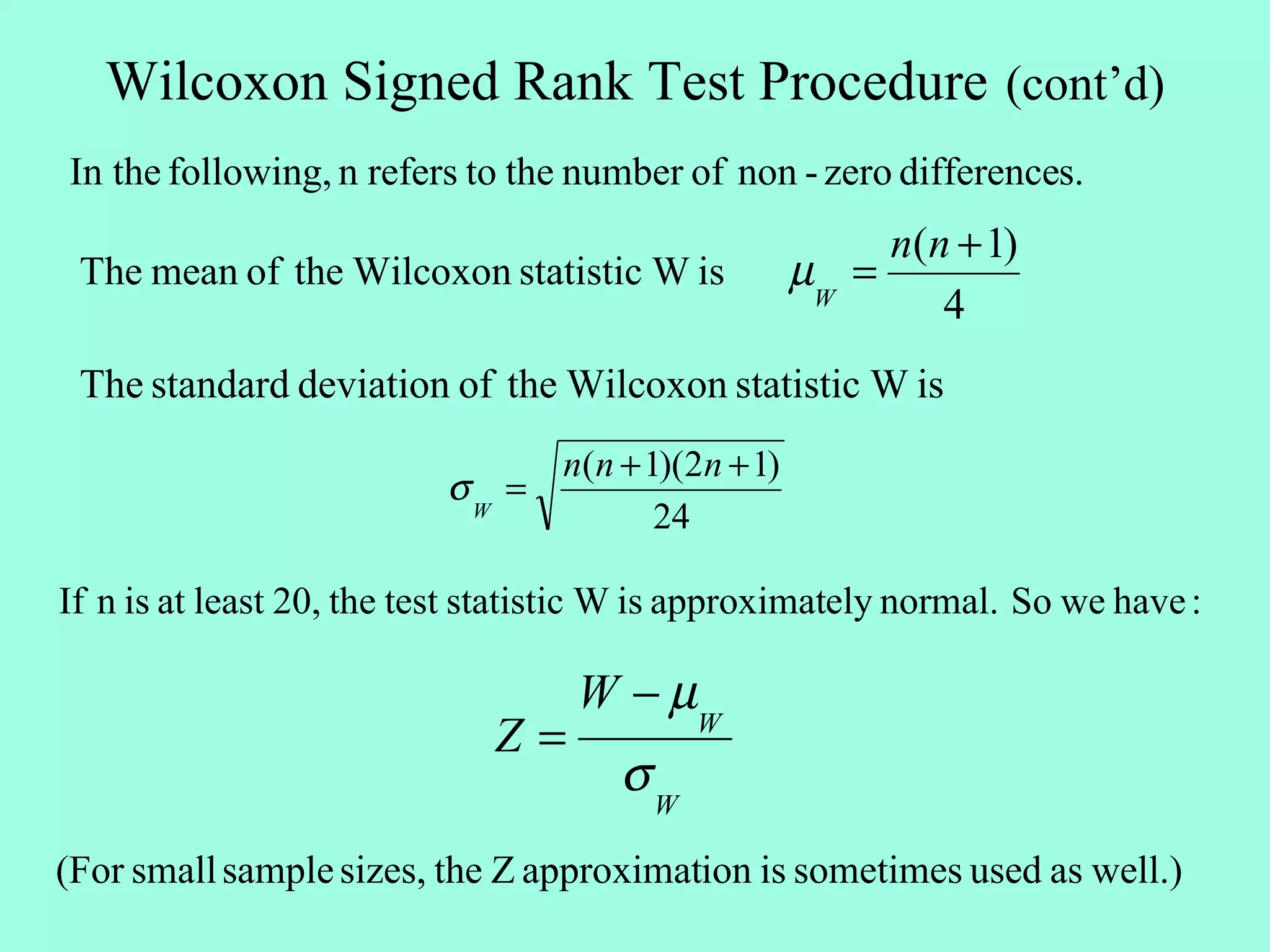
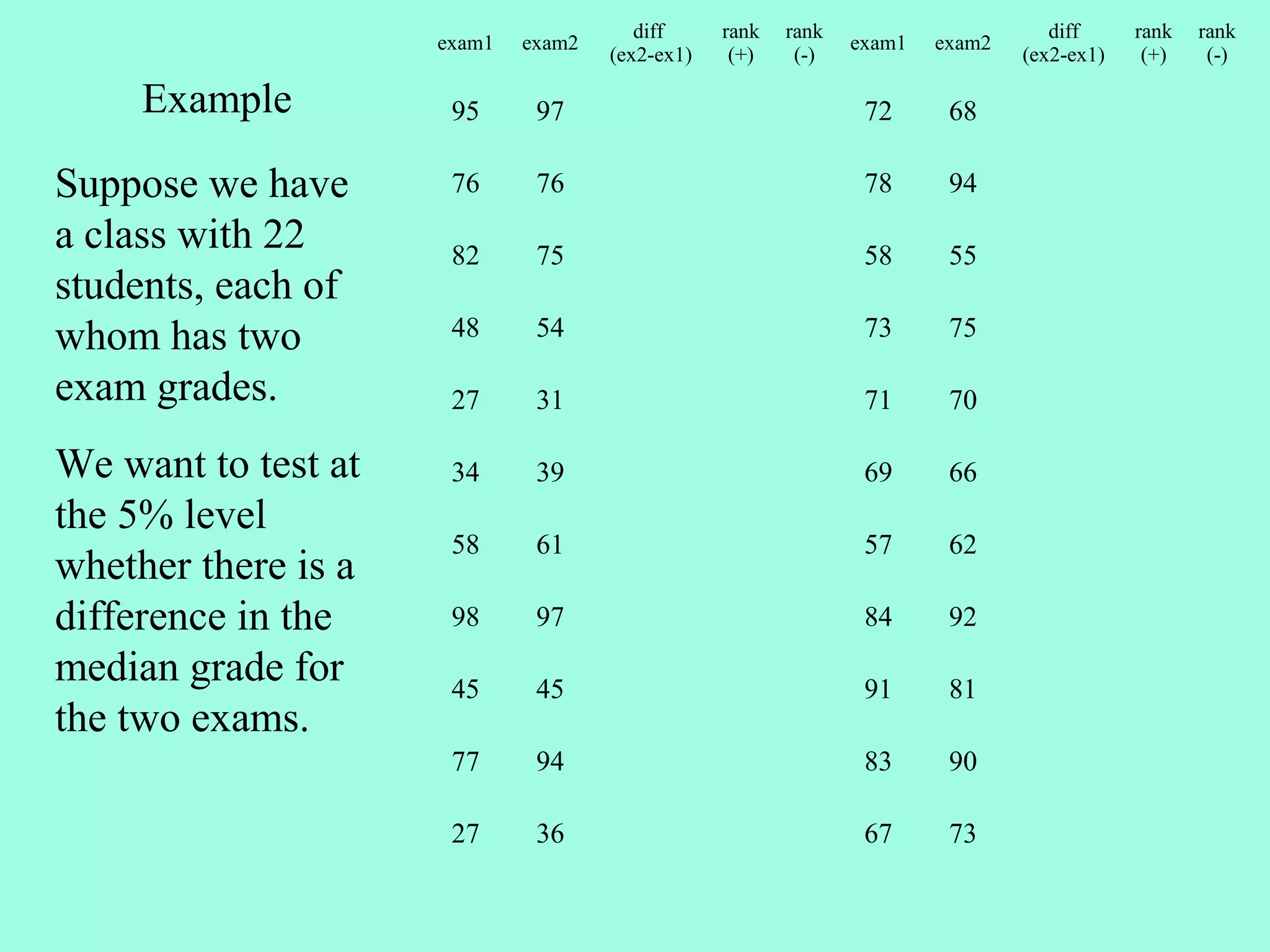
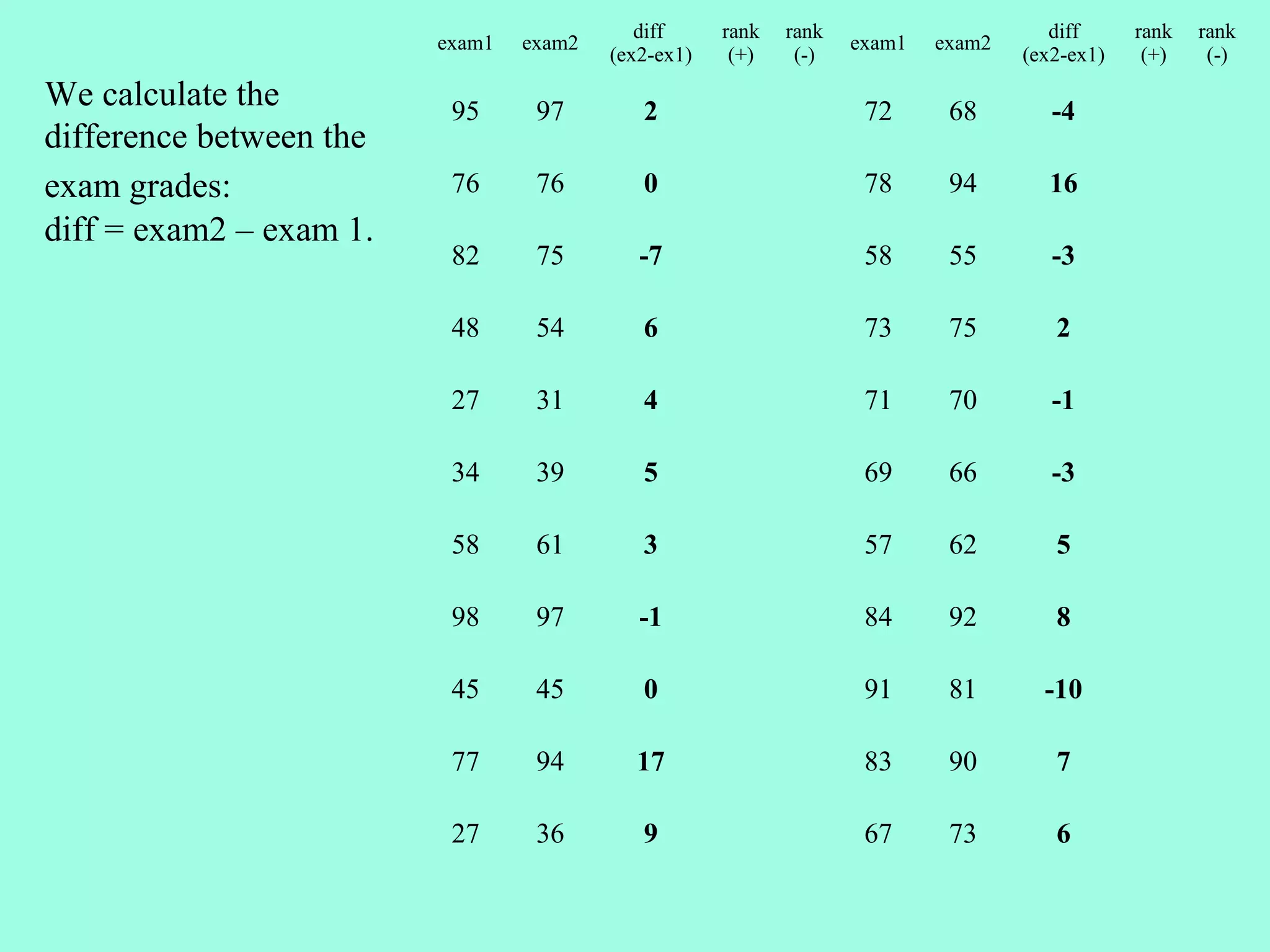
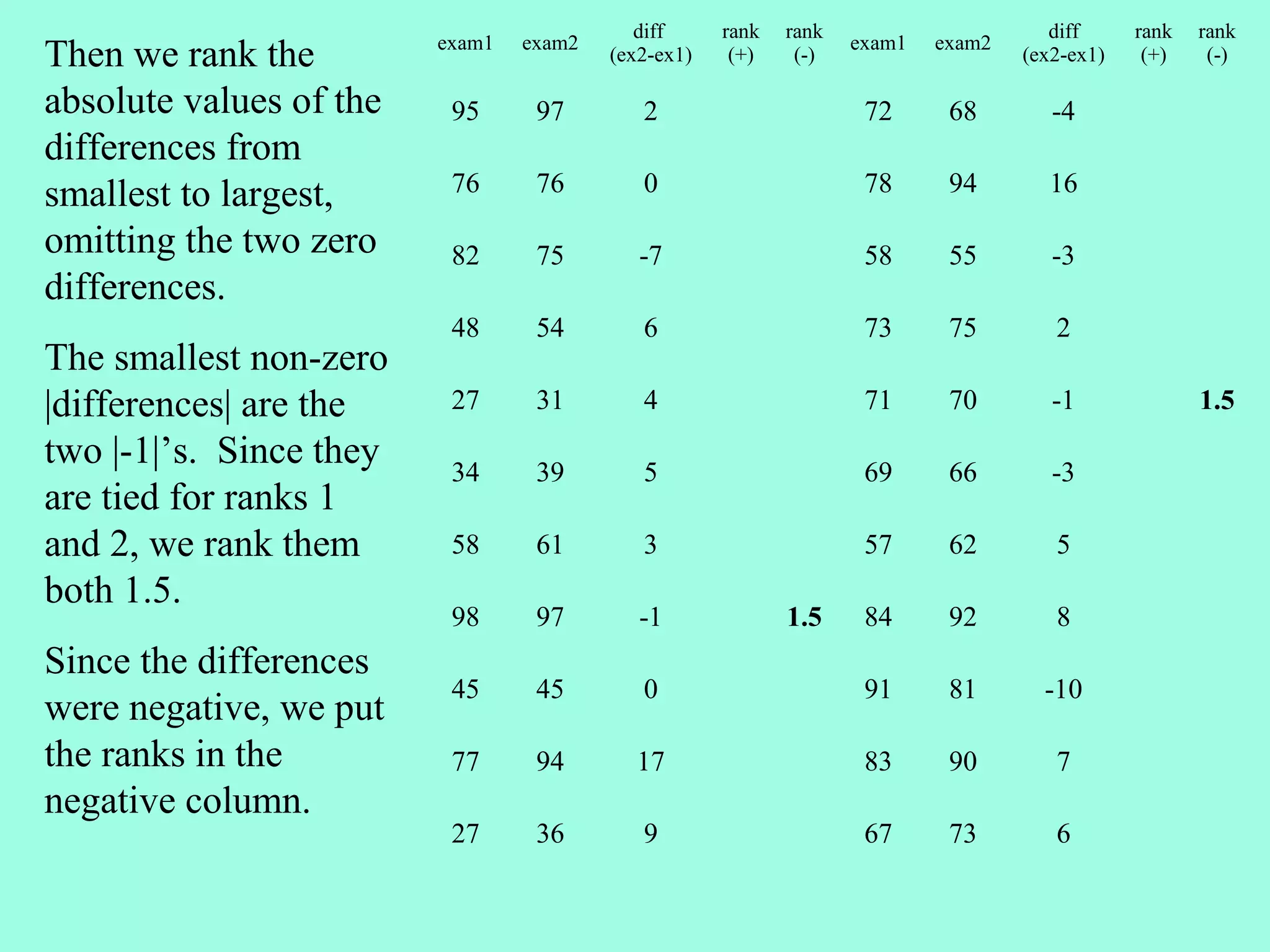
