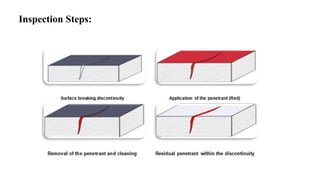
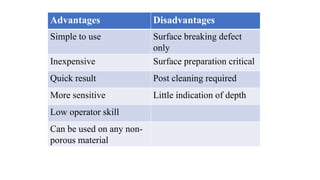
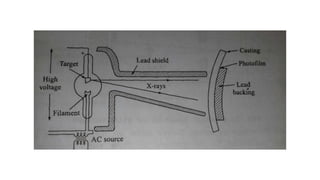
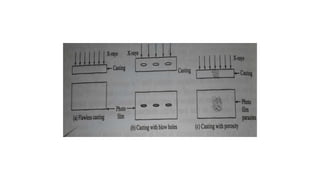
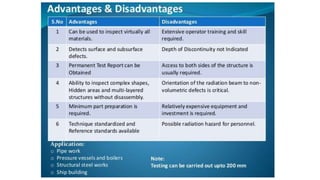
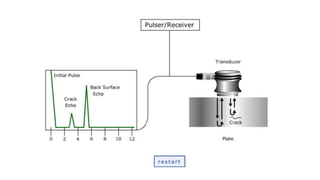
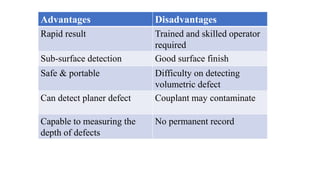
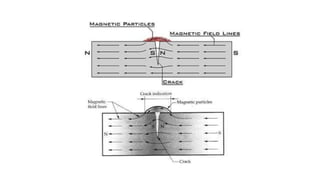
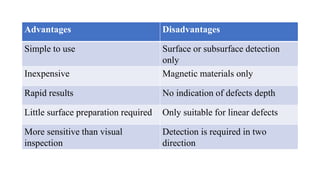
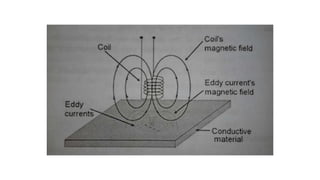
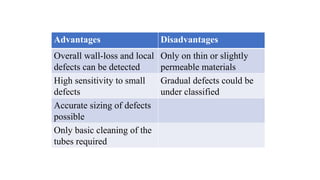
This document provides an overview of non-destructive testing (NDT) methods presented by Mr. Ruturajsinh Gurav. It describes NDT as testing materials without destroying them to detect flaws. The objectives of NDT are outlined as detecting internal/surface flaws to prevent failure and evaluate material properties. Various NDT methods are introduced, including visual inspection, liquid penetrant testing, radiography, ultrasonic testing, magnetic particle testing, and eddy current testing. Advantages and disadvantages are listed for each method.