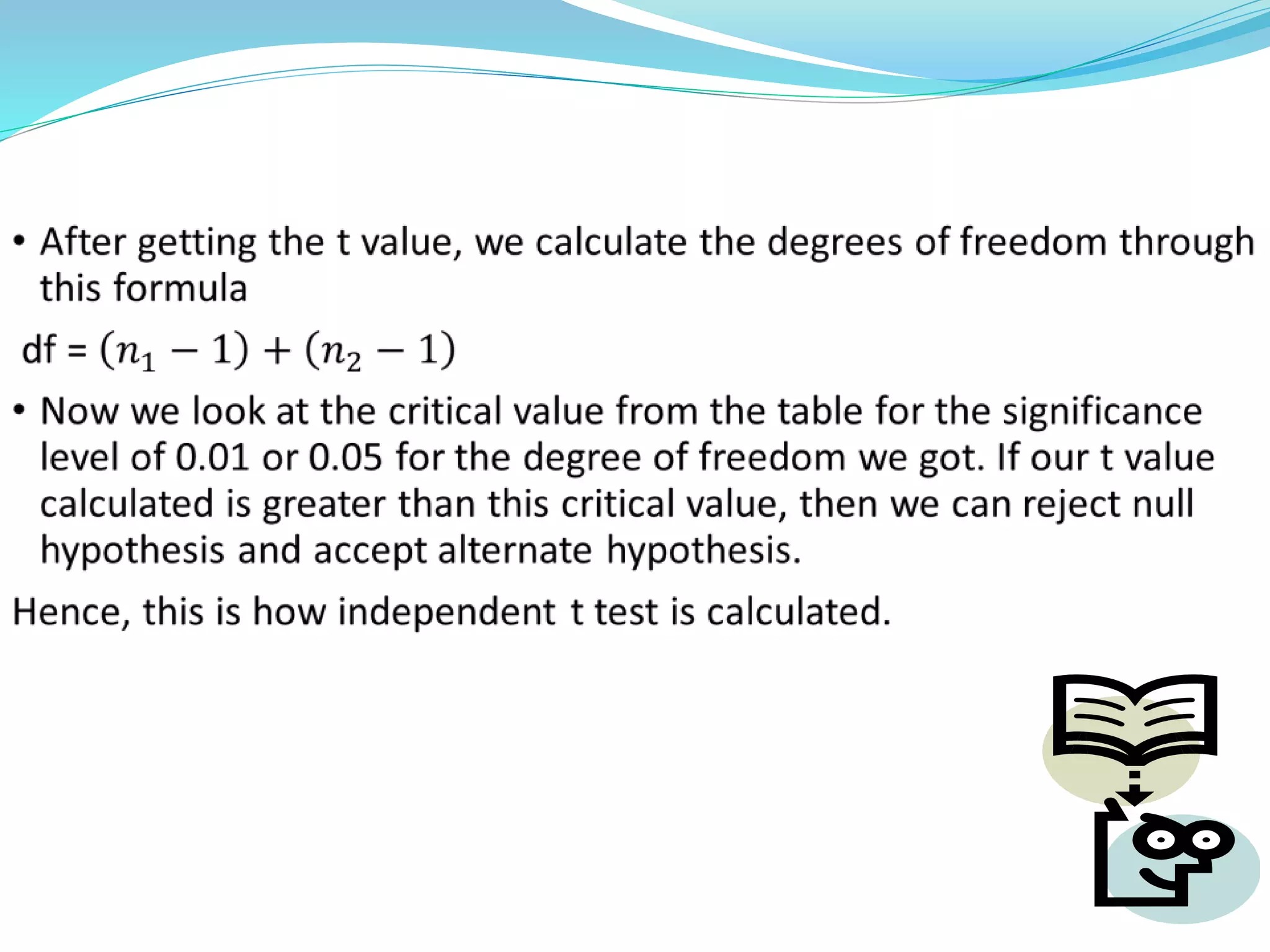
Amrita Kumari from Banaras Hindu University submitted an application discussing parametric tests. Parametric tests were developed by R. Fisher and make assumptions about the population distribution from which a sample is drawn. The key assumptions are that the population is normally distributed, observations are independent, populations have equal variance, and data is on a ratio or interval scale. Parametric tests can be used even when distributions are skewed or variances differ, and they have more statistical power than non-parametric tests. Common parametric tests include t-tests, z-tests, and ANOVA. The document then discusses one-sample, dependent, and independent t-tests in more detail. Both advantages like precision and disadvantages like sensitivity