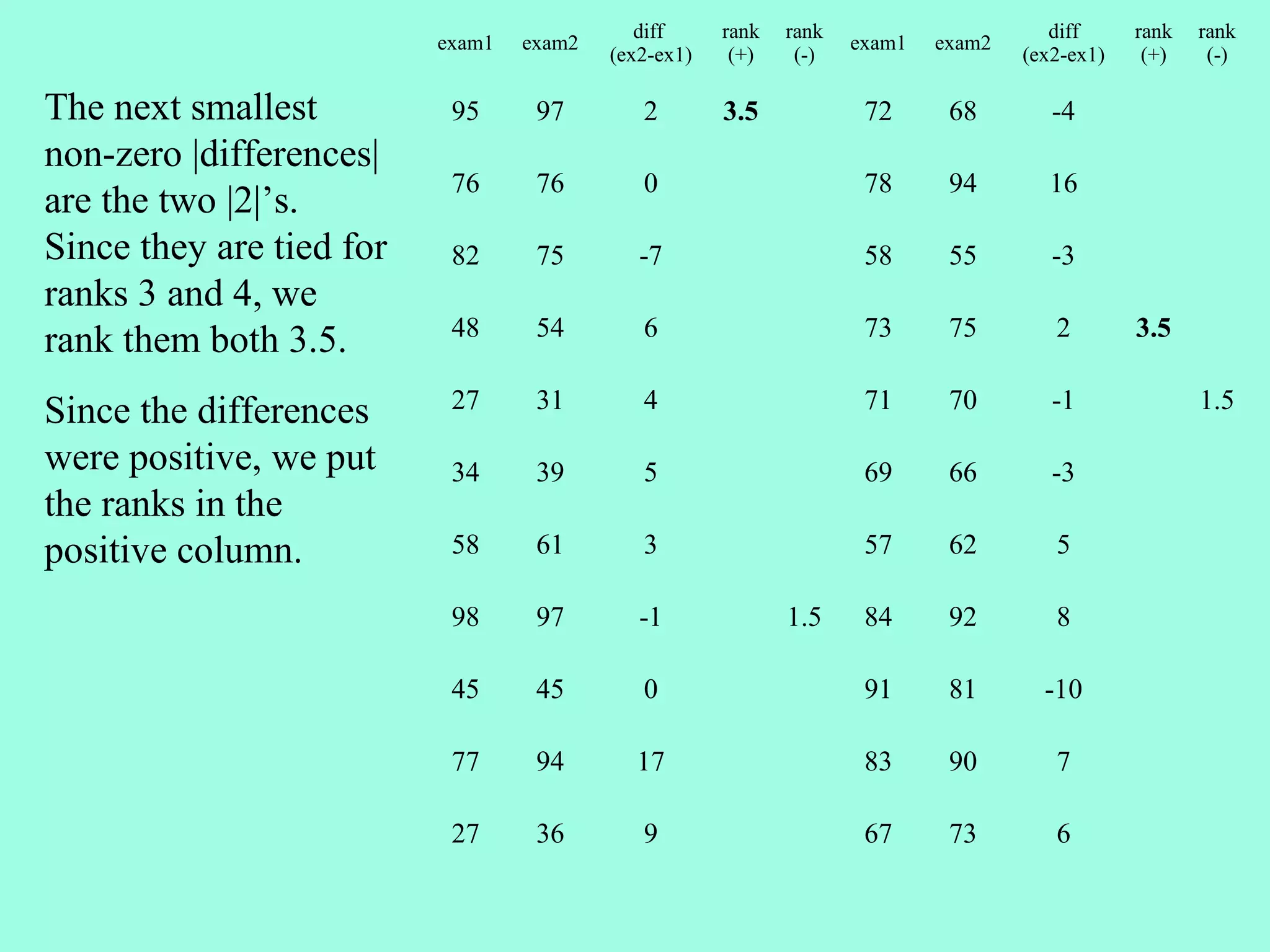
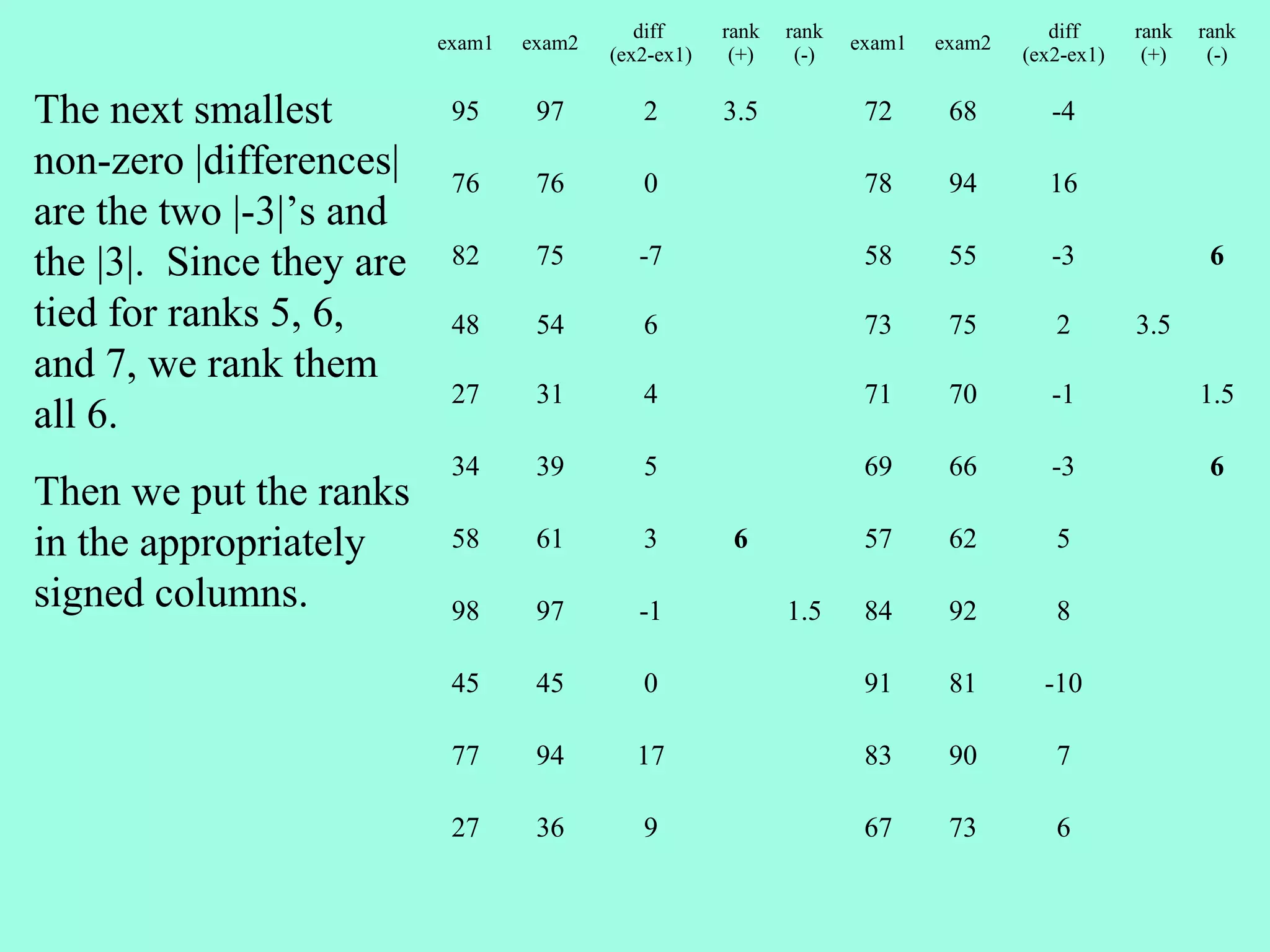
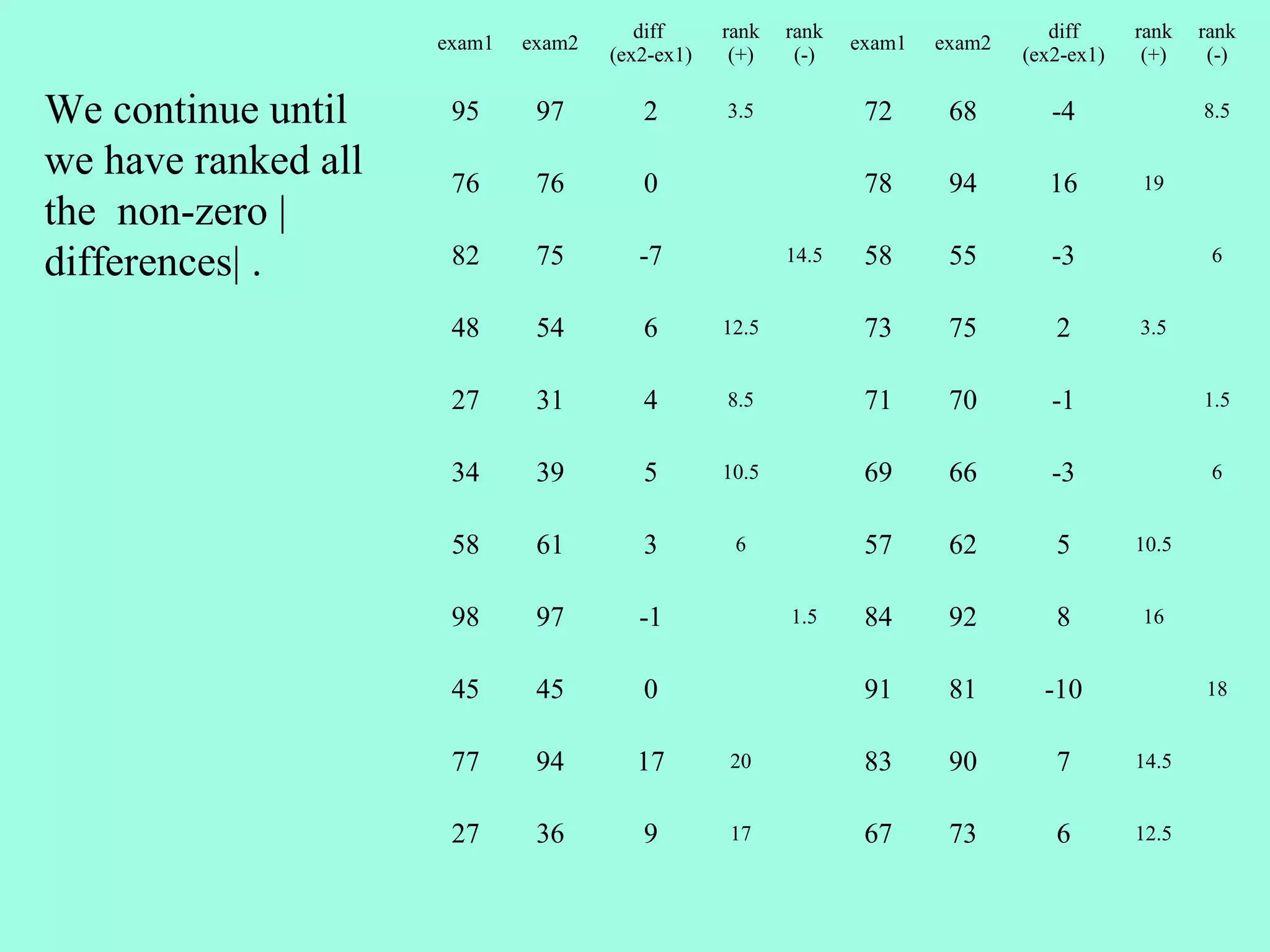
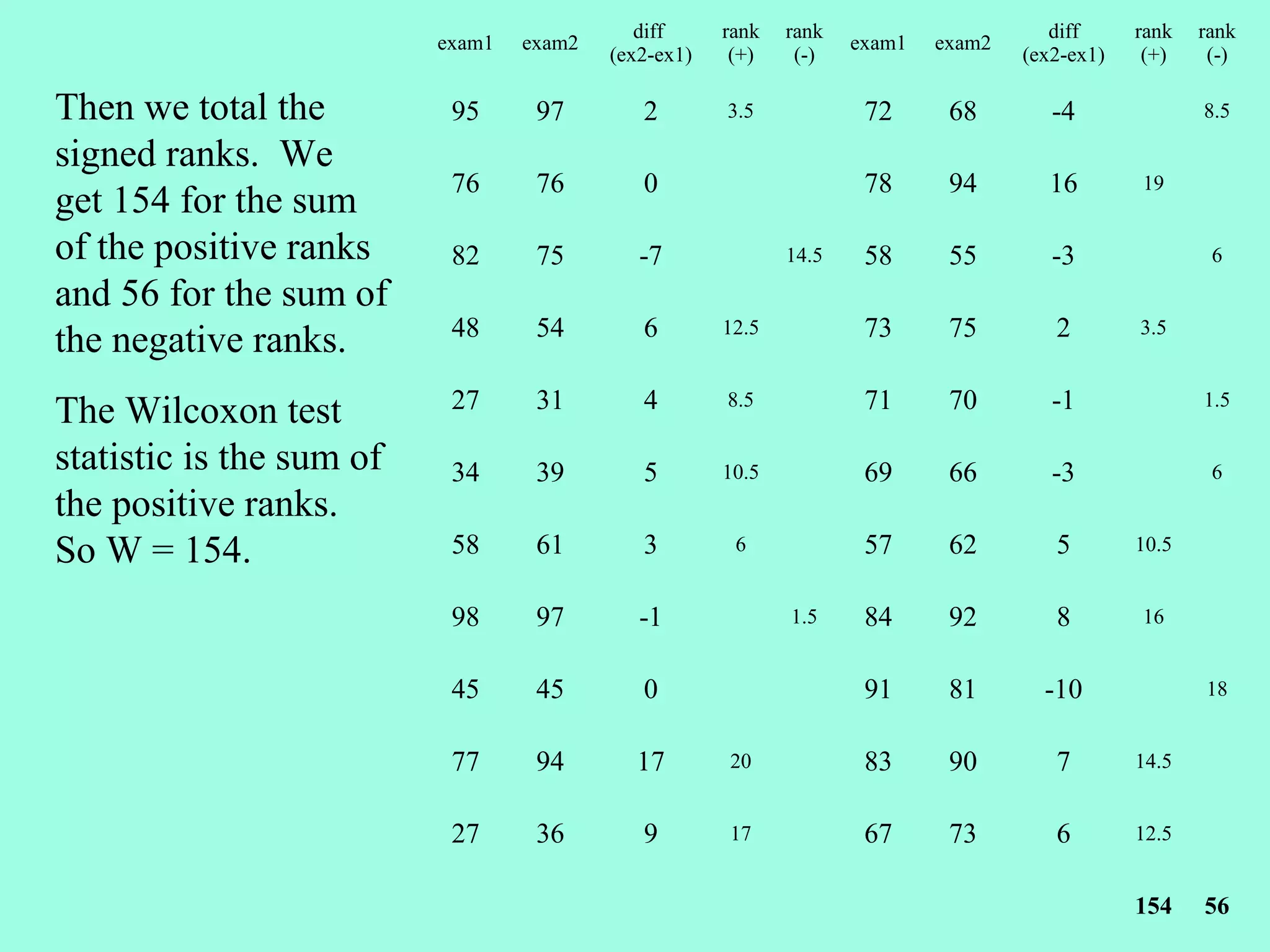
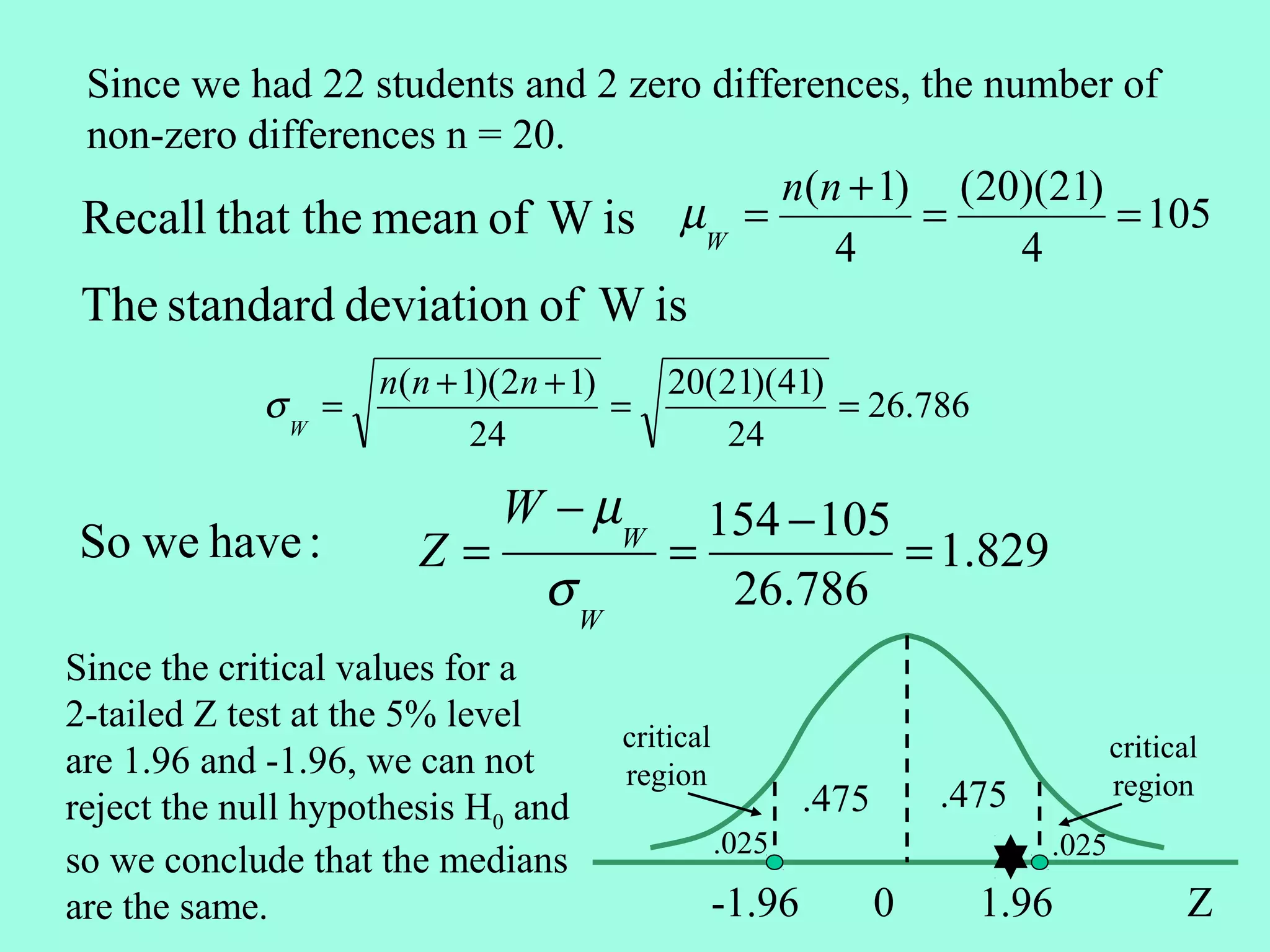
2. The Wilcoxon Signed Rank Test compares the medians of two dependent/paired samples and is an alternative to the paired t-test. It calculates the differences between pairs, ranks their absolute values, and sums the ranks of positive differences.
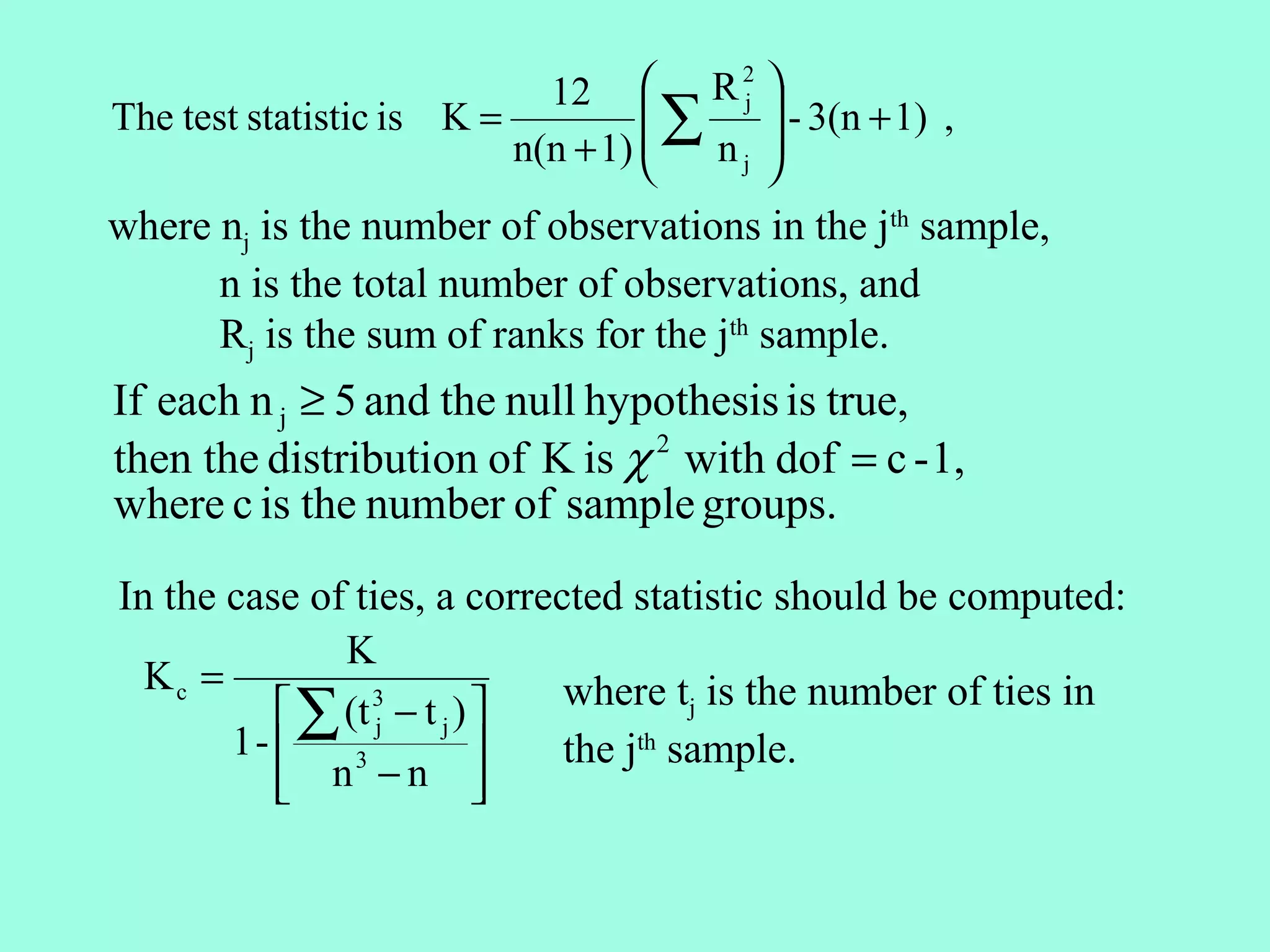
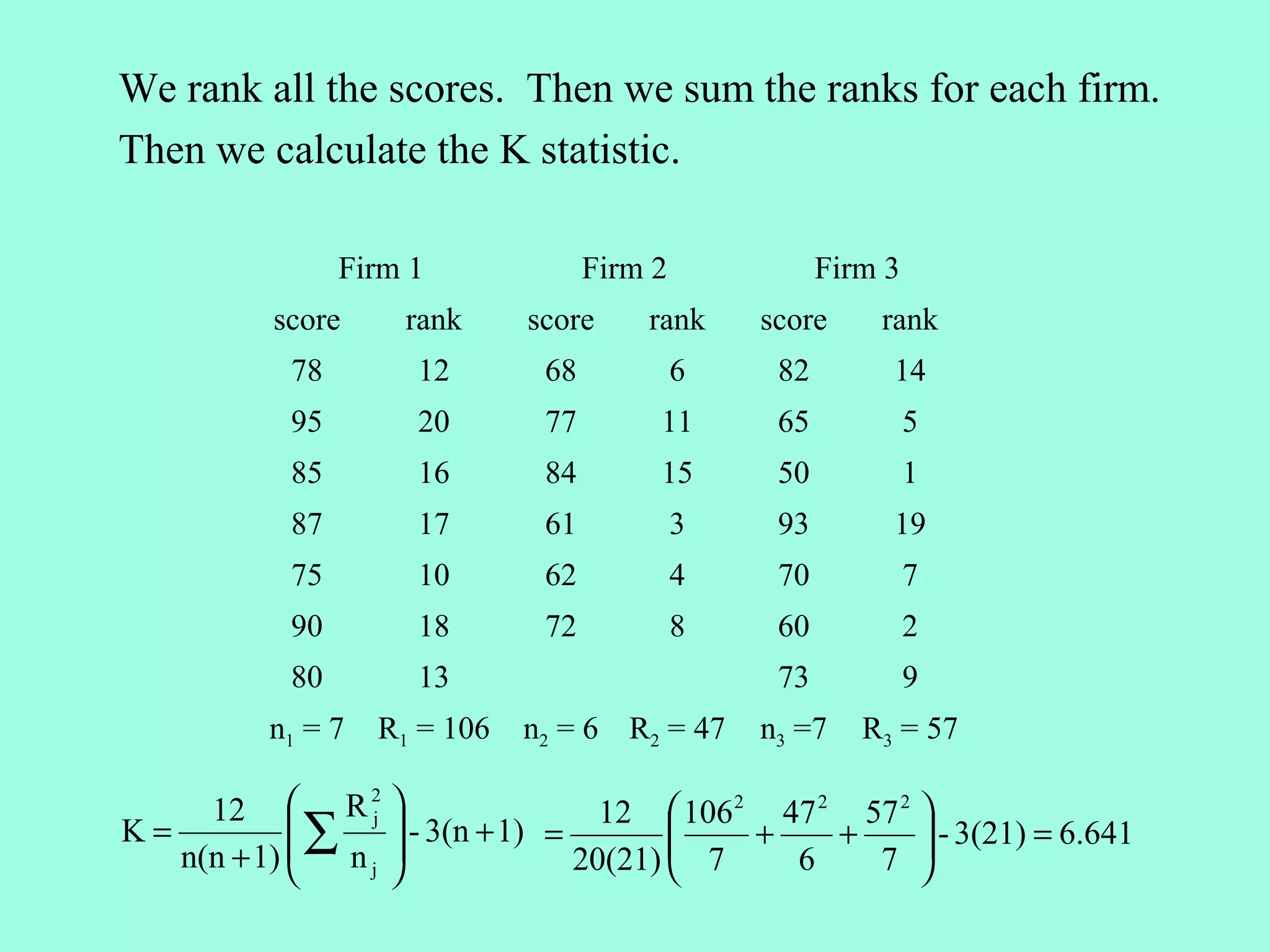
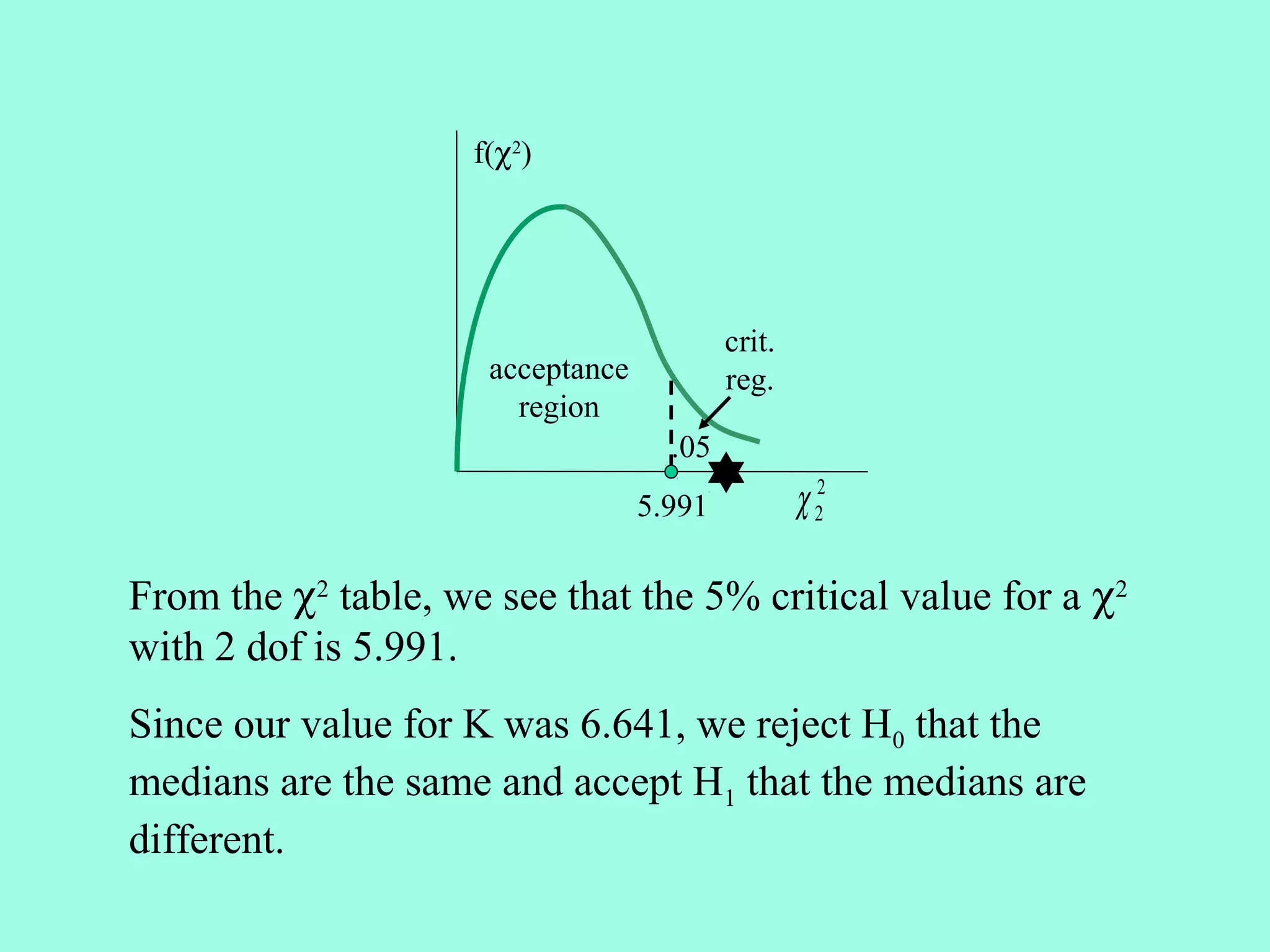
3. The Kruskal-Wallis Test compares more than two independent samples.
4. The Runs Test examines the randomness of a single sample by counting runs, or streaks, of




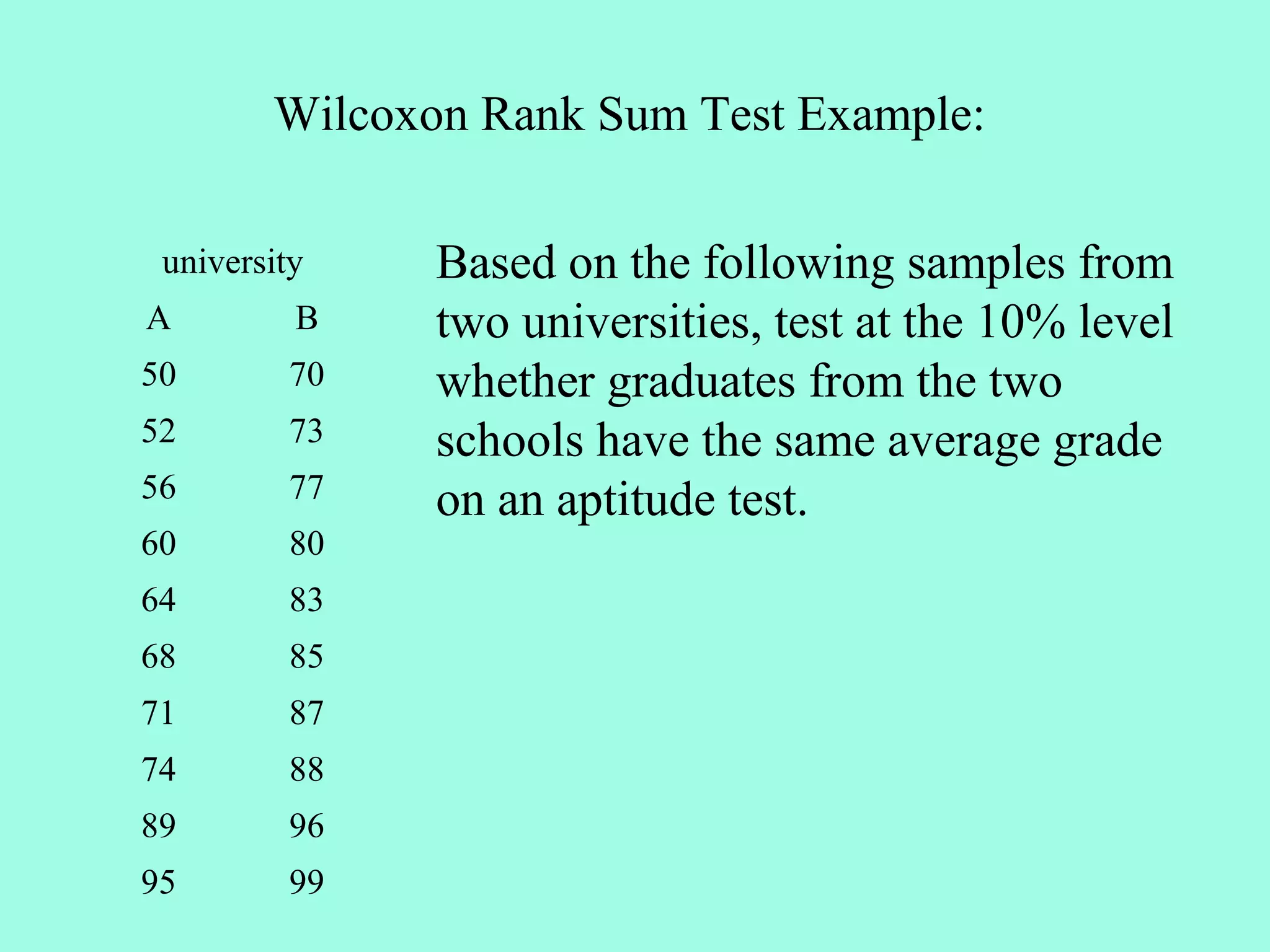
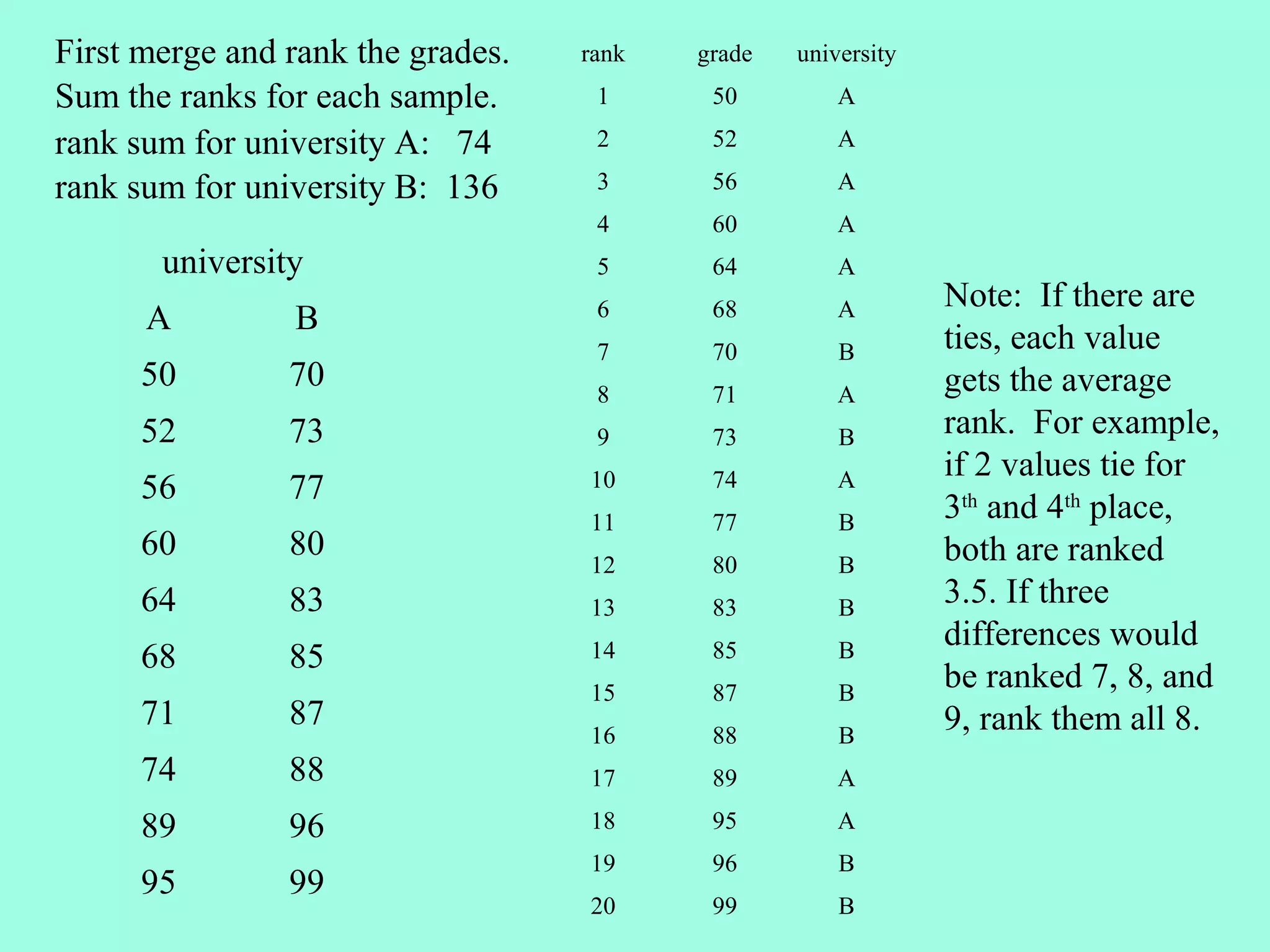
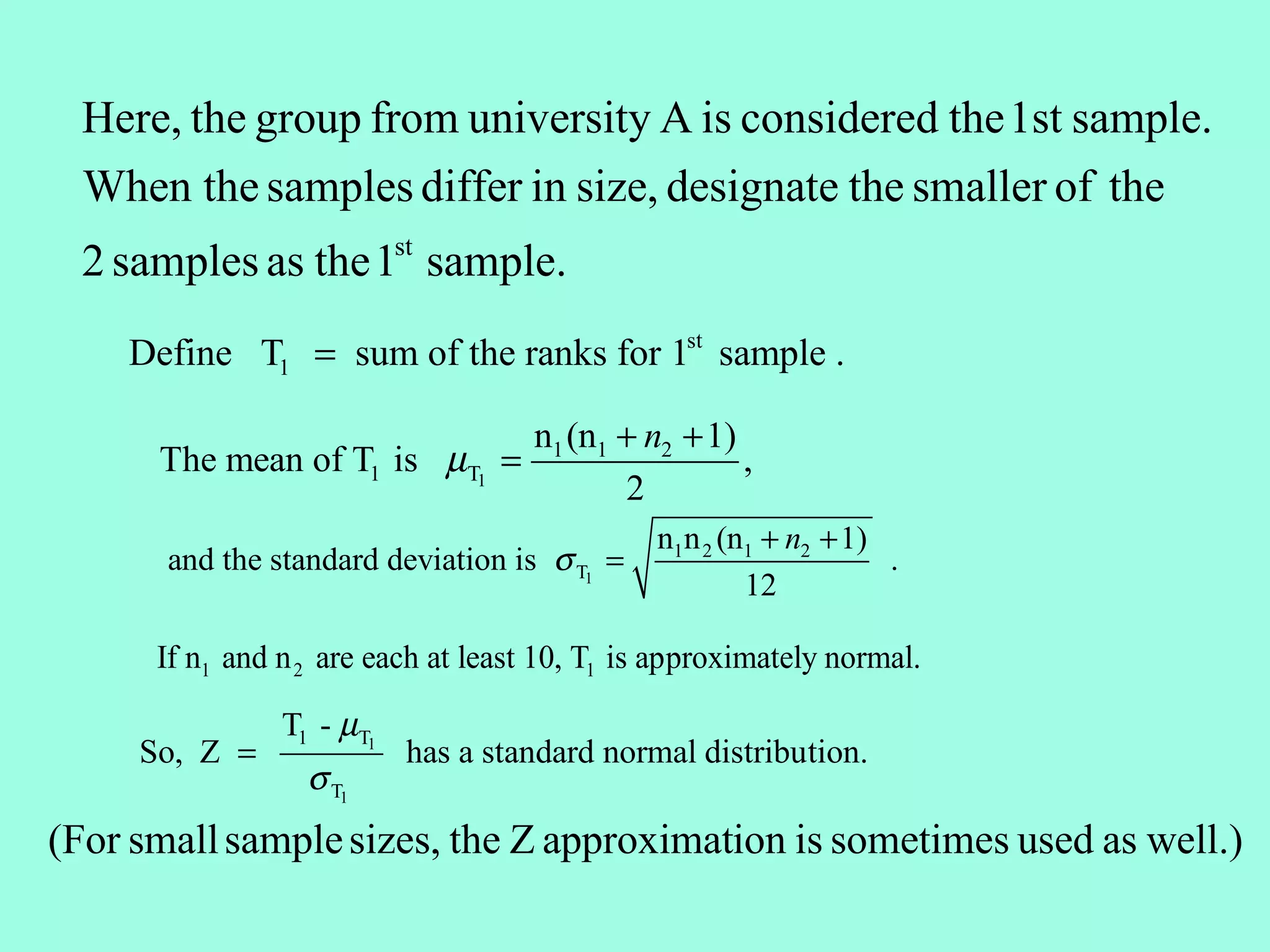
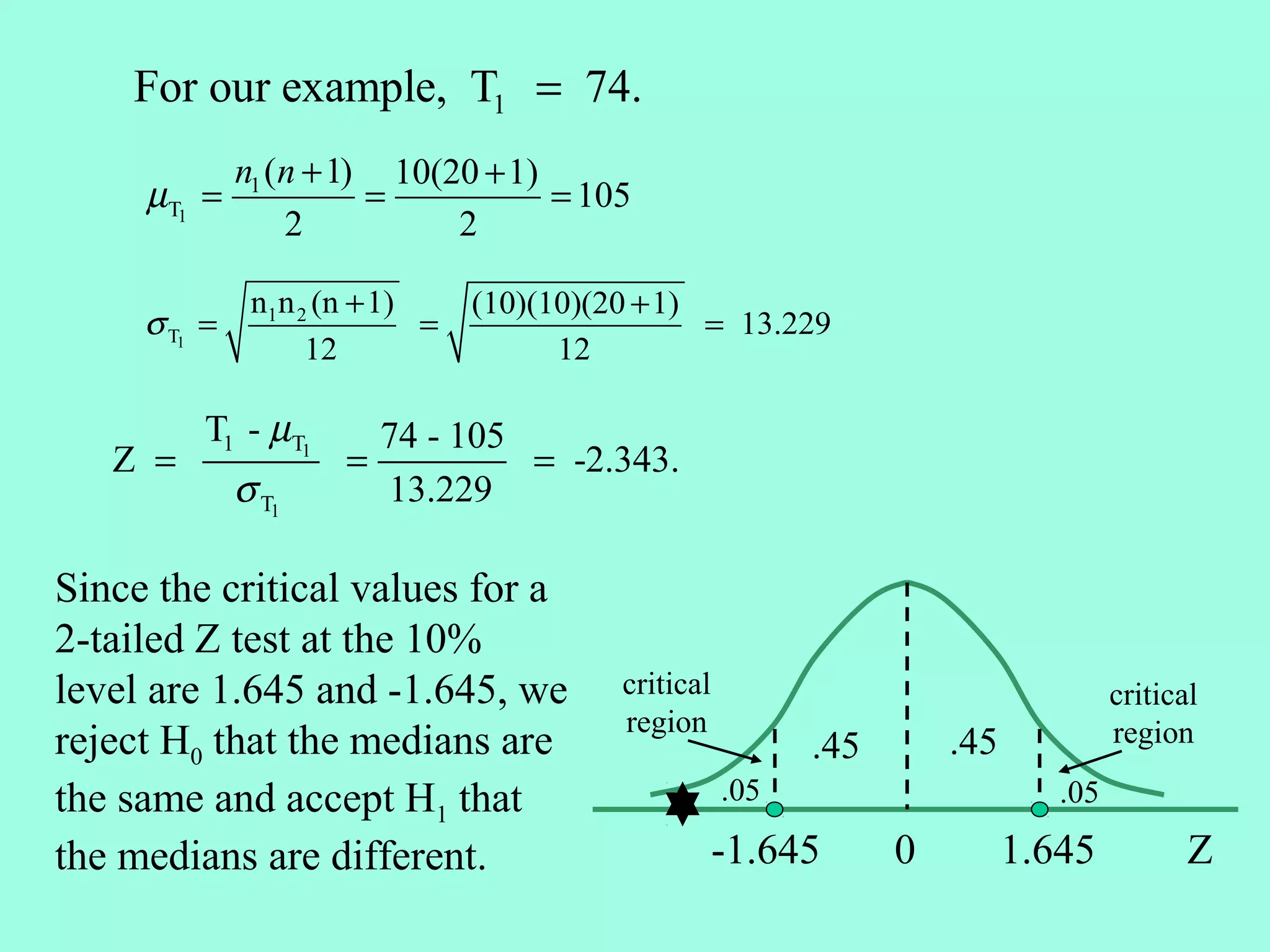










![Example: A stock exhibits the following price increase (+)
and decrease (−) behavior over 25 business days. Test at the
1% whether the pattern is random.
r =16,
+ + + − − + − − − + + − + − + − − + + − + + − + − n1 (+) = 13,
2n1n 2 n2 (−) =
2(13)(12)
μr = +1 = + 1 = 13.48 12
n1 + n 2 13 + 12
2n1n 2 (2n1n 2 - n1 - n 2 ) 2(13)(12) [(2(13)(12) - 13 - 12]
σr = = = 2.44
(n1 + n 2 ) (n1 + n 2 − 1)
2
(13 + 12) (13 + 12 − 1)
2
r - µ r 16 - 13.48
Z= = = 1.03 critical critical
σr 2.44 region .495 .495
acceptance
region
.005
.005
Since the critical values for a 2-tailed 1% region
test are 2.575 and -2.575, we accept H0 -2.575 0 2.575 Z
that the pattern is random.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/nonparametricstatistics-121123001959-phpapp02/75/Nonparametric-statistics-31-2048.jpg)